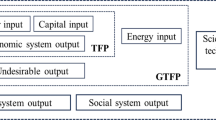
Abstract
This study takes China's oil and gas resource-based cities as the research object and builds a green growth efficiency evaluation index system from the four dimensions of social economy, resources and environment, science and technology, and government policy. Based on the non-radial and non-angle SBM model combining with the Malmquist–Luenberger (ML) index model for undesired output, it measures the green growth efficiency of oil and gas resource-based cities in China from 2010 to 2017 from both static and dynamic perspectives. It also analyzes the changing trend and room for growth of the green growth level of oil and gas resource-based cities. The results show that: (1) Using the combined SBM and ML methods can scientifically evaluate the green growth efficiency of China's oil and gas resource-based cities; (2) The green growth level of China's oil and gas resource-based cities generally rose first in 2010–2017 and then showed the declining wave momentum. The green growth efficiency has a lot of room for improvement; (3) The green technology progress index (TC) shows a U-shaped changing trend, and however, the TC is greater than 0.7 and approaching to 1 between 2011 and 2017, indicating that green technology progress has a promoting effect on green growth efficiency; (4) Indicating green technological progress is the main factor for improving the green growth efficiency of oil and gas resource-based cities.
Graphic abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Research base of scientific development concept and economic sustainable development of Beijing Normal University. 2012 China green index annual report - regional comparison. Beijing: Beijing Normal University Press 2012
Carson R (1987) Silent spring. Forestry 304:704
Colby ME (1991) Environmental management in development:The evolution of paradigms. Ecol Econ 3(3): 01–213
Fare R, Grosskopf S, Lindgren B (1992) Productivity changes in Swedish pharmacies 1980–1989: a non-parametric Malmquist approach. J Prod Anal 3:81–97
Fisher-Vanden K, Jefferson GH, Liu H (2004) What is driving China’s decline in energy intensity? Resou Energy Econ 26:77–97
GGGI. GGGI informational brochure. Seoul: GGGI 2010
Guo YH (2020) The effect of industrial agglomeration on green development efficiency in Northeast China since the revitalization. J Clean Prod 258:1–15
Hallegatte SH, Geoffrey MF (2011) From growth to green growth-a framework. Social ence Electronic Publishin
Jacobs M (2013) The handbook of global climate and environment policy
Jiao LL, Guo LL, Wu CY (2018) Research on the measurement of green growth efficiency of coastal cities in China. Sci Technol Manag Res 038:241–246
Khan JS, Zakaria R, Aminudin E et al (2019) Embedded life cycle costing elements in green building rating tool [J]. Civ Eng J 5(4):750–758
Kim SE, Kim H, Chae Y (2014) A new approach to measuring green growth: application to the OECD and Korea. Futures 63:37–48
Kumar S (2006) Environmentally sensitive productivity growth: a global analysis using Malmquist-Luenberger index. Ecol Econ 56:280–293
Li YC, Hou XN, Wu GC (2016) Sustainable development of resource-based cities based on green growth. J Henan Agric Univ 050:404–410
Lu XF, Lu XL (2016) Evaluation of green growth capacity of resource-based cities. Sci Res Manag 037:89–97
Max N, Lars R, Rasmus N (2014) Green growth in fisheries. Mar Pol 46(5):43–52
Michael EC (1991) Environmental management in development the evolution of paradigms. Ecol Econ 3:0–213
Ming CQ, Zhong SH (2013) Review on the research of “green growth evaluation” abroad. Soc Sci Abroad 5:75–84
OECD. Declaration on green growth .Singapore 2009.
OECD (2010) Interim Report of the Green Growth Strategy - Implementing our commitment for a sustainable future. sourceoecd environment & sustainable development 95:1–94
OECD (2011) Towards green growth: monitoring progress OECD indicator. OECD
Okeke FO, Ibem E, Akabuilo UC et al (2020) City as habitat; assembling the Fragile City [J]. Civ Eng J 6(6):1143–1154
Pierce DW, Anil M (1989) Blueprint for a green economy. Earthscan, London
Pinheiro AP (2020) Architectural rehabilitation and sustainability of green buildings in historic preservation [J]. http://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.28991/HIJ-2020-01-04-04
Platform GGK (2013) Moving towards a common approach on green growth indicators. green growth knowledge platform
Publishing O (2011) OECD Green Growth Studies Towards Green Growth: Monitoring Progress: OECD Indicators. Sourceoecd environment & sustainable development 7:1–146
Qu YG (2015) Research on R & D innovation efficiency and total factor productivity of industrial enterprises from the perspective of green growth. Sci Technol Manag Res 35:48–53
Qu Y, Liu W, Zhou WJ (2017) Green growth efficiency measurement of pollution intensive industries in Liaoning Province. Sci Technol Manag 19:1–7
Reilly JM (2012) Green growth and the efficient use of natural resources. Energy Econ 34:S85–S93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2012.08.033
Saufi NAA, Daud SHH (2016) Green growth and corporate sustainability performance. Procedia Econ Finan 35:374–378
Schmalensee R (2012) From “Green Growth” to sound policies: an overview. Energy Econ 34:2–6
Sustainable development strategy research group of Chinese Academy of Sciences (2011). 2011 China sustainable development strategy report: realizing green economic transformation [M]. Science Press.
UNESCAP.MCED 2005 bulletin: a summary report of the fifth ministerial conference on environment and development in Asia and the Pacific.Souel:International Institute for Sustainable Development(IISD) 2005
Sten M (1953) Index numbers and indifference surfaces. Trabajos De Estadistica 4:209–242
Sun JL, Zhu PY (2019) One of the key provinces one belt, one road, based on SBM-Malmquist-Tobit, and the evaluation of green economic efficiency and its influencing factors. Sci Technol Manag Res 39:230–237
Tone KA (2001) Slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Op Res 3:498–509
Translated by Zheng, T. T., translated by Wei, L. J. Basic law of low carbon and green growth in South Korea. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology (SOCIAL SCIENCE EDITION) 2013; 03: 23–36
UNEP. Measuring progress towards an inclusive green economy. UNEP 2012
Vazquez-Brust D, Smith AM, Sarkis J (2014) Managing the transition to critical green growth: The ‘Green Growth State.’ Futures 64:38–50
World Bank. Inclusive green growth: the pathway to sustainable development. World Bank 2012
Yu WS, Wu CY, Guo LL (2015) Green growth evaluation of countries based on doughnut theory. Econ Manag Res 36:3–9
Zhang JX, Wang XW (2013) Study on green growth index and its influencing factors of regional industry in China. Soft Sci 10:96–100
Zhang HC, Li F, Zhang JP (2017) Evaluation of two-stage technological innovation efficiency of resource-based regional industrial enterprises from the perspective of green growth. Sci Technol Manag Res 8:69–76
Zhao Ao, Guo JF (2017) Evaluation of green growth in China - integration based on rough set, catastrophe progression model and TOPSIS method. Technol Econ 36(12):123–130
Zhu BZ, Zhang MF (2019) Exploring the effect of industrial structure adjustment on interprovincial green development efficiency in China: a novel integrated approach. Energy Pol 134:1–13
Zhu BZ, Zhang MF (2020) Exploring the effect of carbon trading mechanism on China’s green development efficiency: a novel integrated approach. Energy Econ 85:1–16
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the financial support provided by National Social Science Foundation of China (NO.19BJY068), Heilongjiang Province Educational Science Planning Key Project (NO.GJB1319022), Daqing Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project (NO.DSGB2020033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
An approach integrating SBM and Malmquist–Luenberger index methods to evaluate green growth efficiency of oil and gas resource-based cities in China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Zhu, Z. et al. Evaluation of green growth efficiency of oil and gas resource-based cities in China. Clean Techn Environ Policy 23, 1785–1795 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02060-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02060-9