Abstract
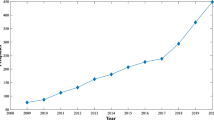
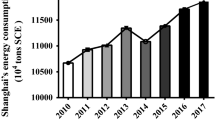
This study primarily investigated the forecasting of the growth trend in renewable energy consumption in China. Only 22 samples were acquired for this study because renewable energy is an emerging technology. Because historical data regarding renewable energy were limited in sample size and the data were not normally distributed, forecasting methods used for analyzing large amounts of data were unsuitable for this study. Grey system theory is applied to system models involving incomplete information, unclear behavioral patterns, and unclear operating mechanisms. In addition, it can be used to perform comprehensive analyses, observe developments and changes in systems, and conduct long-term forecasts. The most prominent feature of this theory is that a minimum of only four data sets are required for establishing a model and that making stringent assumptions regarding the distribution of the sample population is not required. However, to address the limitations of previous studies on grey forecasting and to enhance the forecasting accuracy, this study adopted the grey model (1, 1) [GM(1, 1)] and the nonlinear grey Bernoulli model (1, 1) [(NGBM)] for theoretical derivation and verification. Subsequently, the two models were compared with a regression analysis model to determine the models’ predictive accuracy and goodness of fit. According to the indexes of mean absolute error, mean square error, and mean absolute percentage error, NGBM(1, 1) exhibited the most accurate forecasts, followed by GM(1, 1) and regression analysis model. The results indicated that the modified NGBM(1, 1) grey forecasting models demonstrated superior predictive abilities among the compared models.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akay D, Boran FE, Yilmaz M, Atak M (2013) The evaluation of power plants investment alternatives with grey relational analysis approach for Turkey. Energy Sour Part B: Econ Plan Policy 8(1):35–43
Avinash S, Vipul J, Felix TS (2012) An integrated approach for machine tool selection using fuzzy analytical hierarchy process and grey relational analysis. Inter J Prod Res 50(12):3211–3221
Bardi U, Asmar TE, Lavacchi A (2013) Turning electricity into food: the role of renewable energy in the future of agriculture. J Clean Prod 53(8):224–231
Chang AY (2012) Prioritising the types of manufacturing flexibility in an uncertain environment. Inter J Prod Res 50(8):2133–2149
Chang CJ, Li DC, Dai WL, Chen CC (2013) Utilizing an adaptive grey model for short-term time series forecasting—a case study of wafer-level packaging. Math Prob Eng 2013:1–6
Chen SM, Chen CD (2011) Handling forecasting problems based on high-order fuzzy logical relationships. Exp Syst Appl 38(4):3857–3864
Cucchiella Federica, D’Adamo Idiano (2015) Residential photovoltaic plant: environmental and economical implications from renewable support policies. Clean Technol Env Policy. doi:10.1007/s10098-015-0913-1
Deborah P, Giuseppe G, Enrico B, Daniele R (2013) Production of green energy from co-digestion: perspectives for the Province of Cuneo, energetic balance and environmental sustainability. Clean Technol Env Policy 15(6):1055–1062
Deng JL (1982) Control problems of grey system. Syst Cont Lett 1(5):288–294
Deng JL (2003) Literalizing GRA axioms. J Grey Syst 4:399–400
Deng JL (2004) Grey management: grey situation decision making in management science. J Grey Sys 2:93–96
Farah H, Armin D, Ali K (2013) Production of biodiesel as a renewable energy source from castor oil. Clean Technol Env Policy 15(6):1063–1068
Farhad M, Hossain M Hasanuzzaman, Rahim NA, Ping HW (2015) Impact of renewable energy on rural electrification in Malaysia: a review. Clean Technol Env Policy 17(4):859–871
Feng SJ, Ma YD, Song ZL, Ying J (2012) Forecasting the energy consumption of China by the grey prediction model. Energy Sou Part B: Econ Plan Policy 7(4):376–389
Herbig P, Milewicz J, Golden JE (1993) Forecast: who, what, when, and how. J Bus Forecast 15(5):395–412
Hu PY (2004) Using a grey multipurpose decision system for car purchasing. J Grey Sys 7(1):11–14
Igliński B, Piechota G, Iglińska A, Cichosz M, Buczkowski R (2015) The study on the SWOT analysis of renewable energy sector on the example of the Pomorskie Voivodeship (Poland). Clean Technol Env Policy. doi:10.1007/s10098-015-0989-7
Kayacan E, Ulutas B, Kaynak O (2010) Grey system theory-based models in time series prediction. Exp Syst Appl 37(2):1784–1789
Khoie Rahim, Yee Victoria E (2015) A forecast model for deep penetration of renewables in the Southwest, South Central, and Southeast regions of the United States. Clean Technol Env Policy 17(4):957–971
Kwonpongsagoon S, Bader HP, Scheidegger R (2007) Modelling cadmium flows in Australia on the basis of a substance flow analysis. Clean Technol Env Policy 9(4):313–323
Lee YC, Wu CH, Tsai SB (2014) Grey system theory and fuzzy time series forecasting for the growth of green electronic materials. Inter J Prod Res 52(10):2931–2945
Lewis CD (1982) Industrial and business forecasting methods. Butterworths, London
Li DC, Yeh CW, Chang CJ (2009) An improved grey-based approach for early manufacturing data forecasting. Comp Indus Eng 57(4):1161–1167
Li GD, Masuda S, Wang CH, Nagai M (2010) The hybrid grey-based model for cumulative curve prediction in manufacturing system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47(4):337–349
Li DC, Chang CJ, Chen WC, Chen CC (2011) An extended grey forecasting model for omnidirectional forecasting considering data gap difference. Appl Math Mod 35(10):5051–5058
McLellan BC, Corger GD, Giurco DP, Ishihara KN (2012) Renewable energy in the minerals industry: a review of global potential. J Clean Prod 32(9):32–44
National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China (2013) China energy statistical year book. China Statistics Press, Beijing 2013
Prakash K, Urmila D, Heriberto C (2013) Model-based approach to study the impact of biofuels on the sustainability of an ecological system. Clean Technol Env Policy 15(1):21–33
Sadeghi M, Hajiagfa SH, Hashemi SS (2013) A fuzzy grey goal programming approach for aggregate production planning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64(9–12):1715–1727
Wang CH (2010) Predicting tourism demand using fuzzy time series and hybrid grey theory. Tour Manag 25(3):367–374
Xiong W, Liu L, Xiong M (2010) Application of gray correlation analysis for cleaner production. Clean Technol Env Policy 12(4):401–405
Zhang Q, Zhou D, Fang X (2014) Analysis on the policies of biomass power generation in China. Renew Sust Energy Rev 32:926–935
Zhao X, Burnett JW, Fletcher JJ (2014) Spatial analysis of China province-level CO2 emission intensity. Renew Sust Energy Rev 33(May):1–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, SB. Using grey models for forecasting China’s growth trends in renewable energy consumption. Clean Techn Environ Policy 18, 563–571 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-1017-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-1017-7