Abstract
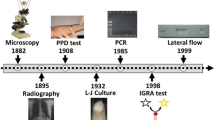
Xpert MTB/RIF assay, a real-time PCR assay designed to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis, has proven sensitive and specific when performed on respiratory samples in a high prevalence setting. However, it was suggested as less accurate in a low-incidence environment. We evaluated the accuracy of the Xpert for the diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB) on pulmonary and extrapulmonary samples in Geneva (Switzerland), where the prevalence of active TB is very low. From March 2009 to February 2013, the Xpert was performed on clinical samples. All specimens were also processed using auramine, AFB staining, and mycobacterial culture with both solid and liquid media. The accuracy of both microscopy and Xpert was determined retrospectively using cultures as the reference method. A total of 732 clinical specimens were processed with the Xpert. The Xpert had a high specificity (97.5%; 95% confidence interval (CI), 95.8–98.5%) and revealed much more sensitive (82.7%; 95% CI, 74.1–89.0%) than microscopy (55.5%; 95% CI, 45.7–64.8%) for the diagnosis of TB, with a high negative predictive value (96.8%; 95% CI, 95.0–98.0%). The advantage of PCR over microscopy was even more pronounced for extrapulmonary specimens (sensitivity of 70% (95% CI, 50.4–84.6%) compared with 23.3% (95% CI, 10.6–42.7%)). Despite the low prevalence of TB in Switzerland, results performance for respiratory samples was similar to that reported in high prevalence countries. The high negative predictive value is clinically helpful in our setting, where pulmonary TB needs to be reasonably ruled out. When considering extrapulmonary samples, microscopy performed poorly compared with Xpert. This study shows that the Xpert remains accurate and useful in a low-incidence setting.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Global tuberculosis report 2018. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
Steingard KR, Henry M, Ng V, Hopewell PC, Ramsay A, Cunningham J, Urbanczik R, Perkins MD, Aziz MA, Pai M (2006) Fluorescence versus conventional suptum smear microscopy for tuberculosis: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis 6(9):570–581
Boehme CC, Nabeta P, Hillemann D, Nicol MP, Shenai S, Krapp F, Allen J, Tahrli R, Blakemore R, Rustomjee R et al (2010) Rapid molecular detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance. N Engl J Med 363(11):1005–1015
Sohn H, Aero AD, Menzies D, Behr M, Schartzmann Km Alvarez GG, Dan A, McIntosh F, Pai M, Denkinger CM. Xpert MTB/RIF testing in a low tuberculosis incidence, high-resource setting: limitations in accuracy and clinical impact. Clin Infect Dis 2014;58(7) :970–976
Office fédéral de la santé publique, www.bag.admin.ch
Steingard K, Schiller I, Horne DJ, Pai M, Boehme C, Dendukuri N (2014) Xpert® MTB/RIF assay for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD009593
Food and Drug Administration. FDA permits marketing of first U.S. test labeled for simultaneous detection of tuberculosis bacteria and resistance to the antibiotic rifampin. Available at : http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm362602.htm. Accessed 25 July 2013
Luetkemeyer AF, Firnhaber C, Kendall MA et al (2016) Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF versus AFB smear and culture to identify pulmonary tuberculosis in patients with suspected tuberculosis from low and higher prevalence settings. Clin Infect Dis 62(9):1081–1088
Parcell J, Jarchow-MacDonald AA, Seagar AL, Laurenson IF, Prescott GJ, Lockhart M (2017) Three year evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF in a low prevalence tuberculosis setting: a Scottish perspective. J Inf Secur 74(5):466–472
Chiang TY, Fan SY, Jou R (2018) Performance of an Xpert-based diagnostic algorithm for the rapid detection of drug-resistant tuberculosis among high-risk populations in a low-incidence setting. PLoS One 13(7):e0200755
Dharan NJ, Blakemore R, Sloutsky A, Kaur D, Alexander RC, Ghajar M et al (2016 Dec 20) Performance of the G4 Xpert® MTB/RIF assay for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rifampin resistance: a retrospective case-control study of analytical and clinical samples from high- and low-tuberculosis prevalence settings. BMC Infect Dis 16(1):764
Davis JL, Kawamura LM, Chaisson LH, Grinsdale J, Benhammou J, Ho C, Babst A, Banouvong H et al (2014) Impact of GeneXpert MTB/RIF on patients and tuberculosis programs in a low-burden setting. A hypothetical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 189(12):1551–1559
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the bacteriology laboratory staff for the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical aspects
Patient consent was not requested for this study as it implicated only the analysis of anonymized data from the laboratory without any intervention on patient care, neither in terms of sampling nor in terms of treatment.
Patient consent
Not requested
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, TT., Schrenzel, J., Janssens, JP. et al. Performances and usefulness of Xpert MTB/RIF assay in low-incidence settings: not that bad?. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39, 1645–1649 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03887-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03887-8