Abstract
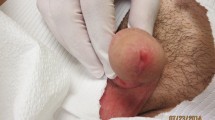
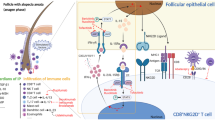
Blastocystis is one of the most common intestinal protozoan parasites worldwide, which is linked to cutaneous lesions and urticaria. In a setting of systematic review, the data on the association of Blastocystis infection with cutaneous lesions were searched in order to summarize the main clinical symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment, and outcome of the patients. The search identified 28 eligible articles, including 12 cross-sectional studies and 16 case reports/case series (including 23 cases). A diverse spectrum of skin symptoms, mainly urticaria, rash, and itching, was reported from the studies. Of the 23 infected cases with the skin symptoms, gastrointestinal symptoms were reported from the 16 cases, whereas 7 cases with urticaria had asymptomatic infection. The most frequent subtypes were ST1, ST2, and ST3, respectively. Metronidazole, paromomycin, and tinidazole were the most prescribed drugs in patients with single Blastocystis infection. Notably, urticaria and other cutaneous symptoms of all treated patients were resolved after treatment. In conclusion, this study indicates that Blastocystis infection can be a neglected cause of urticaria and skin disorders. Since the treatment of Blastocystis infection is simple, screening and treatment of this infection should be considered in patients with urticaria and other skin disorders.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark CG, van der Giezen M, Alfellani MA, Stensvold CR (2013) Recent developments in Blastocystis research. In: Adv Parasitol, vol 82. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 1–32
Alexeieff A (1911) Sur la nature des formations dites kystes de Trichomonas intestinalis. CR Soc Biol 71:296–298
Stensvold CR, Clark CG (2016) Current status of Blastocystis: a personal view. Parasitol Int 65(6):763–771
Ajjampur SS, Tan KS (2016) Pathogenic mechanisms in Blastocystis spp.—interpreting results from in vitro and in vivo studies. Parasitol Int 65(6):772–779
Tan KS, Singh M, Yap EH (2002) Recent advances in Blastocystis hominis research: hot spots in terra incognita. Int J Parasitol 32(7):789–804
Andersen LOB, Stensvold CR (2016) Blastocystis in health and disease: are we moving from a clinical to a public health perspective? J Clin Microbiol 54(3):524–528
Coyle CM, Varughese J, Weiss LM, Tanowitz HB (2011) Blastocystis: to treat or not to treat. Clin Infect Dis 54(1):105–110
Cifre S, Gozalbo M, Ortiz V, Soriano JM, Merino JF, Trelis M (2018) Blastocystis subtypes and their association with irritable bowel syndrome. Med Hypotheses 116:4–9
Rasti S, Hassanzadeh M, Hooshyar H, Momen-Heravi M, Mousavi SGA, Abdoli A (2017) Intestinal parasitic infections in different groups of immunocompromised patients in Kashan and Qom cities, Central Iran. Scand J Gastroenterol 52(6–7):738–741
Roberts T, Stark D, Harkness J, Ellis J (2014) Update on the pathogenic potential and treatment options for Blastocystis sp. Gut Pathogens 6(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-4749-6-17
Lepczyńska M, Chen WC, Dzika E (2016) Mysterious chronic urticaria caused by Blastocystis spp.? Int J Dermatol 55(3):259–266
Armentia A, Mendez J, Gomez A, Sanchis E, Fernandez A, Sánchez P (1993) Urticaria by Blastocystis hominis. Successful treatment with paromomycin. Allergol Immunopathol 21(4):149–151
Biedermann T, Hartmann K, Sing A, Przybilla B (2002) Hypersensitivity to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and chronic urticaria cured by treatment of Blastocystis hominis infection. Brit J Dermatol 146(6):1113–1114
Scanlan PD, Stensvold CR (2013) Blastocystis: getting to grips with our guileful guest. Trends Parasitol 29(11):523–529
Stensvold CR, van der Giezen M (2018) Associations between gut microbiota and common luminal intestinal parasites. Trends Parasitol 34(5):369–377
Lepczyńska M, Białkowska J, Dzika E, Piskorz-Ogórek K, Korycińska J (2017) Blastocystis: how do specific diets and human gut microbiota affect its development and pathogenicity? Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 36(9):1531–1540
Greaves M (2000) Chronic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol 105(4):664–672
Kaplan AP (2004) Chronic urticaria: pathogenesis and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114(3):465–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2004.02.049
Greaves MW (1995) Chronic urticaria. New Engl J Med 332(26):1767–1772. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199506293322608
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. System Rev 4(1):1
Cakir F, Cicek M, Yildirim IH (2019) Determination the subtypes of Blastocystis sp. and evaluate the effect of these subtypes on pathogenicity. Acta Parasitol 64(1):7–12
El Saftawy EA, Amin NM, Hamed DH, Elkazazz A, Adel S (2019) The hidden impact of different Blastocystis genotypes on C-3 and IgE serum levels: a matter of debate in asthmatic Egyptian children. J Parasit Dis 43(3):443451
Tunalı V, Öztürk EA, Ünver A, Turgay N (2018) The prevalence of Blastocystosis among patients with gastrointestinal and dermatologic complaints and effects of Blastocystis spp. density on symptomatology. Türkiye Parazitolojii Dergisi 42(4):254–257
Salvador F, Sulleiro E, Sánchez-Montalvá A, Alonso C, Santos J, Fuentes I, Molina I (2016) Epidemiological and clinical profile of adult patients with Blastocystis sp. infection in Barcelona, Spain. Parasit Vectors 9(1):548
Ertuğ S, Malatyalı E, Ertabaklar H, Özlem SÇ, Bozdoğan B (2015) Subtype distribution of Blastocystis isolates and evaluation of clinical symptoms detected in Aydin province, Turkey. Mikrobiyol Bul 49(1):98–104
Beyhan YE, Yilmaz H, Cengiz ZT, Ekici A (2015) Clinical significance and prevalence of Blastocystis hominis in Van, Turkey. Saudi Med J 36(9):1118–1121
Bálint A, Dóczi I, Bereczki L, Gyulai R, Szűcs M, Farkas K, Urbán E, Nagy F, Szepes Z, Wittmann T (2014) Do not forget the stool examination!—cutaneous and gastrointestinal manifestations of Blastocystis sp. infection. Parasitol Res 113(4):1585–1590
Giacometti A, Cirioni O, Antonicelli L, D'Amato G, Silvestri C, Del Prete MS, Scalise G (2003) Prevalence of intestinal parasites among individuals with allergic skin diseases. J Parasitol 89(3):490–493
Casero RD, Mongi F, Sánchez A, Ramírez JD (2015) Blastocystis and urticaria: examination of subtypes and morphotypes in an unusual clinical manifestation. Acta Trop 148:156–161
Yilmaz EA, Karaatmaca B, Sackesen C, Sahiner UM, Cavkaytar O, Sekerel BE, Soyer O (2016) Parasitic infections in children with chronic spontaneous urticaria. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 171(2):130–135
Hameed DMA, Hassanin OM, Zuel-Fakkar NM (2011) Association of Blastocystis hominis genetic subtypes with urticaria. Parasitol Res 108(3):553–560
Aydin M, Yazici M, Demirkazik M, Koltas IS, Cikman A, Gulhan B, Duran T, Yilmaz A, Kara M (2019) Molecular characterization and subtyping of Blastocystis in urticarial patients in Turkey. Asian Pac J Trop Med 12(10):450–456
Pielok Ł, Frąckowiak K, Kłudkowska M (2019) Disseminated skin rash and blood eosinophilia in a polish traveler diagnosed Strongyloides stercoralis, Trichuris trichiura. Schistosoma sp and Blastocystis sp coinfection. Annals Parasitol 65(1):99–102
Pawlowska J, Pawlowska-Iwanicka K, Stelmach I (2018) Blastocystis infection in a 5-year-old boy-a case report. Pediatr Med Rodz 14(3):324–326
Verma R, Delfanian K (2013) Blastocystis hominis associated acute urticaria. Am J Med Sci 346(1):80–81
Kick G, Rueff F, Przybilla B (2002) Palmoplantar pruritus subsiding after Blastocystis hominis eradication. Acta Derm Venereol 82(1):60–60
Pasqui A, Savini E, Saletti M, Guzzo C, Puccetti L, Auteri A (2004) Chronic urticaria and Blastocystis hominis infection. A case report. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 8:117–120
Cassano N, Scoppio BM, Loviglio MC, Vena G (2005) Remission of delayed pressure urticaria after eradication of Blastocystis hominis. Acta Derm Venerol 85(4):357–358
Katsarou-Katsari A, Vassalos CM, Tzanetou K, Spanakos G, Papadopoulou C, Vakalis N (2008) Acute urticaria associated with amoeboid forms of Blastocystis sp. subtype 3. Acta Derm Venereol 88(1):80–81
Valsecchi R, Leghissa P, Greco V (2004) Cutaneous lesions in Blastocystis hominis infection. Acta Derm Venereol 84(4):322–323
Vogelberg C, Stensvold CR, Monecke S, Ditzen A, Stopsack K, Heinrich-Gräfe U, Pöhlmann C (2010) Blastocystis sp. subtype 2 detection during recurrence of gastrointestinal and urticarial symptoms. Parasitol Int 59(3):469–471
Lee MG, Rawlins SC, Didier M, DeCeulaer K (1990) Infective arthritis due to Blastocystis hominis. Ann Rheum Dis 49(3):192
Rajič B, Arapović J, Raguž K, Bošković M, Babić SM, Maslać S (2015) Eradication of Blastocystis hominis prevents the development of symptomatic Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: a case report. J Infect Dev Ctries 9(07):788–791
Gupta R, Parsi K (2006) Chronic urticaria due to Blastocystis hominis. Aust J Dermatol 47(2):117–119
Shah M, Tan CB, Rajan D, Ahmed S, Subramani K, Rizvon K, Mustacchia P (2012) Blastocystis hominis and Endolimax nana co-infection resulting in chronic diarrhea in an immunocompetent male. Case Rep Gastroenterol 6(2):358–364
Stensvold C, Arendrup M, Nielsen H, Bada A, Thorsen S (2008) Symptomatic infection with Blastocystis sp. subtype 8 successfully treated with trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 102(3):271–274
Kantardjiev V, Galev A, Broshtilova V (2019) Urticaria associated with amoeboid forms of Blastocystis spp. Asian J Res Infect Dis:1–4
Hennino A, Bérard F, Guillot I, Saad N, Rozières A, Nicolas J-F (2006) Pathophysiology of urticaria. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 30(1):3–11. https://doi.org/10.1385/criai:30:1:003
Kolkhir P, Balakirski G, Merk HF, Olisova O, Maurer M (2016) Chronic spontaneous urticaria and internal parasites–a systematic review. Allergy 71(3):308–322
Rostami A, Riahi SM, Haghighi A, Saber V, Armon B, Seyyedtabaei SJ (2017) The role of Blastocystis sp. and Dientamoeba fragilis in irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasitol Res 116(9):2361–2371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5535-6
Kasperska-Zajac A, Grzanka A, Machura E, Misiolek M, Mazur B, Jochem J (2013) Increased serum complement C3 and C4 concentrations and their relation to severity of chronic spontaneous urticaria and CRP concentration. J Inflamm 10(1):22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-9255-10-22
Hide M, Francis DM, Grattan C, Hakimi J, Kochan JP, Greaves MW (1993) Autoantibodies against the high-affinity IgE receptor as a cause of histamine release in chronic Urticaria. New Engl J Med 328(22):1599–1604. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199306033282204
Tong LJ, Balakrishnan G, Kochan JP, Kinét J-P, Kaplan AP (1997) Assessment of autoimmunity in patients with chronic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol 99(4):461–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(97)70071-X
Grattan CE, Francis DM, Hide M, Greaves MW (1991) Detection of circulating histamine releasing autoantibodies with functional properties of anti-IgE in chronic urticaria. Clin Exp Allergy 21(6):695–704. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb03198.x
Magen E, Mishal J, Feldman V, Zeldin Y, Schlesinger M, Kidon M, Sthoeger Z (2010) Increased mean platelet volume and C-reactive protein levels in patients with chronic urticaria with a positive autologous serum skin test. Am J Med Sci 339(6):504–508. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3181db6ed5
Kasperska-Zajac A, Sztylc J, Machura E, Jop G (2011) Plasma IL-6 concentration correlates with clinical disease activity and serum C-reactive protein concentration in chronic urticaria patients. Clin Exp Allergy 41(10):1386–1391. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03789.x
Kasperska-Zajac A, Grzanka A, Machura E, Mazur B, Misiolek M, Czecior E, Kasperski J, Jochem J (2013) Analysis of procalcitonin and CRP concentrations in serum of patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria. Inflamm Res 62(3):309–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-012-0580-1
Lynch SV, Pedersen O (2016) The human intestinal microbiome in health and disease. New Engl J Med 375(24):2369–2379. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1600266
Nabizadeh E, Jazani NH, Bagheri M, Shahabi S (2017) Association of altered gut microbiota composition with chronic urticaria. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 119(1):48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2017.05.006
Lu T, Chen Y, Guo Y, Sun J, Shen W, Yuan M, Zhang S, He P, Jiao X (2019) Altered gut microbiota diversity and composition in chronic urticaria. Dis Markers 2019:11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6417471
Valerio I, Floriana S, Valentina T, Fabrizio P, Anatole M, Veronica DC, David DC, Serena S, Federica B, Rossella DA (2016) Gut microbiota related to Giardia duodenalis, Entamoeba spp. and Blastocystis hominis infections in humans from Côte d’Ivoire. J infect Dev Ctries 10 (09). https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.8179
O’Brien Andersen L, Karim AB, Roager HM, Vigsnæs LK, Krogfelt KA, Licht TR, Stensvold CR (2016) Associations between common intestinal parasites and bacteria in humans as revealed by qPCR. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 35(9):1427–1431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2680-2
Salem I, Ramser A, Isham N, Ghannoum MA (2018) The gut microbiome as a major regulator of the gut-skin axis. Front Microbiol 9(1459). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01459
Acknowledgments
We give thanks to Dr. Zahra Asadgol (Department of Environmental Health Engineering, School of Public Health, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran) for her great technical assistance in designing some graphs.
Funding sources
This study was supported by Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences, Sanandaj, Iran, and Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Jahrom, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FB and AA conceived the study design and performed the initial search for inclusion; FB and EB screened the articles according to title and abstract; FB, EB, AB, and TRR prepared the tables; FB and AA designed the figures; FB and EB wrote the draft of the paper; FB, AB, and AA revised the paper according to the reviewer’s comments; and AA performed a final revision for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahrami, F., Babaei, E., Badirzadeh, A. et al. Blastocystis, urticaria, and skin disorders: review of the current evidences. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39, 1027–1042 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03793-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03793-8