Abstract
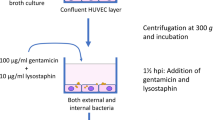
Staphylococcus aureus endovascular infections retain a high morbidity and mortality despite antibiotics and supportive care. The destruction of endothelial cells (ECs) is a critical step in the pathogenesis of S. aureus endovascular infections. In order to better understand S. aureus-induced EC damage, we systematically screened a collection of two-component regulatory system mutants of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) USA300 strain JE2 for damage induction in human umbilical vein ECs (HUVECs). This screen revealed that the two-component regulatory system ArlRS is required for maximum damage: arlRS inactivation leads to a > 70% reduction in damage. In a different genetic S. aureus background (RN6390, MSSA strain) arlRS inactivation had a smaller but also significant effect on EC damage. In both strains, the reduction in EC damage was accompanied by a significant reduction in internalization. In conclusion, we determined a novel role of ArlRS in S. aureus-induced EC damage, which will help to better understand the pathogenesis of S. aureus endovascular infection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wisplinghoff H, Bischoff T, Tallent SM, Seifert H, Wenzel RP, Edmond MB (2004) Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin Infect Dis 39(3):309–317
Lemichez E, Lecuit M, Nassif X, Bourdoulous S (2010) Breaking the wall: targeting of the endothelium by pathogenic bacteria. Nat Rev Micro 8(2):93–104
Garzoni C, Kelley WL (2009) Staphylococcus aureus: new evidence for intracellular persistence. Trends Microbiol 17(2):59–65
Haslinger-Löffler B, Kahl BC, Grundmeier M, Strangfeld K, Wagner B, Fischer U, Cheung AL, Peters G, Schulze-Osthoff K, Sinha B (2005) Multiple virulence factors are required for Staphylococcus aureus-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells. Cell Microbiol 7(8):1087–1097
Sinha B, Fraunholz M (2010) Staphylococcus aureus host cell invasion and post-invasion events. Int J Med Microbiol 300(2-3):170–175
Grundmeier M, Tuchscherr L, Brueck M, Viemann D, Roth J, Willscher E, Becker K, Peters G, Loeffler B (2010) Staphylococcal strains vary greatly in their ability to induce an inflammatory response in endothelial cells. J Infect Dis 201(6):871–880
Ythier M, Entenza JM, Bille J, Vandenesch F, Bes M, Moreillon P, Sakwinska O (2010) Natural variability of in vitro adherence to fibrinogen and fibronectin does not correlate with in vivo infectivity of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun 78(4):1711–1716
Seidl K, Bayer AS, McKinnell JA, Ellison S, Filler SG, Xiong YQ (2011) In vitro endothelial cell damage is positively correlated with enhanced virulence and poor vancomycin responsiveness in experimental endocarditis due to methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Cell Microbiol 13(10):1530–1541
Krut O, Utermohlen O, Schlossherr X, Kronke M (2003) Strain-specific association of cytotoxic activity and virulence of clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Infect Immun 71(5):2716–2723
Seidl K, Leemann M, Palheiros Marques M, Rachmühl C, Leimer N, Andreoni F, Achermann Y, Zinkernagel AS (2017) High level methicillin resistance correlates with reduced Staphylococcus aureus endothelial cell damage. Intern. J Med Microbiol 307(1):11–20
Chorianopoulos E, Bea F, Katus H, Frey N (2009) The role of endothelial cell biology in endocarditis. Cell Tissue Res 335(1):153–163
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG, Minick CR (1973) Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins: Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest 52(11):2745–2756
Fey PD, Endres JL, Yajjala VK, Widhelm TJ, Boissy RJ, Bose JL, Bayles KW (2013) A genetic resource for rapid and comprehensive phenotype screening of nonessential Staphylococcus aureus genes. MBio 4(1):e00537–12
Fournier B, Klier A, Rapoport G (2001) The two-component system ArlS–ArlR is a regulator of virulence gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 41(1):247–261
Quiblier C, Seidl K, Roschitzki B, Zinkernagel AS, Berger-Bächi B, Senn MM (2013) Secretome analysis defines the major role of SecDF in Staphylococcus aureus virulence. PLoS ONE 8(5):e63513
Seidl K, Zinkernagel A (2013) The MTT assay is a rapid and reliable quantitative method to assess Staphylococcus aureus induced endothelial cell damage. J Microbiol Methods 92(3):307–309
Cheung AL, Bayles KW (2007) Tissue culture assays used to analyze invasion by Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Protoc Microbiol 9C(4):1
Seidl K, Solis N, Bayer A, Abdel Hady W, Ellison S, Klashman MC, Xiong YQ, Filler S (2012) Divergent responses of different endothelial cell types to infection with Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 7(6):e39633
Martin PK, Li T, Sun D, Biek DP, Schmid MB (1999) Role in cell permeability of an essential two-component system in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 181(12):3666–3673
Liang X, Zheng L, Landwehr C, Lunsford D, Holmes D, Ji Y (2005) Global regulation of gene expression by ArlRS, a two-component signal transduction regulatory system of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 187(15):5486–5492
Luong T, Lee C (2006) The arl locus positively regulates Staphylococcus aureus type 5 capsule via an mgrA-dependent pathway. Microbiology 152(10):3123–3131
Walker JN, Crosby HA, Spaulding AR, Salgado-Pabón W, Malone CL, Rosenthal CB, Schlievert PM, Boyd JM, Horswill AR (2013) The Staphylococcus aureus ArlRS two-component system is a novel regulator of agglutination and pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog 9(12):e1003819
Meier S, Goerke C, Wolz C, Seidl K, Homerova D, Schulthess B, Kormanec J, Berger-Bachi B, Bischoff M (2007) {sigma}B and the {sigma}B-dependent arlRS and yabJ-spoVG loci affect capsule formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun 75(9):4562–4571
Memmi G, Nair DR, Cheung A (2012) Role of ArlRS in autolysis in methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Bacteriol 194(4):759–767
Acknowledgements
We thank Esther Kleiner-Blatter (Department of Obstetrics, Zurich University Hospital, Switzerland) for her help with umbilical cords.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants of the Foundation for Research at the Medical Faculty, University of Zurich, Switzerland (to AZ and KS), a research Grant 2013 by the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) (to KS), a Grant from the Novartis Foundation (to AZ) and from the Swiss National Science Foundation (310030_146295/1 to AZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted in compliance with the current version of the Declaration of Helsinki, as well as all national legal and regulatory requirements, and was approved by the cantonal ethics committee Zurich (KEK-StV-Nr.07/07).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all women donating umbilical cords.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seidl, K., Leemann, M. & Zinkernagel, A.S. The ArlRS two-component system is a regulator of Staphylococcus aureus-induced endothelial cell damage. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 37, 289–292 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-017-3130-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-017-3130-5