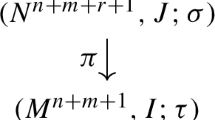Abstract
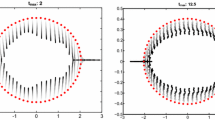
This paper proposes a Newton-type method to solve numerically the eigenproblem of several diagonalizable matrices, which pairwise commute. A classical result states that these matrices are simultaneously diagonalizable. From a suitable system of equations associated to this problem, we construct a sequence that converges quadratically towards the solution. This construction is not based on the resolution of a linear system as is the case in the classical Newton method. Moreover, we provide a theoretical analysis of this construction and exhibit a condition to get a quadratic convergence. We also propose numerical experiments, which illustrate the theoretical results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Absil, P.-A., Gallivan, K.A.: Joint diagonalization on the oblique manifold for independent component analysis. In 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing Proceedings, volume 5, pages V–V, (2006)
Absil, P.-A., Mahony, R., Sepulchre, R.: Optimization Algorithms on Matrix Manifolds. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2008)
Afsari, B.: Sensitivity analysis for the problem of matrix joint diagonalization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 30, 1148–1171 (2008)
Andruchow, E., Larotonda, G., Recht, L., Varela, A.: The left invariant metric in the general linear group. J. Geom. Phys. 86, 241–257 (2014)
Bouchard, F., Afsari, B., Malick, J., Congedo, M.: Approximate joint diagonalization with Riemannian optimization on the general linear group. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 41(1), 152–170 (2020)
Bro, R.: Parafac tutorial and applications. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 38(2), 149–171 (1997)
Bunse-Gerstner, A., Byers, R., Mehrmann, V.: A chart of numerical methods for structured eigenvalue problems. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 13(2), 419–453 (1992)
Bunse-Gerstner, A., Byers, R., Mehrmann, V.: Numerical methods for simultaneous diagonalization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 14(4), 927–949 (1993)
Bürgisser, P., Clausen, M., Shokrollahi, M.A.: Algebraic Complexity Theory, vol. 315. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin (2013)
Cardoso, J.-F., Souloumiac, A.: Blind beamforming for non gaussian signals. IEE Proc.-F 140, 362–370 (1993)
Cardoso, J.-F., Souloumiac, A.: Jacobi angles for simultaneous diagonalization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 17(1), 161–164 (1996)
Carroll, J.D., Chang, J.-J.: Analysis of individual differences in multidimensional scaling via an n-way generalization of Eckart-Young decomposition. Psychometrika 35(3), 283–319 (1970)
Cichocki, A., Mandic, D., De Lathauwer, L., Zhou, G., Zhao, Q., Caiafa, C., Phan, H.A.: Tensor decompositions for signal processing applications: from two-way to multiway component analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 32(2), 145–163 (2015)
Comon, P., Jutten, C.: Handbook of Blind Source Separation: Independent Component Analysis and Applications, 1st edn. Academic Press Inc., USA (2010)
Cox, D.A., Little, J.B., O’Shea, D.: Using Algebraic Geometry. Number 185 in Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2005)
De Lathauwer, L.: A link between the canonical decomposition in multilinear algebra and simultaneous matrix diagonalization. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 28(3), 642–666 (2006)
Douglas, S.C.: Self-stabilized gradient algorithms for blind source separation with orthogonality constraints. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 11(6), 1490–1497 (2000)
Elkadi, M., Mourrain, B.: Introduction à la résolution des systèmes polynomiaux. Mathématiques et Applications, vol. 59. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Flury, B.D., Neuenschwander, B.E.: Simultaneous diagonalization algorithms with applications in multivariate statistics. In: Approximation and Computation: A Festschrift in Honor of Walter Gautschi, pp. 179–205. Springer, Birkhäuser, Boston, MA (1994)
Flury, B.N., Gautschi, W.: An algorithm for simultaneous orthogonal transformation of several positive definite symmetric matrices to nearly diagonal form. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 7(1), 169–184 (1986)
Françoise, C.: Simultaneous newton’s iteration for the eigenproblem. Computing 5, 67–74 (1984)
Hoeven, J.V.D., Mourrain, B.: Efficient certification of numeric solutions to eigenproblems. In: Blömer, J., Kotsireas, I., Kutsia, T., Simos, D. (eds.) Mathematical Aspects of Computer and Information Sciences. MACIS 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 10693. Springer, Cham (2017)
Horn, R.A., Charles, C.R.: Topics in Matrix Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1991)
Horn, R.A., Johnson, C.R.: Matrix Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012)
Jiang, R., Li, D.: Simultaneous diagonalization of matrices and its applications in quadratically constrained quadratic programming. SIAM J. Optim. 26(3), 1649–1668 (2016)
Joho, M., Rahbar, K.: Joint diagonalization of correlation matrices by using Newton methods with application to blind signal separation. In: Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop Proceedings, 2002, 403–407 (2002)
Joho, M.: Newton method for joint approximate diagonalization of positive definite Hermitian matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 30(3), 1205–1218 (2008)
Joho, M., Rahbar, K.: Joint diagonalization of correlation matrices by using newton methods with application to blind signal separation. In: Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop Proceedings, 2002, pp. 403–407. IEEE, (2002)
Jolliffe, I.: Principal Component Analysis, pp. 1094–1096. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin (2011)
Laub, A., Heath, M., Paige, C., Ward, R.: Computation of system balancing transformations and other applications of simultaneous diagonalization algorithms. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 32(2), 115–122 (1987)
Luciani, X., Albera, L.: Canonical polyadic decomposition based on joint eigenvalue decomposition. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 132, 152–167 (2014)
Mahony, R.E.: The constrained newton method on a lie group and the symmetric eigenvalue problem. Linear Algebra Appl. 248, 67–89 (1996)
Mesloub, A., Belouchrani, A., Abed-Meraim, K.: Efficient and stable joint eigenvalue decomposition based on generalized givens rotations. In: 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), pp. 1247–1251. IEEE, (2018)
Nikpour, M., Manton, J., Hori, G.: Algorithms on the Stiefel manifold for joint diagonalisation. In: 2002 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 2, II–1481–II–1484 (2002)
Nishimori, Y., Akaho, S.: Learning algorithms utilizing quasi-geodesic flows on the Stiefel manifold. Neurocomput. 67, 106–135 (2005)
Rahbar, K., Reilly, J.P.: Geometric optimization methods for blind source separation of signals. In: in Proc. ICA, pp. 375–380, (2000)
Rosser, B., Lanczos, C., Hestenes, M.R., Karush, W.: Separation of close eigen-values of a real symmetric matrix. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 47, 291–297 (1950)
Sato, H.: Riemannian newton-type methods for joint diagonalization on the stiefel manifold with application to independent component analysis. Optimization 66(12), 2211–2231 (2017)
Sidiropoulos, N.D., Bro, R.: On the uniqueness of multilinear decomposition of n-way arrays. J. Chemom. 14(3), 229–239 (2000)
Sidiropoulos, N.D., Lathauwer, L.D., Xiao, F., Huang, K., Papalexakis, E.E., Faloutsos, C.: Tensor decomposition for signal processing and machine learning. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65(13), 3551–3582 (2017)
Sørensen, M., De Lathauwer, L.: Multidimensional harmonic retrieval via coupled canonical polyadic decomposition-part i: model and identifiability. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65(2), 517–527 (2016)
Sørensen, M., De Lathauwer, L.: Multidimensional harmonic retrieval via coupled canonical polyadic decomposition-part ii: algorithm and multirate sampling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65(2), 528–539 (2016)
Sørensen, M., Domanov, I., De Lathauwer, L.: Coupled canonical polyadic decompositions and multiple shift invariance in array processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 66(14), 3665–3680 (2018)
Sørensen, M., Van Eeghem, F., De Lathauwer, L.: Blind multichannel deconvolution and convolutive extensions of canonical polyadic and block term decompositions. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65(15), 4132–4145 (2017)
van der Hoeven, J., Yakoubsohn, J.-C..: Certified singular value decomposition. Technical Report HAL 01941987, (2018)
Vollgraf, R., Obermayer, K.: Quadratic optimization for simultaneous matrix diagonalization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(9), 3270–3278 (2006)
Wang, W., Sanei, S., Chambers, J.: Penalty function-based joint diagonalization approach for convolutive blind separation of nonstationary sources. In: IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol.53, pp. 1654–1669 (2005)
Weyl, H.: Das asymptotische verteilungsgesetz der eigenwerte linearer partieller differentialgleichungen (mit einer anwendung auf die theorie der hohlraumstrahlung). Math. Ann. 71, 441–479 (1912)
Yeredor, A.: Non-orthogonal joint diagonalization in the least-squares sense with application in blind source separation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50(7), 1545–1553 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicting interest that is directly or indirectly related to the work submitted for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khouja, R., Mourrain, B. & Yakoubsohn, JC. Newton-type methods for simultaneous matrix diagonalization. Calcolo 59, 38 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10092-022-00484-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10092-022-00484-3
Keywords
- Simultaneous diagonalization
- Newton-type method
- eigenproblem
- eigenvalues
- certification
- high precision computation