Abstract
Background
Understanding the benefits and risks of endovascular therapy (EVT) is crucial for elderly patients with large ischemic cores, as the combination of advanced age and extensive brain infarction may negatively impact clinical outcomes.
Methods
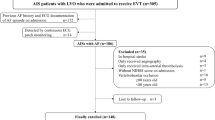
The study retrospectively analyzed clinical outcomes for elderly stroke patients (age ≥ 70) with large ischemic cores (Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score [ASPECTS] < 6 or ischemic cores ≥ 70 ml) in the anterior circulation using data from our prospective database between June 2018 and January 2022. The effectiveness and risks of EVT in those patients were investigated, with the primary outcome being fair outcome (modified Rankin Scale, mRS ≤ 3).
Results
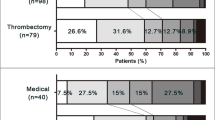
Among 182 elderly patients with large ischemic core volume (120 in the EVT group and 62 in the non-EVT group), 20.9% (38/182, 22.5% in the EVT group vs. 17.7% in the non-EVT group) achieved a fair outcome. Meanwhile, 49.5% (90/182, 45.8% in the EVT group vs. 56.5% in the non-EVT group) of them died at 3 months. The benefits of EVT numerically exceeded non-EVT treatment for those aged ≤ ~ 85 years or with a mismatch volume ≥ ~ 50 ml. However, after adjustment, EVT was associated with an increased risk of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (aOR 4.24, 95%CI 1.262–14.247).
Conclusions
This study highlights the clinical challenges faced by elderly patients with large infarctions, resulting in poor outcomes at 3 months. EVT may still provide some benefits in this population, but it also carries an increased risk of intracranial hemorrhage.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are available from the corresponding authors.
References
Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH et al (2016) Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 387:1723–1731. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00163-X. 2016/02/24
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T et al (2019) Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 50:e344–e418. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
Nogueira RG, Haussen DC, Liebeskind D et al (2021) Stroke Imaging Selection Modality and Endovascular Therapy Outcomes in the Early and Extended Time Windows. Stroke 52:491–497. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.031685
Nogueira RG, Jadhav AP, Haussen DC et al (2018) Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N Engl J Med 378:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1706442. 2017/11/14
Finitsis S, Epstein J, Richard S et al (2021) Age and Outcome after Endovascular Treatment in Anterior Circulation Large-Vessel Occlusion Stroke: ETIS Registry Results. Cerebrovasc Dis 50:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1159/000512203. 2020/12/16
Yoshimura S, Sakai N, Yamagami H et al (2022) Endovascular Therapy for Acute Stroke with a Large Ischemic Region. N Engl J Med 386:1303–1313. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2118191
Sarraj A, Grotta JC, Pujara DK et al (2020) Triage imaging and outcome measures for large core stroke thrombectomy - a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg 12:1172–1179. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-015509
Campbell BCV, Majoie C, Albers GW et al (2019) Penumbral imaging and functional outcome in patients with anterior circulation ischaemic stroke treated with endovascular thrombectomy versus medical therapy: a meta-analysis of individual patient-level data. Lancet Neurol 18:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30314-4. 2018/11/11
Lehrieder D, Layer K, Muller HP et al (2021) Association of Infarct Volume Before Hemicraniectomy and Outcome After Malignant Infarction. Neurology 96:e2704–e2713. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000011987
Luo Y, Chen M, Fang J, et al. (2022) Relationship Between Body Temperature and Early Neurological Deterioration after Endovascular Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke with Large Vessel Occlusion. Neurocrit Care https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-021-01416-9
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C et al (1998) Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet 352:1245–1251. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(98)08020-9
Alawieh A, Starke RM, Chatterjee AR et al (2019) Outcomes of endovascular thrombectomy in the elderly: a ‘real-world’ multicenter study. J Neurointerv Surg 11:545–553. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2018-014289. 2018/11/06
Ospel J, Kappelhof M, Groot AE et al (2020) Combined Effect of Age and Baseline Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score on Post-Thrombectomy Clinical Outcomes in the MR CLEAN Registry. Stroke 51:3742–3745. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.031773
Ospel JM, Kappelhof M, Kashani N et al (2021) Effect of age and baseline ASPECTS on outcomes in large-vessel occlusion stroke: results from the HERMES collaboration. J Neurointerv Surg 13:790–793. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-016621. 2020/09/16
Yang W, Zhang L, Yao Q et al (2020) Endovascular treatment or general treatment: how should acute ischemic stroke patients choose to benefit from them the most?: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 99:e20187. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000020187
Pohjasvaara T, Erkinjuntti T, Vataja R et al (1997) Comparison of stroke features and disability in daily life in patients with ischemic stroke aged 55 to 70 and 71 to 85 years. Stroke 28:729–735. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.28.4.729
Meyer L, Alexandrou M, Flottmann F et al (2020) Endovascular Treatment of Very Elderly Patients Aged >/=90 With Acute Ischemic Stroke. J Am Heart Assoc 9:e014447. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.119.014447
Garcia-Esperon C, Bivard A, Johns H, et al. (2022) Association of Endovascular Thrombectomy With Functional Outcome in Patients With Acute Stroke With a Large Ischemic Core. Neurology https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000200908
Sarraj A, Hassan AE, Savitz S et al (2019) Outcomes of Endovascular Thrombectomy vs Medical Management Alone in Patients With Large Ischemic Cores: A Secondary Analysis of the Optimizing Patient’s Selection for Endovascular Treatment in Acute Ischemic Stroke (SELECT) Study. JAMA Neurol 76:1147–1156. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.2109
Yoshimoto T, Inoue M, Tanaka K et al (2021) Identifying large ischemic core volume ranges in acute stroke that can benefit from mechanical thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg 13:1081–1087. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-016934. 2020/12/17
Zaidat OO, Liebeskind DS, Jadhav AP et al (2021) Impact of Age and Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score 0 to 5 on Mechanical Thrombectomy Outcomes: Analysis From the STRATIS Registry. Stroke 52:2220–2228. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032430
Seners P, Oppenheim C, Turc G et al (2021) Perfusion Imaging and Clinical Outcome in Acute Ischemic Stroke with Large Core. Ann Neurol 90:417–427. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26152
Alexandre AM, Pedicelli A, Valente I et al (2020) endovascular thrombectomy without CT perfusion improve clinical outcome? Clin Neurol Neurosurg 198:106207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106207
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q.L. and L.H. developed the initial idea for this study. Q.L., J.H.F., M.K.Z., and L.H. formulated the study design. L.H. and M.K.Z. were consulted about clinical issues. Q.L. contributed to the original draft. J.F., M.K.Z., and L.H. were responsible for the revision of the draft. X.J., Q.L., T.D., Y.X.L., L.J.G., S.J.D. and M.M.M. contributed to data collection. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval statement
This document complies with ethical guidelines and has obtained approval for the observational study from the Biomedical Research Ethics Committee of West China Hospital, Sichuan University. The informed consent was waived due to its retrospective design.
Conflict of interest
All authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Fang, J., Jiang, X. et al. Endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke in elderly patients with large ischemic cores. Neurol Sci 45, 663–670 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-023-06995-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-023-06995-3