Abstract
Background and aim
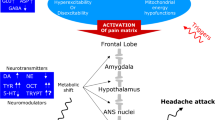
The pathogenesis of the pain that occurs in episodic migraine attack is due to the activation of the trigeminal system’s first neuron receptors located on vessel wall. The release from the endothelium of nitric oxide, a product of arginine metabolism, causes vasodilation and stretching of the vascular trigeminal system and promotes pain. It is unknown whether this same metabolic event is involved in the pain accompanying chronic migraine. To understand the possible role of arginine in the pathogenesis of chronic migraine patients, we evaluated the metabolism of arginine in plasma of chronic migraine and control subjects.
Methods
We evaluated the metabolism of arginine in a group of patients affected by chronic migraine. Quantification of arginine, ornithine, citrulline, monomethyl arginine (NMMA), dimethylarginines (ADMA, SDMA), and tyramine was performed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer.
Results
Chronic migraine patients showed low plasma levels of arginine, significantly elevated levels of ornithine, ADMA, and NMMA whereas the levels of citrulline and SDMA were in the range of controls.
Conclusions
The elevated levels of ADMA and NMMA, inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase, suggest that the metabolism of arginine may be inhibited with a possible reduction of NO release in the circulation of chronic patients. This suggests that the origin of pain may not be related to the vasodilation of trigeminal vascular system that occurs in episodic migraine patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets that support the finding of this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ADMA:
-
NG,NG-Dimethyl-l-arginine
- ARG:
-
L-Arginine
- ORN:
-
L-Ornithine
- CIT:
-
L-Citrulline
- CM:
-
Chronic migraine
- CTRL:
-
Controls
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- E:
-
Adrenalin
- 5-HT:
-
Serotonin
- MS/MS:
-
Tandem mass spectrometry
- NE:
-
Norepinephrine
- NMMA:
-
NG-Methyl-l-arginine
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- SDMA:
-
Symmetric dimethylarginine
- TAAR:
-
Trace amine-associated receptor
- TYRA:
-
Tyramine
- UPLC:
-
Ultra-performance liquid chromatography
References
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache S (2013) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia Int J Headache 33(9): 629–808
Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, Sliwinski M (1996) Classification of daily and near-daily headaches: field trial of revised IHS criteria. Neurology 47(4):871–875
Olesen J, Bousser MG, Diener HC, Dodick D, First M, Goadsby PJ, Gobel H, Lainez MJ, Lance JW, Lipton RB, Nappi G, Sakai F, Schoenen J, Silberstein SD, Steiner TJ (2006) New appendix criteria open for a broader concept of chronic migraine. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 26(6):742-6
D'Amico D, Grazzi L, Usai S, Raggi A, Leonardi M, Bussone G (2011) Disability in chronic daily headache: state of the art and future directions. Neurol Sci 32 Suppl 1S71–6.
Katsarava Z, Schneeweiss S, Kurth T, Kroener U, Fritsche G, Eikermann A, Diener HC, Limmroth V (2004) Incidence and predictors for chronicity of headache in patients with episodic migraine. Neurology 62(5):788–790
Manack AN, Buse DC, Lipton RB (2010) Chronic migraine: epidemiology and disease burden. Curr Pain Headache Rep 15(1):70–78
D’Andrea G, Cananzi AR, Perini F, Alecci M, Zamberlan F, Hasselmark L, Welch KM, (1994) Decreased collagen-induced platelet aggregation and increased platelet arginine levels in migraine: a possible link with the NO pathway. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 14(5):352–6
D’Andrea G, Toldo M, Cortelazzo S, Milone FF (1982) Platelet activity in migraine. Headache 22(5):207–212
Perini F, D’Andrea G, Galloni E, Pignatelli F, Billo G, Alba S, Bussone G, Toso V (2005) Plasma cytokine levels in migraineurs and controls. Headache 45(7):926–931
Edvinsson L, Haanes KA, Warfvinge K, Krause DN (2018) CGRP as the target of new migraine therapies - successful translation from bench to clinic. Nat Rev 14(6):338–350
Edvinsson L (2017) The trigeminovascular pathway: role of CGRP and CGRP receptors in migraine. Headache 57(Suppl):247–255
Sarchielli P, Alberti A, Codini M, Floridi A, Gallai V, (2000) Nitric oxide metabolites, prostaglandins and trigeminal vasoactive peptides in internal jugular vein blood during spontaneous migraine attacks. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 20(10):907–18
Tsikas D, Wu G (2015) Homoarginine, arginine, and relatives: analysis, metabolism, transport, physiology, and pathology. Amino Acids 47(9):1697–1702
Flam BR, Eichler DC, Solomonson LP (2007) Endothelial nitric oxide production is tightly coupled to the citrulline-NO cycle. Nitric Oxide 17(3–4):115–121
Gainetdinov RR, Hoener MC, Berry MD (2018) Trace Amines and Their Receptors. Pharmacol Rev 70(3):549–620
Koh AHW, Chess-Williams R, Lohning AE (2019) Differential mechanisms of action of the trace amines octopamine, synephrine and tyramine on the porcine coronary and mesenteric artery. Sci Rep 9(1):10925
Grazzi L, Raggi A, D’Amico D, Sansone E, Leonardi M, Andrasik F, Gucciardi A, Guido D, D’Andrea G (2019) A prospective pilot study of the effect on catecholamines of mindfulness training vs pharmacological prophylaxis in patients with chronic migraine and medication overuse headache. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 39(5):655–664
Gray N, Plumb RS, Wilson ID, Nicholson JK (2019) A validated UPLC-MS/MS assay for the quantification of amino acids and biogenic amines in rat urine. J Chromatogr 1106–110750–57
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Methodol 57(1): 289–300
Bode-Boger SM, Scalera F, Kielstein JT, Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Breithardt G, Fobker M, Reinecke H (2006) Symmetrical dimethylarginine: a new combined parameter for renal function and extent of coronary artery disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 17(4):1128–1134
D’Andrea G, D’Arrigo A, Dalle Carbonare M, Leon A (2012) Pathogenesis of migraine: role of neuromodulators. Headache 52(7):1155–1163
D’Andrea G, Gucciardi A, Perini F, Leon A (2019) Pathogenesis of Cluster Headache: From Episodic to Chronic Form, the Role of Neurotransmitters and Neuromodulators. Headache 59(9):1665–1670
Borowsky B, Adham N, Jones KA, Raddatz R, Artymyshyn R, Ogozalek KL, Durkin MM, Lakhlani PP, Bonini JA, Pathirana S, Boyle N, Pu X, Kouranova E, Lichtblau H, Ochoa FY, Branchek TA, Gerald C (2001) Trace amines: identification of a family of mammalian G protein-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(16):8966–8971
Pradhan AA, Bertels Z, Akerman S (2018) Targeted Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitors for Migraine. Neurotherapeutics 15(2):391–401
D’Andrea G, Gucciardi A, Perini F, Leon A (2019) The role of neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in the pathogenesis of cluster headache: a review. Neurol Sci 40(Suppl 1):39–44
D’Andrea G, Cevoli S, Colavito D, Leon A (2015) Biochemistry of primary headaches: role of tyrosine and tryptophan metabolism. Neurol Sci 36(Suppl):117–122
Funding
The research was partially funded by the F.I.CEF Charity (Italian Foundation for Headache, Naples, Italy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Neurological Institute C. Besta of Milan, Italy, and was performed in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient prior the onset of the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D’Andrea, G., Gucciardi, A., Giordano, G. et al. Study of arginine metabolism in medication overuse chronic migraine: possible defect in NO synthesis. Neurol Sci 43, 2745–2749 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05672-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05672-7