Abstract
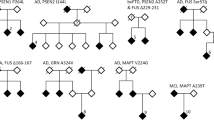
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) can be either sporadic or familial, and familial forms of AD accounts for only 5% of the cases. So far, autosomal dominantly inherited mutations in “Presenilin 1” (PSEN1), “Presenilin 2” (PSEN2), and “Amyloid precursor protein” (APP) genes were associated with familial AD. Amid the others, pathogenic mutations in the PSEN2 gene are less common. In this study, we describe a novel heterozygous PSEN2 (c.524C>T, p.Ser175Phe) alteration identified in a 58-year-old Turkish patient from a family with multiple dementia cases. This variant was further present in the patient’s clinically affected maternal cousin as well as in the asymptomatic mother and two maternal aunts who were carriers of the APOE ε2/ε3 genotype. The variant is located in the conserved residue of transmembrane domain III encoded by exon 6 of the major transcript. In silico protein structure analyses predicted that this variant might change the architecture of interaction between the two alpha helixes of PSEN2. We propose that p.Ser175Phe may have a pathogenic effect on protein function and may play a significant role in the molecular pathways leading to Alzheimer’s disease in this family.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cacace R, Sleegers K, Van Broeckhoven C (2016) Molecular genetics of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease revisited. Alzheimers Dement 12:733–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.01.012
Guerreiro RJ, Gustafson DR, Hardy J (2012) The genetic architecture of Alzheimer’s disease: beyond APP, PSENs and APOE. Neurobiol Aging 33:437–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.03.025
Park KW, An SS, Bagyinszky E, Kim S (2017) A case of possibly pathogenic PSEN2 R62C mutation in a patient with probable early-onset Alzheimer’s dementia supported by structure prediction. Clin Interv Aging 12:367–375. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S128884
Binetti G, Signorini S, Squitti R, Alberici A, Benussi L, Cassetta E, Frisoni GB, Barbiero L, Feudatari E, Nicosia F, Testa C, Zanetti O, Gennarelli M, Perani D, Anchisi D, Ghidoni R, Rossini PM (2003) Atypical dementia associated with a novel presenilin-2 mutation. Ann Neurol 54:832–836. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.10760
McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR Jr, Kawas CH, Klunk WE, Koroshetz WJ, Manly JJ, Mayeux R, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rossor MN, Scheltens P, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Weintraub S, Phelps CH (2011) The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 7:263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev SR (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 4:248–249. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth0410-248
Schwarz JM, Cooper DN, Schuelke M, Seelow D (2014) MutationTaster2: mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat Methods 11:361–362. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2890
Choi Y, Sims GE, Murphy S, Miller JR, Chan AP (2012) Predicting the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. PLoS One 7:e46688. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046688
Rentzsch P, Witten D, Cooper GM, Shendure J, Kircher M (2019) CADD: predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D886–D894. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1016
1000 Genomes Project Consortium, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Garrison EP, Kang HM, Korbel JO, Marchini JL, McCarthy S, McVean GA, Abecasis GR (2015) A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 526:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15393
Sherry ST, Ward MH, Kholodov M, Baker J, Phan L, Smigielski EM, Sirotkin K (2001) dbSNP: the NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res 29:308–311. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.1.308
Guerreiro R, Sassi C, Gibbs JR, Edsall C, Hernandez D, Brown K, Lupton MK, Parkinnen L, Ansorge O, Hodges A, Ryten M, for the UK Brain Expression Consortium, Tienari PJ, Van Deerlin VM, Trojanowski JQ, Morgan K, Powell J, Singleton A, Hardy J, Bras J (2018) A comprehensive assessment of benign genetic variability for neurodegenerative disorders, bioRxiv. 270686. doi:10.1101/270686
Ashkenazy H, Abadi S, Martz E, Chay O, Mayrose I, Pupko T, Ben-Tal N (2016) ConSurf 2016: an improved methodology to estimate and visualize evolutionary conservation in macromolecules. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W344–W350. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw408
Piscopo P, Talarico G, Crestini A, Gasparini M, Malvezzi-Campeggi L, Piacentini E, Lenzi GL, Bruno G, Confaloni A (2010) A novel mutation in the predicted TMIII domain of the PSEN2 gene in an Italian pedigree with atypical Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 20:43–47. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2010-1369
Guerreiro RJ, Baquero M, Blesa R, Boada M, Brás JM, Bullido MJ, Calado A, Crook R, Ferreira C, Frank A, Gómez-Isla T, Hernández I, Lleó A, Machado A, Martínez-Lage P, Masdeu J, Molina-Porcel L, Molinuevo JL, Pastor P, Pérez-Tur J, Relvas R, Oliveira CR, Ribeiro MH, Rogaeva E, Sa A, Samaranch L, Sánchez-Valle R, Santana I, Tàrraga L, Valdivieso F, Singleton A, Hardy J, Clarimón J (2010) Genetic screening of Alzheimer’s disease genes in Iberian and African samples yields novel mutations in presenilins and APP. Neurobiol Aging 31:725–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.06.012
Wojtas A, Heggeli KA, Finch N, Baker M, Dejesus-Hernandez M, Younkin SG, Dickson DW, Graff-Radford NR, Rademakers R (2012) C9ORF72 repeat expansions and other FTD gene mutations in a clinical AD patient series from Mayo Clinic. Am J Neurodegener Dis 1:107–118
Shi Z, Wang Y, Liu S, Liu M, Liu S, Zhou Y, Wang J, Cai L, Huo YR, Gao S, Ji Y (2015) Clinical and neuroimaging characterization of Chinese dementia patients with PSEN1 and PSEN2 mutations. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 39:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1159/000366272
Wang JC, Alinaghi S, Tafakhori A, Sikora E, Azcona LJ, Karkheiran S, Goate A, Paisán-Ruiz C, Darvish H (2018) Genetic screening in two Iranian families with early-onset Alzheimer’s disease identified a novel PSEN1 mutation, Neurobiol Aging. 62 244.e15-244.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.10.011.
Taddei K, Kwok JB, Kril JJ, Halliday GM, Creasey H, Hallupp M, Fisher C, Brooks WS, Chung C, Andrews C, Masters CL, Schofield PR, Martins RN (1998) Two novel presenilin-1 mutations (Ser169Leu and Pro436Gln) associated with very early onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport 9:3335–3339. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-199810050-00034
Ezquerra M, Carnero C, Blesa R, Gelpí JL, Ballesta F, Oliva R (1999) A presenilin 1 mutation (Ser169Pro) associated with early-onset AD and myoclonic seizures. Neurology. 52:566–570. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.52.3.566
Guo J, Wei J, Liao S, Wang L, Jiang H, Tang B (2010) A novel presenilin 1 mutation (Ser169del) in a Chinese family with early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 468:34–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2009.10.055
Giau VV, Pyun JM, Bagyinszky E, An SSA, Kim S (2018) A pathogenic PSEN2 p.His169Asn mutation associated with early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Interv Aging 13:1321–1329. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S170374
Xia M, Chen S, Shi Y, Huang Y, Xu J, Zhao T, He S, Wu Y, Xu C, Zang W, J. Zhang (2015) Probable novel PSEN2 Pro123Leu mutation in a Chinese Han family of Alzheimer’s disease, Neurobiol Aging. 36, 3334.e13-3334.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.09.003.
Vélez JI, Lopera F, Sepulveda-Falla D, Patel HR, Johar AS, Chuah A, Tobón C, Rivera D, Villegas A, Cai Y, Peng K, Arkell R, Castellanos FX, Andrews SJ, Silva Lara MF, Creagh PK, Easteal S, de Leon J, Wong ML, Licinio J, Mastronardi CA, Arcos-Burgos M (2016) APOE*E2 allele delays age of onset in PSEN1 E280A Alzheimer's disease. Mol Psychiatry 21:916–924. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.177
Arboleda-Velasquez JF, Lopera F, O'Hare M, Delgado-Tirado S, Marino C, Chmielewska N, Saez-Torres KL, Amarnani D, Schultz AP, Sperling RA, Leyton-Cifuentes D, Chen K, Baena A, Aguillon D, Rios-Romenets S, Giraldo M, Guzmán-Vélez E, Norton DJ, Pardilla-Delgado E, Artola A, Sanchez JS, Acosta-Uribe J, Lalli M, Kosik KS, Huentelman MJ, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Reiman RA, Luo J, Chen Y, Thiyyagura P, Su Y, Jun GR, Naymik M, Gai X, Bootwalla M, Ji J, Shen L, Miller JB, Kim LA, Tariot PN, Johnson KA, Reiman EM, Quiroz YT (2019) Resistance to autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease in an APOE3 Christchurch homozygote: a case report. Nat Med 25:1680–1683. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0611-3
Sherrington R, Froelich S, Sorbi S, Campion D, Chi H, Rogaeva EA, Levesque G, Rogaev EL, Lin C, Liang Y, Ikeda M, Mar L, Brice A, Agid Y, Percy ME, Clerget-Darpoux F, Piacentini S, Marcon G, Nacmias B, Amaducci L, Frebourg T, Lannfelt L, Rommens JM, St George-Hyslop PH (1996) Alzheimer’s disease associated with mutations in presenilin 2 is rare and variably penetrant. Hum Mol Genet 5:985–988. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/5.7.985
Finckh U, Muller-Thomsen T, Mann U, Eggers C, Marksteiner J, Meins W, Binetti G, Alberici A, Hock C, Nitsch RM, Gal A (2000) High prevalence of pathogenic mutations in patients with early-onset dementia detected by sequence analyses of four different genes. Am J Hum Genet 66:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1086/302702
Ezquerra M, Lleó A, Castellví M, Queralt R, Santacruz P, Pastor P, Molinuevo JL, Blesa R, Oliva R (2003) A novel mutation in the PSEN2 gene (T430M) associated with variable expression in a family with early-onset Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 60(8):1149–1151. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.60.8.1149
Lalli MA, Bettcher BM, Arcila ML, Garcia G, Guzman C, Madrigal L, Ramirez L, Acosta-Uribe J, Baena A, Wojta KJ, Coppola G, Fitch R, de Both MD, Huentelman MJ, Reiman EM, Brunkow ME, Glusman G, Roach JC, Kao AW, Lopera F, Kosik KS (2015) Whole-genome sequencing suggests a chemokine gene cluster that modifies age at onset in familial Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 20(11):1294–1300. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.131
Piaceri I, Chiari A, Galli C, Bagnoli S, Ferrari C, Trujillo Saavedra S, Molinari MA, Vinceti G, Sorbi S, Nacmias B (2020) Incomplete penetrance in familial Alzheimer’s disease with PSEN1 Ala260Gly mutation. Neurol Sci 41(8):2263–2266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04421-6
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the family for their generous participation. The authors also thank Cagla Donmez, Rukiye Aslan, and Utku Uyan for their help in obtaining the samples. We would also like to acknowledge Khusan Khodzhaev, for technical assistance towards the construction of the artwork. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not for profit sectors.
Availability of data and material
All data analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of Istanbul Faculty of Medicine, Istanbul University. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from legal guardians or all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1.
Sanger sequencing chromatograms showing the PSEN2 p.Ser175Phe mutation site in family members. (PDF 4332 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guven, G., Samanci, B., Gulec, C. et al. A novel PSEN2 p.Ser175Phe variant in a family with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci 42, 2497–2504 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05243-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05243-w