Abstract
Background and purpose
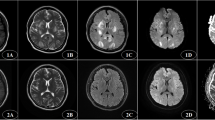
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a clinical and radiologic entity for which eclampsia is one of the most common predisposing conditions. Despite the imaging changes typically reported, the predisposing factors and clinical implications of atypical presentations have yet to be fully clarified.
Methods
A total of 56 patients with PRES were selected for study. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data were analyzed, focusing on atypical presentations of PRES. Multiple logistic regression was applied to identify factors impacting such atypical presentations, and functional outcomes were assessed upon patient discharge.
Results
Overall, 22 of the 56 patients (39.3%) displayed features of atypical PRES. By multiple logistic regression, headache (OR = 5.39; 95% CI, 1.24–23.51; p = 0.025) and frequent convulsions (OR = 4.41; 95% CI, 1.09–17.91; p = 0.038) proved to be independent factors associated with atypical PRES. Ultimately, outcomes of 18 patients were gauged as poor, based on the modified Rankin Scale (mRS). Logistic regression indicated that visual disturbances (OR = 9.02; 95% CI, 1.37–59.35; p = 0.02), frequent convulsions (OR = 9.47; 95% CI, 1.67–53.63; p = 0.01), and restricted diffusion on imaging (OR = 11.96; 95% CI, 1.76–81.11; p = 0.01) were independently associated with poor outcomes in patients with eclampsia-related PRES.
Conclusion
Headache and frequent convulsions are independently associated with atypical presentations of PRES. If present, restricted diffusion may help in predicting poor outcomes of such patients upon discharge.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, Pessin MS, Lamy C, Mas JL, Caplan LR (1996) A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med 334(8):494–500. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199602223340803
Fugate JE, Rabistein AA (2015) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: clinical and radiological manifestations, pathophysiology, and outstanding questions. Lancet Neurol 14(9):914-925
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF (2007) Distinct imaging patterns and lesion distribution in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Am J Neuroradiol 28(7):1320–1327. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0549
Chen Z, Xu M, Shang D, Luo B (2012) A case of reversible splenial lesions in late postpartum preeclampsia. Intern Med 51(7):787–790. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.51.6500
Benziada-Boudour A, Schmitt E, Kremer S, Foscolo S, Riviere AS, Tisserand M, Boudour A, Bracard S (2009) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a case of unusual diffusion-weighted MR images. J Neuroradiol 36(2):102–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurad.2008.08.003
Ishikura K, Hamasaki Y, Sakai T, Hataya H, Goto T, Miyama S, Kono T, Honda M (2011) Children with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome associated with atypical diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient. Clin Exp Nephrol 15(2):275–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-010-0380-2
Pande AR, Ando K, Ishikura R, Nagami Y, Takada Y, Wada A, Watanabe Y, Miki Y, Uchino A, Nakao N (2006) Clinicoradiological factors influencing the reversibility of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a multicenter study. Radiat Med 24(10):659–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-006-0086-2
Li Y, Gor D, Walicki D, Jenny D, Jones D, Barbour P, Castaldo J (2012) Spectrum and potential pathogenesis of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 21(8):873–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2011.05.010
Wagner SJ, Acquah LA, Lindell EP, Craici IM, Wingo MT, Rose CH, White WM, August P, Garovic VD (2011) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and eclampsia: pressing the case for more aggressive blood pressure control. Mayo Clin Proc 86(9):851–856. https://doi.org/10.4065/mcp.2011.0090
Bartynski WS (2008) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, part 2: controversies surrounding pathophysiology of vasogenic edema. Am J Neuroradiol 29(6):1043–1049. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0929
Hod T, Cerdeira AS, Karumanchi SA (2015) Molecular mechanisms of preeclampsia. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 5(10). https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a023473
Liman TG, Bohner G, Heuschmann PU, Scheel M, Endres M, Siebert E (2012) Clinical and radiological differences in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome between patients with preeclampsia-eclampsia and other predisposing diseases. Eur J Neurol 19(7):935–943. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03629.x
Karampekios SK, Contopoulou E, Basta M, Tzagournissakis M, Gourtsoyiannis N (2004) Hypertensive encephalopathy with predominant brain stem involvement: MRI findings. J Hum Hypertens 18(2):133–134. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001654
Chen TY, Lee HJ, Wu TC, Tsui YK (2009) MR imaging findings of medulla oblongata involvement in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome secondary to hypertension. Am J Neuroradiol 30(4):755–757. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1337
Ekawa Y, Shiota M, Tobiume T, Shimaoka M, Tsuritani M, Kotani Y, Mizuno Y, Hoshiai H (2012) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome accompanying eclampsia: correct diagnosis using preoperative MRI. Tohoku J Exp Med 226(1):55–58. https://doi.org/10.1620/tjem.226.55
Tari Capone F, Candela S, Bozzao A, Orzi F (2015) A new case of brainstem variant of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: clinical and radiological features. Neurol Sci 36(7):1263–1265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-014-1999-7
Hinduja A, Habetz K, Raina S, Ramakrishnaiah R, Fitzgerald RT (2017) Predictors of poor outcome in patients with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Int J Neurosci 127(2):135–144. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2016.1152966
Golombeck SK, Wessig C, Monoranu C-M, Schutz A, Solymosi L, Melzer N, Kleinschnitz C (2013) Fatal atypical reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a case report. J Med Case Rep 7:14–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-1947-7-14
O'Kane M, Elhalwagy H, Kumar S, Badawi C (2014) Unusual presentation of PRES in the postnatal period. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2013-203406
Li Q, Lv F, Wei Y, Yan B, Xie P (2013) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus after cessation of oral prednisone. Neurol Sci 34(12):2241–2242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1479-5
American College of O, Gynecologists, Task Force on Hypertension in P (2013) Hypertension in pregnancy. Report of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 122(5):1122–1131. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.aog.0000437382.03963.88
Porcello Marrone LC, Marrone BF, Gadonski G, Huf Marrone AC, da Costa JC (2012) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 10(9):614–615
Schweitzer AD, Parikh NS, Askin G, Nemade A, Lyo J, Karimi S, Knobel A, Navi BB, Young RJ, Gupta A (2017) Imaging characteristics associated with clinical outcomes in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Neuroradiology 59(4):379–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1815-1
Singh RR, Ozyilmaz N, Waller S, U-King-Im J-M, Lim M, Siddiqui A, Sinha MD (2014) A study on clinical and radiological features and outcome in patients with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES). Eur J Pediatr 173(9):1225–1231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-014-2301-y
Provenzale JM, Petrella JR, Cruz LCH, Wong JC, Engelter S, Barboriak DP (2001) Quantitative assessment of diffusion abnormalities in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Am J Neuroradiol 22(8):1455–1461
McKinney AM, Short J, Truwit CL, McKinney ZJ, Kozak OS, SantaCruz KS, Teksam M (2007) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: incidence of atypical regions of involvement and imaging findings. Am J Roentgenol 189(4):904–912. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.07.2024
Aracki-Trenkic A, Stojanov D, Trenkic M, Radovanovic Z, Ignjatovic J, Ristic S, Trenkic-Bozinovic M (2016) Atypical presentation of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: clinical and radiological characteristics in eclamptic patients. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 16(3):180–186. https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2016.1201
Bloch RF (1988) Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 19(11):1448–1448
Tavares M, Arantes M, Chacim S, Campos Junior A, Pinto A, Mariz JM, Sonin T, Pereira S (2015) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children with hematologic malignancies. J Child Neurol 30(12):1669–1675. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073815578525
Alp A, Akdam H, Akar H, Koseoglu K, Ozkul A, Meteoglu I, Yenicerioglu Y (2014) Polyarteritis nodosa complicated by posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a case report. Nefrologia 34(6):789–796. https://doi.org/10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2014.Sep.12510
Zhao B, Wei Q, Wang Y, Chen Y, Shang H (2014) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in acute intermittent porphyria. Pediatr Neurol 51(3):457–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.05.016
Lin JT, Wang SJ, Fuh JL, Hsiao LT, Lirng JF, Chen PM (2003) Prolonged reversible vasospasm in cyclosporin A-induced encephalopathy. Am J Neuroradiol 24(1):102–104
Rykken JB, McKinney AM (2014) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Seminars In Ultrasound Ct And Mri 35(2):118–135. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.sult.2013.09.007
Donmez FY, Basaran C, Ulu EMK, Yildirim M, Coskun M (2010) MRI features of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in 33 patients. J Neuroimaging 20(1):22–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2008.00306.x
Kastrup O, Schlamann M, Moenninghoff C, Forsting M, Goericke S (2015) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: the spectrum of MR imaging patterns. Clin Neuroradiol 25(2):161–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0293-7
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF (2008) Catheter angiography, MR angiography, and MR perfusion in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Am J Neuroradiol 29(3):447–455. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0839
Stevens CJ, Heran MKS (2012) The many faces of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Br J Radiol 85(1020):1566–1575. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/25273221
de Groot PG, Urbanus RT, Roest M (2012) Platelet interaction with the vessel wall. Handb Exp Pharmacol 210:87–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29423-5_4
Shankar J, Banfield J (2017) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a review. Can Assoc Radiol J 68(2):147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carj.2016.08.005
Sibai BM (2005) Diagnosis, prevention, and management of eclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 105(2):402–410. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.aog.0000152351.13671.99
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This study conformed to Ethical Guidelines for Medical and Health Research Involving Human Subjects endorsed by the Chinese government and was authorized by the Ethics Committee of Shengjing Hospital at China Medical University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, X., Nao, J. Influential factors and clinical significance of an atypical presentation of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with eclampsia. Neurol Sci 40, 377–384 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3642-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3642-5