Abstract
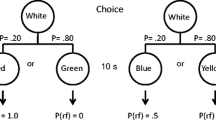
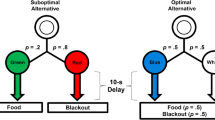
When pigeons are given a choice between 50% signaled reinforcement and 100% reinforcement they typically do not choose optimally, sometimes even preferring 50% reinforcement. Smith and Zentall (J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 42:212–220, 2016) proposed that choice depends primarily on the predictive value of the signal for reinforcement associated with each alternative (both 100% reinforcement) and not the frequency of the signal for reinforcement (50% vs. 100%). With extended training, however, Case and Zentall (Behav Process, 2018) found that pigeons actually show a reliable preference for the 50% reinforcement alternative. They suggested that contrast between the expected outcome at the time of choice (50% reinforcement) and the value of the signal for reinforcement (100% reinforcement) is the mechanism responsible for the preference for the suboptimal alternative (for the optimal alternative there should be no contrast). In the present research, we tested the contrast hypothesis by increasing the probability of reinforcement for choice of the suboptimal alternative to 75%, thereby reducing the contrast between expected and obtained reinforcement and found a reduced preference for the suboptimal alternative. That is, increasing the probability of reinforcement for choice of the suboptimal alternative decreased suboptimal choice. Thus, preference for the suboptimal alternative appears to result from two mechanisms: (1) the value of the signal for reinforcement that follows choice of the alternative and (2) positive contrast between the expected and obtained probability of reinforcement. We compared this interpretation with other hypotheses.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainslie GW (1975) Specious reward: a behavioral theory of impulsiveness and impulsive control. Psychol Bull 82:463–496
Beierholm UR, Dayan P (2010) Pavlovian-instrumental interaction in ‘observing behavior’. PLoS Comput Biol 6(9):e1000903
Belke TW, Spetch ML (1994) Choice between reliable and unreliable reinforcement alternatives revisited: preference for unreliable reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav 62(3):353. https://doi.org/10.1901/jeab.1994.62-353
Case JP, Zentall TR (2018) Suboptimal choice in pigeons: does the predictive value of the conditioned reinforcer alone determine choice? Behav Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2018.07.018
Fantino E (1969) Choice and rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav 12:723–730
Fantino E, Moore J (1980) Uncertainty reduction, conditioned reinforcement, and observing. J Exp Anal Behav 33(1):3–13. https://doi.org/10.1901/jeab.1980.33-3
Fantino E, Dunn R, Meck W (1979) Percentage reinforcement and choice. J Exp Anal Behav 32:335–340
Kendall SB (1974) Preference for intermittent reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav 21(3):463–473. https://doi.org/10.1901/jeab.1974.21-463
Kendall SB (1985) A further study of choice and percentage reinforcement. Behav Proc 10:399–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-6357(85)90040-3
Laude JR, Stagner JP, Zentall TR (2014) Suboptimal choice by pigeons may result from the diminishing effect of nonreinforcement. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 40:12–21
Mazur JE (1989) Theories of probabilistic reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav 51(1):87–99. https://doi.org/10.1901/jeab.1989.51-87
McDevitt MA, Spetch ML, Dunn R (1997) Contiguity and conditioned reinforcement in probabilistic choice. J Exp Anal Behav 68:317–327
McDevitt MA, Dunn RM, Spetch ML, Ludvig EA (2016) When good news leads to bad choices. J Exp Anal Behav 105:23–40
Molet M, Miller HC, Laude JR, Kirk C, Manning B, Zentall TR (2012) Decision- making by humans as assessed by a choice task: do humans, like pigeons, show suboptimal choice? Learn Behav 40:439–447. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13420-012-0065-7
Rescorla RA (1969) Pavlovian conditioned inhibition. Psychol Bull 72:77–94
Roper KL, Zentall TR (1999) Observing behavior in pigeons: the effect of reinforcement probability and response cost using a symmetrical choice procedure. Learn Motiv 30:201–220
Smith AP, Zentall TR (2016) Suboptimal choice in pigeons: choice is based primarily on the value of the conditioned reinforcer rather than overall reinforcement rate. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 42:212–220
Spetch ML, Dunn R (1990) Choice with uncertain outcomes: conditioned reinforcement effects. J Exp Anal Behav 53:201–218
Spetch M, Belke T, Barnet R, Dunn R, Pierce W (1990) Suboptimal choice in a percentage reinforcement procedure: effects of signal condition and terminal-link length. J Exp Anal Behav 53(2):219–234. https://doi.org/10.1901/jeab.1990.53-219
Spetch M, Mondloch M, Belke T, Dunn R (1994) Determinants of pigeons’ choice between certain and probabilistic outcomes. Anim Learn Behav 22(3):239–251. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03209832
Stagner JP, Zentall TR (2010) Suboptimal choice behavior by pigeons. Psychon Bull Rev 17:412–416
Stephens DW, Krebs JR (1986) Foraging theory. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Tatham TA, Zurn KR (1989) The Med-PC experimental apparatus programming system. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comp 21:294–302
Vasconcelos M, Monteiro T, Kacelnik A (2015) Irrational choice and the value of information. Sci Rep 5:13874
Zentall TR, Stagner JP (2011) Maladaptive choice behavior by pigeons: an animal analog of gambling (sub-optimal human decision making behavior). Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 278:1203–1208
Zentall TR, Laude JR, Stagner JP, Smith AP (2015) Suboptimal choice by pigeons: evidence that the value of the conditioned reinforcer rather than its frequency determines choice. Psychol Rec 65:223–229
Funding
This study was not funded by a government or private grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Thomas R. Zentall declares that he has no conflict of interest. Danielle M. Andrews declares that she has no conflict of interest. Jacob P. Case declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zentall, T.R., Andrews, D.M. & Case, J.P. Contrast between what is expected and what occurs increases pigeon’s suboptimal choice. Anim Cogn 22, 81–87 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-018-1223-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-018-1223-x