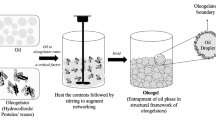
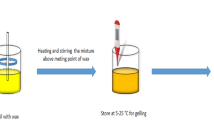
Abstract
The harmful effects of trans and saturated fatty acids have attracted worldwide attention. Edible oleogels, which can structure liquid oils, are promising healthy alternatives to traditional fats. Active research on oleogels is focused on the interaction between unsaturated oils with different fatty acid compositions and low molecular weight or polymer oleogels. The unique network structure inside oleogels has facilitated their application in candies, spreads, meat, and other products. However, the micro- and macro-properties, as well as the functional properties of oleogels vary by preparation method and the system composition. This review discusses the characteristics of oleogels, serving as a reference for the application of oleogels in food products. Specifically, it (i) classifies oleogels and explains the influence of gelling factors on their gelation, (ii) describes the methods for measuring the physicochemical properties of oleogels, and (iii) discusses the current applications of oleogels in food products.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- 3ITT:
-
Three-interval thixotropy test
- AFM:
-
Atomic force microscopy
- BW:
-
Beeswax
- BWO:
-
Beeswax oleogel
- CA:
-
Cluster analysis
- CB:
-
Cocoa butter
- CW:
-
Carnauba wax
- CWO:
-
Carnauba wax oleogel
- Cryo-TEM:
-
Cryo-transmission electron microscopy
- DFA:
-
Discriminant factor analysis
- EC:
-
Ethyl cellulose
- ECO:
-
Ethyl cellulose oleogel
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- G′:
-
Storage modulus
- G′′:
-
Loss modulus
- HMWPO:
-
High molecular weight polymer oleogel
- HPMC:
-
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose
- LDA:
-
Linear discriminant analysis
- LMMWO:
-
Low multicomponent/composite molecular weight oleogel
- LMWO:
-
Low molecular weight oleogel
- LSMWO:
-
Low single molecular weight oleogel
- MAG:
-
Monoacylglycerol
- MAGO:
-
Monoacylglycerol oleogel
- MO:
-
Monoglyceryl stearate oleogel
- Mw:
-
Molecular weight
- OBC:
-
Oil binding capacity
- p-AV:
-
p-Anisidine value
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- PLM:
-
Polarized light microscopy
- pNMR:
-
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- PV:
-
Peroxide value
- P/Y:
-
Phytosterol + γ-oryzanol
- RBW:
-
Rice bran wax
- S/L:
-
β-Sitosterol + lecithin
- S/LO:
-
β-Sitosterol + lecithin oleogel
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- SFA:
-
Saturated fatty acid
- SAXS:
-
Small-angle X-ray scattering
- SW:
-
Sunflower wax
- TAG:
-
Triglyceride
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances
- TFA:
-
Trans Fatty acid
- TPA:
-
Texture profile analysis
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
Abdollahi M, Goli SAH, Soltanizadeh N. Physicochemical properties of foam‐templated oleogel based on gelatin and xanthan gum. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology. 122: 1900196 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201900196
Abdolmaleki K, Alizadeh L, Nayebzadeh K, Baranowska HM, Kowalczewski PŁ, Mousavi KA. Potential application of hydrocolloid-based oleogel and beeswax oleogel as partial substitutes of solid fat in margarine. Applied Sciences. 12: 12136 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312136
Abdolmaleki K, Alizadeh L, Nayebzadeh K, Hosseini SM, Shahin R. Oleogel production based on binary and ternary mixtures of sodium caseinate, xanthan gum, and guar gum: optimization of hydrocolloids concentration and drying method. Journal of Texture Studies. 51: 290-299 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1111/jtxs.12469
Adili L, Roufegarinejad L, Tabibiazar M, Hamishehkar H, Alizadeh A. Development and characterization of reinforced ethyl cellulose based oleogel with adipic acid: its application in cake and beef burger. LWT. 126: 109277 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109277
Aguilar-Zárate M, Macias-Rodriguez BA, Toro-Vazquez JF, Marangoni AG. Engineering rheological properties of edible oleogels with ethylcellulose and lecithin. Carbohydrate Polymers. 205: 98-105 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.032
Airoldi R, da Silva TLT, Ract JNR, Foguel A, Colleran HL, Ibrahim SA, da Silva RC. Potential use of carnauba wax oleogel to replace saturated fat in ice cream. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society. 99: 1085-1099 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1002/aocs.12652
Alavi F, Tian Z, Chen L, Emam-Djomeh Z. Effect of CaCl2 on the stability and rheological properties of foams and high-sugar aerated systems produced by preheated egg white protein. Food Hydrocolloids. 106: 105887 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105887
Alexandri E, Ahmed R, Siddiqui H, Choudhary MI, Tsiafoulis CG, Gerothanassis IP. High resolution NMR spectroscopy as a structural and analytical tool for unsaturated lipids in solution. Molecules. 22: 1663 (2017) https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101663
Alvarez-Ramirez J, Vernon-Carter EJ, Carrera-Tarela Y, Garcia A, Roldan-Cruz C. Effects of candelilla wax/canola oil oleogel on the rheology, texture, thermal properties and in vitro starch digestibility of wheat sponge cake bread. LWT. 130: 109701 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109701
Ash D, Majee SB, Biswas GR. Span 40/Tween 80-based soybean oleogels: Modeling of gelation kinetics and drug release. IJPSR. 10: 1000-09 (2019) https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Dipanjana-Ash/publication/334536825_SPAN_40TWEEN_80-BASED_SOYBEAN_OLEOGELS_MODELING_OF_GELATION_KINETICS_AND_DRUG_RELEASE/links/5d30395a458515c11c39523e/SPAN-40-TWEEN-80-BASED-SOYBEAN-OLEOGELS-MODELING-OF-GELATION-KINETICS-AND-DRUG-RELEASE.pdf
Badem Ş, Baştürk A. Oxidative stability and characterization of oleogels obtained from safflower oil‐based beeswax and rice bran wax and their effect on the quality of cake samples. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society (2023) https://doi.org/10.1002/aocs.12694
Barragán-Martínez LP, Alvarez-Poblano L, Vernon-Carter EJ, Alvarez-Ramirez J. Effects of β-carotene on the color, textural, rheological and structural properties of canola oil/beeswax oleogel. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization. 16: 3946-3956 (2022a) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-022-01449-4
Barragán-Martínez LP, Román-Guerrero A, Vernon-Carter EJ, Alvarez-Ramirez J. Impact of fat replacement by a hybrid gel (canola oil/candelilla wax oleogel and gelatinized corn starch hydrogel) on dough viscoelasticity, color, texture, structure, and starch digestibility of sugar-snap cookies. International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science. 29: 100563 (2022b) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgfs.2022.100563
Bascuas S, Espert M, Llorca E, Quiles A, Salvador A, Hernando I. Structural and sensory studies on chocolate spreads with hydrocolloid-based oleogels as a fat alternative. LWT 135: 110228 (2021a) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110228
Bascuas S, Morell P, Quiles A, Salvador A, Hernando I. Use of oleogels to replace margarine in steamed and baked buns. Foods. 10: 1781 (2021b) https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10081781
Blake AI, Co ED, Marangoni AG. Structure and physical properties of plant wax crystal networks and their relationship to oil binding capacity. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society. 91: 885-903 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-014-2435-0
Borriello A, Miele NA, Masi P, Aiello A, Cavella S. Effect of fatty acid composition of vegetable oils on crystallization and gelation kinetics of oleogels based on natural wax. Food Chemistry. 375: 131805 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131805
Brito GB, Peixoto VODS, Martins MT, Rosário DK, Ract JN, Conte-Júnior CA, Castelo-Branco VN. Development of chitosan-based oleogels via crosslinking with vanillin using an emulsion templated approach: structural characterization and their application as fat-replacer. Food Structure. 32: 100264 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foostr.2022.100264
Brykczynski H, Wettlaufer T, Flöter E. Revisiting pure component wax esters as basis of wax‐based oleogels. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society. (2022) https://doi.org/10.1002/aocs.12589
Callau M, Sow-Kébé K, Nicolas-Morgantini L, Fameau AL. Effect of the ratio between behenyl alcohol and behenic acid on the oleogel properties. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 560: 874-884 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.10.111
Choi KO, Hwang HS, Jeong S, Kim S, Lee S. The thermal, rheological, and structural characterization of grapeseed oil oleogels structured with binary blends of oleogelator. Journal of Food Science. 85: 3432-3441 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15442
Cofrades S, Saiz A, Pérez-Mateos M, Garcimartín A, Redondo-Castillejo R, Bocanegra A, Álvarez MD. The influence of cellulose ethers on the physico-chemical properties, structure and lipid digestibility of animal fat emulsions stabilized by soy protein. Foods. 11: 738 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11050738
Cumhur O, Kilic-Akyilmaz M. Special processed cheeses, cheese spreads, and analogue cheeses. In Processed Cheese Science and Technology. pp. 269-295 (2022). Woodhead Publishing https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821445-9.00009-1
da Silva TLT, Baeten V, Danthine S. Modifying sucrose esters oleogels properties using different structuration routes. Food Chemistry. 405: 134927 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134927
Demirkesen I, Mert B. Utilization of beeswax oleogel‐shortening mixtures in gluten‐free bakery products. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society. 96: 545-554 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1002/aocs.12195
Doan CD, To CM, De Vrieze M, Lynen F, Danthine S, Brown A, Patel AR. Chemical profiling of the major components in natural waxes to elucidate their role in liquid oil structuring. Food Chemistry. 214: 717-725 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.123
Dong L, Lv M, Gao X, Zhang L, Rogers M, Cao Y, Lan Y. In vitro gastrointestinal digestibility of phytosterol oleogels: Influence of self-assembled microstructures on emulsification efficiency and lipase activity. Food & Function. 11: 9503-9513 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1039/D0FO01642J
Du Q, Zhou L, Lyu F, Liu J, Ding Y. The complex of whey protein and pectin: Interactions, functional properties and applications in food colloidal systems–A review. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 210: 112253 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.112253
Espert M, Hernández MJ, Sanz T, Salvador A. Reduction of saturated fat in chocolate by using sunflower oil-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose based oleogels. Food Hydrocolloids. 120: 106917 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106917
Fayaz G, Calligaris S, Nicoli MC. Comparative study on the ability of different oleogelators to structure sunflower oil. Food Biophysics. 15: 42-49 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-019-09597-9
Feichtinger A, Scholten E. Preparation of protein oleogels: effect on structure and functionality. Foods. 9: 1745 (2020) https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121745
Feichtinger A, Nibbelink DG, Poppe S, Bozzo L, Landman J, Scholten E. Protein oleogels prepared by solvent transfer method with varying protein sources. Food Hydrocolloids. 132: 107821 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107821
Flöter E, Wettlaufer T, Conty V, Scharfe M. Oleogels-their applicability and methods of characterization. Molecules. 26: 1673 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061673
Genovese A, Balivo A, Salvati A, Sacchi R. Functional ice cream health benefits and sensory implications. Food Research International. (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111858
Ghebreyesus TA, Frieden TR. REPLACE: a roadmap to make the world trans fat free by 2023. The Lancet. 391: 1978-1980 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31083-3
Ghorghi ZB, Yeganehzad S, Hesarinejad MA, Faezian A, Kutsenkova V, Gao Z, Nepovinnykh N. Fabrication of novel hybrid gel based on beeswax oleogel: application in the compound chocolate formulation. Food Hydrocolloids. 140: 108599 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108599
Gómez-Estaca J, Herrero AM, Herranz B, Álvarez MD, Jiménez-Colmenero F, Cofrades S. Characterization of ethyl cellulose and beeswax oleogels and their suitability as fat replacers in healthier lipid pâtés development. Food Hydrocolloids. 87: 960-969 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.09.029
Guo S, Song M, Gao X, Dong L, Hou T, Lin X, Lan Y. Assembly pattern of multi-component supramolecular oleogel composed of ceramide and lecithin in sunflower oil: self-assembly or self-sorting? Food Function. 11: 7651-7660 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1039/D0FO00635A
Han C, Wang G, Guo J, Wang J, Yang X. Oral oil release improves lubrication and sensory properties of meat analogs with protein-stabilized oleogel. Food Hydrocolloids. (2023a) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108788
Han Z, Liu S, Cao J, Yue X, Shao JH. A review of oil and water retention in emulsified meat products: the mechanisms of gelation and emulsification, the application of multi-layer hydrogels. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. (2023b) https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2023.2199069
Hong X, Zhao Q, Chen J, Ye T, Fan L, Li J. Fabrication and characterization of oleogels and temperature-responsive water-in-oil emulsions based on candelilla (Euphorbia cerifera) wax. Food Chemistry. 397: 133677 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133677
Hwang HS, Fhaner M, Winkler‐Moser JK, Liu SX. Oxidation of fish oil oleogels formed by natural waxes in comparison with bulk oil. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology. 120: 1700378 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201700378
Hwang HS, Kim S, Winkler‐Moser JK, Lee S, Liu SX. Feasibility of hemp seed oil oleogels structured with natural wax as solid fat replacement in margarine. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society. 99: 1055-1070 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1002/aocs.12619
Igenbayev A, Ospankulova G, Amirkhanov S, Aldiyeva A, Temirova I, Amirkhanov K. Substitution of pork fat with beeswax-structured oleogels in semi-smoked sausages. Applied Sciences. 13: 5312 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095312
Jansen-van Vuuren RD, Naficy S, Ramezani M, Cunningham M, Jessop P. CO 2-responsive gels. Chemical Society Reviews. (2023) https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CS00053A
Jiang Y, Liu L, Wang B, Sui X, Zhong Y, Zhang L, Xu H. Cellulose-rich oleogels prepared with an emulsion-templated approach. Food Hydrocolloids. 77: 460-464 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.10.023
Jung D, Oh I, Lee J, Lee S. Utilization of butter and oleogel blends in sweet pan bread for saturated fat reduction: dough rheology and baking performance. LWT. 125: 109194 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109194
Jung I, Schroeter B, Plazzotta S, De Berardinis L, Smirnova I, Gurikov P, Manzzocco, L. Oleogels from mesoporous whey and potato protein based aerogel microparticles: Influence of microstructural properties on oleogelation ability. Food Hydrocolloids. 108758 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108758
Kavimughil M, Leena MM, Moses JA, Anandharamakrishnan C. 3D printed MCT oleogel as a co-delivery carrier for curcumin and resveratrol. Biomaterials. 287: 121616 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121616
Kim D, Oh I. The characteristic of insect oil for a potential component of oleogel and its application as a solid fat replacer in cookies. Gels. 8: 355 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060355
Lee S. Utilization of foam structured hydroxypropyl methylcellulose for oleogels and their application as a solid fat replacer in muffins. Food Hydrocolloids. 77: 796-802 (2018) https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060355
Li L, Liu G. Engineering effect of oleogels with different structuring mechanisms on the crystallization behavior of cocoa butter. Food Chemistry. (2023a) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136292
Li L, Liu G, Bogojevic O, Pedersen JN, Guo Z. Edible oleogels as solid fat alternatives: Composition and oleogelation mechanism implications. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. 21: 2077-2104 (2022a) https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12928
Li L, Wan W, Cheng W, Liu G, Han L. Oxidatively stable curcumin‐loaded oleogels structured by β-sitosterol and lecithin: physical characteristics and release behaviour in vitro. International Journal of Food Science & Technology. 54: 2502-2510 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14208
Li S, Song Q, Liu K, Zhang Y, Zhao G, Zhou Y. Emulsion-templated oleogels generated through solvent exchange: effects of miscibility of alcohols and oils. LWT. 176: 114545 (2023b) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2023.114545
Li S, Wu G, Jin Q, Wang X, Zhang H. Relationship between the microstructure and physical properties of emulsifier based oleogels and cookies quality. Food Chemistry. 377: 131966 (2022b) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131966
Li S, Wu G, Li X, Jin Q, Wang X, Zhang H. Roles of gelator type and gelation technology on texture and sensory properties of cookies prepared with oleogels. Food Chemistry. 356: 129667 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129667
Li S, Zhu L, Li X, Wu G, Liu T, Qi X, Zhang H. Determination of characteristic evaluation indexes for novel cookies prepared with wax oleogels. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 102: 5544-5553 (2022c) https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.11909
Liu N, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Mao L. Surfactant addition to modify the structures of ethylcellulose oleogels for higher solubility and stability of curcumin. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 165: 2286-2294 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.115
López-Pedrouso M, Lorenzo JM, Gullón B, Campagnol PCB, Franco D. Novel strategy for developing healthy meat products replacing saturated fat with oleogels. Current Opinion in Food Science. 40: 40-45 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2020.06.003
Luo SZ, Hu XF, Jia YJ, Pan LH, Zheng Z, Zhao YY, Jiang ST. Camellia oil-based oleogels structuring with tea polyphenol-palmitate particles and citrus pectin by emulsion-templated method: preparation, characterization, and potential application. Food Hydrocolloids. 95: 76-87 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.04.016
Ma Y, Ye F, Chen J, Ming J, Zhou C, Zhao G, Lei L. The microstructure and gel properties of linseed oil and soy protein isolate based-oleogel constructed with highland barley β-glucan and its application in luncheon meat. Food Hydrocolloids. 140: 108666 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108666
Malvano F, Laudisio M, Albanese D, d’Amore M, Marra F. Olive oil-based oleogel as fat replacer in a sponge cake: a comparative study and optimization. Foods. 11: 2643 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172643
Marangoni AG, Garti N. Edible oleogels: structure and health implications. Elsevier (2018) https://books.google.co.kr/books?hl=zh-CN&lr=&id=kV1gDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=Marangoni,+A.+G.,+%26+Garti,+N.+(Eds.).+(2018).%C2%A0Edible+Oleogels:+Structure+and+Health+Implications.+Elsevier.&ots=TZecFL-SnW&sig=i4l43_4Fx9VwKiybv2zI7B_F3r4&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Marangoni%2C%20A.%20G.%2C%20%26%20Garti%2C%20N.%20(Eds.).%20(2018).%C2%A0Edible%20Oleogels%3A%20Structure%20and%20Health%20Implications.%20Elsevier.&f=false
Martins AJ, Lorenzo JM, Franco D, Vicente AA, Cunha RL, Pastrana LM, Cerqueira MA. Omega‐3 and polyunsaturated fatty acids‐enriched hamburgers using sterol‐based oleogels. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology. 121: 1900111 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201900111
Meng Z, Guo Y, Wang Y, Liu Y. Oleogels from sodium stearoyl lactylate-based lamellar crystals: structural characterization and bread application. Food Chemistry. 292: 134-142 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.042
Moon K, Choi KO, Jeong S, Kim YW, Lee S. Solid fat replacement with canola oil-carnauba wax oleogels for dairy-free imitation cheese low in saturated fat. Foods. 10: 1351 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061351
Oh I, Lee J, Lee HG, Lee S. Feasibility of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose oleogel as an animal fat replacer for meat patties. Food Research International. 122: 566-572 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.01.012
Okuro PK, Martins AJ, Vicente AA, Cunha RL. Perspective on oleogelator mixtures, structure design and behaviour towards digestibility of oleogels. Current Opinion in Food Science. 35: 27-35 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2020.01.001
Okuro PK, Santos TP, Cunha RL. Compositional and structural aspects of hydro-and oleogels: similarities and specificities from the perspective of digestibility. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 111: 55-67 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.02.053
Omonov TS, Bouzidi L, Narine SS. Quantification of oil binding capacity of structuring fats: a novel method and its application. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids. 163: 728-740 (2010) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2010.07.003
Palla CA, Aguilera-Garrido A, Carrín ME, Galisteo-González F, Gálvez-Ruiz MJ. Preparation of highly stable oleogel-based nanoemulsions for encapsulation and controlled release of curcumin. Food Chemistry. 378: 132132 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132132
Pan H, Xu X, Qian Z, Cheng H, Shen X, Chen S, Ye X. Xanthan gum-assisted fabrication of stable emulsion-based oleogel structured with gelatin and proanthocyanidins. Food Hydrocolloids. 115: 106596 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106596
Pang M, Kang S, Liu L, Ma T, Zheng Z, Cao L. Physicochemical properties and cookie-making performance as fat replacer of wax-based rice bran oil oleogels. Gels. 9: 13 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010013
Pascuta MS, Varvara RA, Teleky BE, Szabo K, Plamada D, Nemeş SA, Vodnar DC. Polysaccharide-based edible gels as functional ingredients: Characterization, applicability, and human health benefits. Gels. 8: 524 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080524
Patil U, Patel AR. Polysaccharide-based functional colloids for food applications. In Food, Medical, and Environmental Applications of Polysaccharides. Elsevier pp. 187-229 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819239-9.00004-X
Pérez-Álvarez JÁ, Roldán-Verdú A, Martínez-Mayoral A, Sayas-Barberá E, Vera CNRD, Viuda-Martos M, Fernández-Lopez J. Chia oleogel as a potential new ingredient for healthy cooked meat sausages. In Proceedings. MDPI. Vol. 70, No. 1, p. 76 (2020, November) https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07701
Perța-Crișan S, Ursachi CȘ, Chereji BD, Munteanu FD. Oleogels—innovative technological solution for the nutritional improvement of meat products. Foods. 12: 131 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010131
Perța-Crișan S, Ursachi CȘ, Chereji BD, Tolan I, Munteanu FD. Food-grade oleogels: trends in analysis, characterization, and applicability. Gels. 9: 386 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050386
Pintado T, Cofrades S. Quality characteristics of healthy dry fermented sausages formulated with a mixture of olive and chia oil structured in oleogel or emulsion gel as animal fat replacer. Foods. 9: 830 (2020) https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060830
Pinto TC, Martins AJ, Pastrana L, Pereira MC, Cerqueira MA. Oleogel-based systems for the delivery of bioactive compounds in foods. Gels 7: 86 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7030086
Pugh RJ, Hamlett CAE, Fairhurst DJA. Short overview of bubble in foods and chocolate containing bubbles. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2023.102835
Puşcaş A, Mureşan V. The feasibility of shellac wax emulsion oleogels as low-fat spreads analyzed by means of multidimensional statistical analysis. Gels. 8: 749 (2022a) https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8110749
Pușcaș A, Mureșan V, Muste S. Application of analytical methods for the comprehensive analysis of oleogels—a review. Polymers. 13: 1934 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121934
Pușcaș A, Mureșan V, Socaciu C, Muste S. Oleogels in food: A review of current and potential applications. Foods. 9: 010070 (2020) https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010070
Pușcaș A, Tanislav AE, Mureșan AE, Fărcaș AC, Mureșan V. Walnut oil oleogels as milk fat replacing system for commercially available chocolate butter. Gels. 8: 613 (2022b) https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100613
Qiu HT, Qiu ZZ, Chen ZY, Liu LL, Wang JB, Jiang HY, Liu GQ. Antioxidant properties of blueberry extract in different oleogel systems. LWT. 137: 110364 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110364
Qiu HT, Qu KX, Eun JB, Zhang H. Analysis of thermal oxidation of different multi-element oleogels based on carnauba wax, β-sitosterol/lecithin, and ethyl cellulose by classical oxidation determination method combined with the electronic nose. Food Chemistry. 405: 134970 (2023a) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134970
Qiu HT, Qu KX, Zhang H, Eun JB. Thermal oxidation stability of different multi-element oleogels via 1H NMR spectroscopy. Food Chemistry. 394: 133492 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133492
Qiu HT, Qu KX, Zhang H, Eun JB. Characterization and comparison of physical properties and in vitro simulated digestion of multi-component oleogels with different molecular weights prepared by the direct method. Food Hydrocolloids. 108850 (2023b) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108850
Qu KX, Qiu HT, Zhang H, Yin XF. Characterization of physically stable oleogels transporting active substances rich in resveratrol. Food Bioscience. (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101830
Quilaqueo M, Iturra N, Contardo I, Millao S, Morales E, Rubilar M. Food-grade bigels with potential to replace saturated and trans fats in cookies. Gels. 8: 445 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070445
Salama HH, Hashim AF. A functional spreadable canola and milk proteins oleogels as a healthy system for candy gummies. Scientific Reports. 12: 12619 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16809-9
Scholten E. Edible oleogels: how suitable are proteins as a structurant?. Current Opinion in Food Science. 27: 36-42 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2019.05.001
Shakeel A, Farooq U, Gabriele D, Marangoni AG, Lupi FR. Bigels and multi-component organogels: an overview from rheological perspective. Food Hydrocolloids. 111: 106190 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106190
Silva RCD, Ferdaus MJ, Foguel A, da Silva TLT. Oleogels as a fat substitute in food: a current review. Gels. 9: 180 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9030180
Silva TJ, Barrera‐Arellano D, Ribeiro APB. Oleogel‐based emulsions: concepts, structuring agents, and applications in food. Journal of Food Science. 86: 2785-2801 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15788
Sivakanthan S, Fawzia S, Madhujith T, Karim A. Synergistic effects of oleogelators in tailoring the properties of oleogels: a review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety (2022) https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12966
Sobolev R, Frolova Y, Sarkisyan V, Makarenko M, Kochetkova A. Effect of beeswax and combinations of its fractions on the oxidative stability of oleogels. Food Biosciences. 48: 101744 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101744
Sun P, Xia B, Ni ZJ, Wang Y, Elam E, Thakur K, Wei ZJ. Characterization of functional chocolate formulated using oleogels derived from β-sitosterol with γ-oryzanol/lecithin/stearic acid. Food Chemistry. 360: 130017 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130017
Tarté R, Paulus JS, Acevedo NC, Prusa KJ, Lee SL. High-oleic and conventional soybean oil oleogels structured with rice bran wax as alternatives to pork fat in mechanically separated chicken-based bologna sausage. LWT. 131: 109659 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109659
Tirgarian B, Yadegari H, Bagheri A, Neshagaran E, Mardani M, Farmani J. Reduced-fat chocolate spreads developed by water-in-oleogel emulsions. Journal of Food Engineering. 337: 111233 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2022.111233
Wang Q, Decker EA, Rao J, Chen B. A combination of monoacylglycerol crystalline network and hydrophilic antioxidants synergistically enhances the oxidative stability of gelled algae oil. Food & Function. 10: 315-324 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FO00997J
Wang Q, Rao Z, Chen Y, Lei X, Zhao J, Li F, Ming J. Characterization of responsive zein-based oleogels with tunable properties fabricated from emulsion-templated approach. Food Hydrocolloids. 133: 107972 (2022a) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107972
Wang S, Chen K, Liu G. Monoglyceride oleogels for lipophilic bioactive delivery–Influence of self-assembled structures on stability and in vitro bioaccessibility of astaxanthin. Food Chemistry. 375: 131880 (2022b) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131880
Wang Z, Chandrapala J, Truong T, Farahnaky A. Oleogels prepared with low molecular weight gelators:texture, rheology and sensory properties, a review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition (2022c) https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2027339
Wang Z, Gao Y, Wei Z, Xue C. Ovalbumin fibril-stabilized oleogel-based Pickering emulsions improve astaxanthin bioaccessibility. Food Research International. 161: 111790 (2022d) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111790
Wei F, Lu M, Li J, Xiao J, Rogers MA, Cao Y, Lan Y. Construction of foam-templated oleogels based on rice bran protein. Food Hydrocolloids. 124: 107245 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107245
Whitby CP. Structuring edible oils with fumed silica particles. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems. 4: 585160 (2020) https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2020.585160
Willett SA, Akoh CC. Encapsulation of menhaden oil structured lipid oleogels in alginate microparticles. LWT. 116: 108566 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108566
Wojtunik-Kulesza K, Oniszczuk A, Oniszczuk T, Combrzyński M, Nowakowska, D., & Matwijczuk, A. Influence of in vitro digestion on composition, bioaccessibility and antioxidant activity of food polyphenols—a non-systematic review. Nutrients. 12: 1401 (2020) https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051401
Xia T, Gao Y, Liu Y, Wei Z, Xue C. Lactoferrin particles assembled via transglutaminase-induced crosslinking: Utilization in oleogel-based pickering emulsions with improved curcumin bioaccessibility. Food Chemistry. 374: 131779 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131779
Yao Y, Zhou H, Liu W, Li C, Wang S. The effect of cooling rate on the microstructure and macroscopic properties of rice bran wax oleogels. Journal of Oleo Science. 70: 135-143 (2021) https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess20112
Ye L, Liu CL, Zhu HR, Luo JX. Experimental investigation on effect of cross-flow Reynolds number on film cooling effectiveness. AIAA Journal. 57: 4804-4818 (2019) https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J057943
Yılmaz E. Sensory properties and aromatics profile of edible oleogels. In Development of Trans-free Lipid Systems and their Use in Food Products. Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 315-349 (2022) https://books.google.co.kr/books?hl=zh-CN&lr=&id=G3VdEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT264&dq=Sensory+properties+and+aromatics+profile+of+edible+oleogels.&ots=-azKeg_0mz&sig=ATEAC-_iFjg9UgkVvHVPkVGBu3s&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Sensory%20properties%20and%20aromatics%20profile%20of%20edible%20oleogels.&f=false
Yu Y, Wang T, Gong Y, Wang W, Wang X, Yu D, Wang L. Effect of ultrasound on the structural characteristics and oxidative stability of walnut oil oleogel coated with soy protein isolate-phosphatidylserine. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry. 83: 105945 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.105945
Zhang H, Yang X, Zhong R, Huo Y, Zhu Y, Liang P. Antioxidative properties of fish roe peptides combined with polyphenol on the fish oil oleogel. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 103: 1714-1726 (2023a) https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.12336
Zhang P, Wang Y, Liu Y, Wu Y, Ouyang J. Improved stability of β-carotene by encapsulation in SHMP-corn starch aerogels. Food Chemistry. 406: 135040 (2023b) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135040
Zhang R, Cui M, Ye J, Yuan D, Mao L. Physicochemical stability of oleogel-in-water emulsions loaded with β-carotene against environmental stresses. LWT. 155: 112965 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112965
Zhao W, Wei Z, Xue C. Recent advances on food-grade oleogels: fabrication, application and research trends. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 62: 7659-7676 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1922354
Zhao W, Wei Z, Xue C, Meng Y. Development of food-grade oleogel via the aerogel-templated method: oxidation stability, astaxanthin delivery and emulsifying application. Food Hydrocolloids. 134: 108058 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.108058
Zheng S, Lu M, Xiao J, Zhang X, Li J, Zhang H, Lan Y. A novel strategy for preparation of rice bran protein oleogels based on high internal phase emulsion template. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture (2023) https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.12672
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of the “Key R&D Program of the Northeast Cold Region Beef Cattle Science and Technology Innovation Engineering Research Center” through Project 111 (Project no. D20034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors confirm that this manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by any other journal. The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, H., Zhang, H. & Eun, JB. Oleogel classification, physicochemical characterization methods, and typical cases of application in food: a review. Food Sci Biotechnol 33, 1273–1293 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01501-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01501-z