Abstract
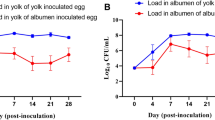
This study explored the temperature-dependent effect on the growth characteristics of Salmonella Enteritidis (SE) on eggshell toward identifying an appropriate storage temperature for unwashed eggs in an actual distribution environment. Among the test storage temperatures (10 °C, 25 °C, and 35 °C), 25 °C was determined to be an appropriate storage temperature, with no effect of changing temperature on the control of SE on eggshell. Regarding the effect of the temperature on egg quality, the quality indicators of egg such as Haugh unit, yolk index, albumin index, and albumin pH were significantly maintained. These results indicated that unwashed eggs should be distributed at 25 °C for SE control, and the storage temperature should be below 10 °C from at least day 4 onward after the start of distribution to maintain egg quality. This study will assist for safety management of unwashed egg in an actual distribution environment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bovill R, Bew J, Baranyi J. Measurements and predictions of growth for Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella during fluctuating temperature: II. Rapidly changing temperatures. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 67: 131-137 (2001)
Bovill R, Bew J, Cook N, D’Agostino M, Wilkinson N, Baranyi J. Predictions of growth for Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella during fluctuating temperature. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 59: 157-165 (2000)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Burden of foodborne illness: findings. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/foodborneburden/2011-foodborne-estimates.html. Accessed 17 Jan 2023.
Choi BG, Min JH, Yoon KS. Effects of washing and storage temperature on quality and safety of washed shell eggs. Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life. 27: 78-87 (2017)
Chousalkar K, Gast R, Martelli F, Pande V. Review of egg-related salmonellosis and reduction strategies in United States, Australia, United Kingdom and New Zealand. Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 44: 290-303 (2018)
Chousalkar KK, Khan S, McWhorter AR. Microbial quality, safety and storage of eggs. Current Opinion in Food Science. 38: 91-95 (2021)
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority), ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA Journal. 16: e05500 (2018)
Food Drug Administration (FDA). 21 CFR Part 118 Production, storage, and transportation of shell eggs. Available from: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-B/part-118. Accessed 18 Jan 2023.
Ha JK, Kim TH, Na JC, Kang BS, Ha GS, Kim DH, Lee SJ. Changes of albumen index and haugh unit by the different position of thick albumen height of eggs measured. Korean Journal of Poultry Science. 29: 157-170 (2002)
Huang J, Luo Y, Zhou B, Zheng J, Nou X. Growth and survival of Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes on fresh-cut produce and their juice extracts: Impacts and interactions of food matrices and temperature abuse conditions. Food Control. 100: 300-304 (2019)
Huopalahti R, Anton M, López-Fandiño R, Schade R. Bioactive egg compounds. Vol. 5. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany. pp. 61-118 (2007)
Jones DR, Ward GE, Regmi P, Karcher DM. Impact of egg handling and conditions during extended storage on egg quality. Poultry Science. 97: 716-723 (2018)
Keener KM, McAvoy KC, Foegeding JB, Curtis PA, Anderson KE, Osborne JA. Effect of testing temperature on internal egg quality measurements. Poultry Science. 85: 550-555 (2006)
Kim BK, Park CE, Kim BS, Kim YS. Quality factors affecting egg freshness and palatability during storage. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology. 46: 295-302 (2014)
Kingsbury JM, Thom K, Soboleva T. Effect of storage temperature on the survival of New Zealand egg-associated Salmonella isolates in and on eggs. Journal of Food Protection. 82: 2161-2168 (2019)
Lee HO, Kim JY, Kim BS. Choosing quality indicators for quality prediction of egg in circulation. Korean Journal of Food Preservation. 21: 609-617 (2014)
Lee MH, Cho EJ, Choi ES, Sohn SH. The effect of storage period and temperature on egg quality in commercial eggs. Korean Journal of Poultry Science. 43: 31-38 (2016)
Lee SM, Hong CH. Changes of egg quality according to eggshell treatment and storage condition. Korean Journal of Veterinary Service. 28: 225-234 (2005)
Lee SM, Yoo HS, Honsg CH. Analysis of biological hazards and control points in layer houses. Korean Journal of Veterinary Research. 44: 593-605 (2004)
Li Y, Salazar JK, He Y, Desai P, Porwollik S, Chu W, Paola P-SS, Tortorello ML, Juarez O, Feng H et al. . Mechanisms of Salmonella attachment and survival on in-shell black peppercorns, almonds, and hazelnuts. Frontiers in Microbiology. 11: 582202 (2020)
Liu M, Yu W, Ren F, Wu J. Formation and characterization of peptides in egg white during storage at ambient temperature. Food Chemistry. 263: 135-141 (2018)
Liu YC, Chen TH, Wu YC, Lee YC, Tan FJ. Effects of egg washing and storage temperature on the quality of eggshell cuticle and eggs. Food Chemistry. 211: 687-693 (2016)
Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA). Detailed criteria for grading of livestock products. Available from: https://www.law.go.kr/%ED%96%89%EC%A0%95%EA%B7%9C%EC%B9%99/%EC%B6%95%EC%82%B0%EB%AC%BC%EB%93%B1%EA%B8%89%ED%8C%90%EC%A0%95%EC%84%B8%EB%B6%80%EA%B8%B0%EC%A4%80/(2020-112,20201229). Accessed 18 Jan 2023.
Martelli F, Davies RH. Salmonella serovars isolated from table eggs: an overview. Food Research International. 45: 745-754 (2012)
Messens W, Grijspeerdt K, Herman L. Eggshell penetration of hen's eggs by Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis upon various storage conditions. British Poultry Science. 47: 554-560 (2006)
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Food poisoning statistics. Available from: https://www.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/portal/healthyfoodlife/foodPoisoningStat.do?menu_no=4425&menu_grp=MENU_NEW02. Accessed 09 Feb 2023.
Park S, Choi S, Kim H, Kim Y, Kim B-s, Beuchat LR, Ryu J-H. Fate of mesophilic aerobic bacteria and Salmonella enterica on the surface of eggs as affected by chicken feces, storage temperature, and relative humidity. Food Microbiology. 48: 200-205 (2015)
Raji A, Aliyu J, Igwebuike J, Chiroma S. Effect of storage methods and time on egg quality traits of laying hens in a hot dry climate. Journal of Agricultural and Biological Science. 4: 1-7 (2009)
Samli HE, Agma A, Senkoylu N. Effects of storage time and temperature on egg quality in old laying hens. Journal of Applied Poultry Research. 14: 548-553 (2005)
Shan Y, Tang D, Wang R, Tu A, Yi Y, Wang X, Liu B, Zhou Y, Huang Q, Lü X. Rheological and structural properties of ovomucin from chicken eggs with different interior quality. Food Hydrocolloids. 100: 105393 (2020)
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). United States standards, grades, and weight classes for shell eggs AMS 56. Available from: https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media/Shell_Egg_Standard%5B1%5D.pdf. Accessed 18 Jan 2023.
Wang J, Omana DA, Wu J. Effect of shell eggs storage on ovomucin extraction. Food and Bioprocess Technology. 5: 2280-2284 (2012)
World Health Organization (WHO). Salmonella (non-typhoidal). Available from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salmonella-(non-typhoidal). Accessed 17 Jan 2023.
Zhang W, Zheng J-X, Xu G-Y. Toward better control of Salmonella contamination by taking advantage of the egg's self-defense system: a review. Journal of Food Science. 76: R76-R81 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant (21153MFDS605) from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety; and the Chung-Ang University Graduate Research Scholarship (Academic scholarship for College of Biotechnology and Natural Resources) in 2021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
An, JH., Lee, HS. Effect of the storage temperature on the quality of eggs inoculated with Salmonella Enteritidis onto shell. Food Sci Biotechnol 33, 1255–1260 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01402-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01402-1