Abstract
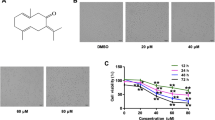
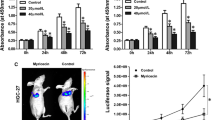
Pinus densiflora sieb. et zucc.(pine needle) is a traditional medicine used in several East Asian countries. However, the efficacy of pine needle has rarely been reported. In this study showed that the anti-proliferative effects and the mechanisms of hexane layer of pine needle MeOH extract (PNH) on gastric cancer cells. At first, PNH inhibited the proliferation of gastric cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, PNH treatment induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest through the increased p27KIP1 expression and decreased cyclin dependent kinase (CDKs) activity. Furthermore, PNH treatment induced premature senescence without oncogenic stress, through the expression of p27KIP1 and Skp2. Taken together, these results showed that PNH inhibited gastric cancer cell proliferation through the induction of G1-cell cycle arrest and premature senescence via induced p27KIP1 expression, as controlled by Skp2 reduction. Also, PNH could be a candidate for anti-gastric cancer treatment and may be useful in the development of anti-gastric cancer drugs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae KH. The Medicinal Plants of Korea. Kyo-Hak, Seoul (2000)
Beausejour CM, Campisi J. Ageing: balancing regeneration and cancer. Nature 443: 404-405 (2006)
Braig M, Lee S, Loddenkemper C, Rudolph C, Peters AH, Schlegelberger B, Stein H, Dorken B, Jenuwein T, Schmitt CA. Oncogene-induced senescence as an initial barrier in lymphoma development. Nature 436: 660-665 (2005)
Braig M, Schmitt CA. Oncogene-induced senescence: putting the brakes on tumor development. Cancer Res. 66: 2881-2884 (2006)
Choi EM. Antinociceptive and antiinflammatory activities of pine (Pinus densiflora) pollen extract. Phytother. Res. 21: 471-475 (2007)
Collado M, Blasco MA, Serrano M. Cellular senescence in cancer and aging. Cell 130: 223-233 (2007)
Coqueret O. New roles for p21 and p27 cell-cycle inhibitors: a function for each cell compartment? Trends Cell Biol. 13: 65-70 (2003)
Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G, Jarrard DF. Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 102: 1536-1546 (2010)
Feitelson MA, Arzumanyan A, Kulathinal RJ, Blain SW, Holcombe RF, Mahajna J, Marino M, Martinez-Chantar ML, Nawroth R, Sanchez-Garcia I, Sharma D, Saxena NK, Singh N, Vlachostergios PJ, Guo S, Honoki K, Fujii H, Georgakilas AG, Bilsland A, Amedei A, Niccolai E, Amin A, Ashraf SS, Boosani CS, Guha G, Ciriolo MR, Aquilano K, Chen S, Mohammed SI, Azmi AS, Bhakta D, Halicka D, Keith WN, Nowsheen S. Sustained proliferation in cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin. Cancer Biol. 35 Suppl: S25-S54 (2015)
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100: 57-70 (2000)
Kim HY, Cho Y, Kang H, Yim YS, Kim SJ, Song J, Chun KH. Targeting the WEE1 kinase as a molecular targeted therapy for gastric cancer. Oncotarget 7: 49902-49916 (2016)
Kim SJ, Lee HW, Kang HG, La SH, Choi IJ, Ro JY, Bresalier RS, Song J, Chun KH. Ablation of galectin-3 induces p27(KIP1)-dependent premature senescence without oncogenic stress. Cell Death Differ. 21: 1769-1779 (2014)
Kim YS, Shin DW. Volatile components and antibacterial effects of pine needle (Pinus densiflora S. and Z.) extracts. Food Microbiol. 22: 37-45 (2005)
Kwak CS, Moon SC, Lee MS. Antioxidant, antimutagenic, and antitumor effects of pine needles (Pinus densiflora). Nutr. Cancer 56: 162-171 (2006)
Lee HJ, Yang HK, Ahn YO. Gastric cancer in Korea. Gastric Cancer 5: 177-182 (2002)
Lee S, Kim WB, Park SH, Kim M, Kim D, Park J, Hwang DY, Lee H. Biological properties of butanol extracts from green pine cone of Pinus densiflora. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 27: 1485-1492 (2018)
Lim L, Michael M, Mann GB, Leong T. Adjuvant therapy in gastric cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 23: 6220-6232 (2005)
Longley DB, Harkin DP, Johnston PG. 5-fluorouracil: mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 3: 330-338 (2003)
Nevins JR. The Rb/E2F pathway and cancer. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10: 699-703 (2001)
Osman I, Drobnjak M, Fazzari M, Ferrara J, Scher HI, Cordon-Cardo C. Inactivation of the p53 pathway in prostate cancer: impact on tumor progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 5: 2082-2088 (1999)
Schmitt CA. Cellular senescence and cancer treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1775: 5-20 (2007)
Schwartz GK, Shah MA. Targeting the cell cycle: a new approach to cancer therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 23: 9408-9421 (2005)
Shay JW, Wright WE. Hallmarks of telomeres in ageing research. J. Pathol. 211: 114-123 (2007)
Sherr CJ. Cancer cell cycles. Science 274: 1672-1677 (1996)
Steller H. Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science 267: 1445-1449 (1995)
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 65: 87-108 (2015)
Toyoshima H, Hunter T. p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell 78: 67-74 (1994)
Viglietto G, Motti ML, Fusco A. Understanding p27(kip1) deregulation in cancer: down-regulation or mislocalization. Cell Cycle 1: 394-400 (2002)
Waldman T, Zhang Y, Dillehay L, Yu J, Kinzler K, Vogelstein B, Williams J. Cell-cycle arrest versus cell death in cancer therapy. Nat. Med. 3: 1034-1036 (1997)
Wang G, Chan CH, Gao Y, Lin HK. Novel roles of Skp2 E3 ligase in cellular senescence, cancer progression, and metastasis. Chin. J. Cancer 31: 169-177 (2012)
Wang J, Lou P, Lesniewski R, Henkin J. Paclitaxel at ultra low concentrations inhibits angiogenesis without affecting cellular microtubule assembly. Anti-cancer Drugs 14: 13-19 (2003)
Wei Z, Jiang X, Liu F, Qiao H, Zhou B, Zhai B, Zhang L, Zhang X, Han L, Jiang H, Krissansen GW, Sun X. Downregulation of Skp2 inhibits the growth and metastasis of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Tumour Biol. 34: 181-192 (2013)
Wen Y, Wang K, Yang K. Inhibiting the role of Skp2 suppresses cell proliferation and tumorigenesis of human gastric cancer cells via the upregulation of p27kip1. Mol. Med. Rep. 14: 3917-3924 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries (IPET) through the High Value-added Food Technology Development Program, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (Grant No. 116010-03-1-CG000) and research fund from Chosun University, 2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicting interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, W., Park, C., Park, J. et al. Pine needle hexane extract promote cell cycle arrest and premature senescence via p27KIP1 upregulation gastric cancer cells. Food Sci Biotechnol 29, 845–853 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00730-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00730-5