Abstract
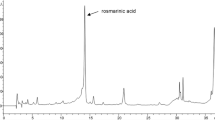
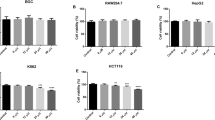
Although chebulic acid isolated from Terminalia chebular has diverse biological effects, its effects on the expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and the expression of downstream genes have not been elucidated. The purpose of this research is to investigate the hepatoprotective mechanism of chebulic acid against oxidative stress produced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP) in liver cells. The treatment with chebulic acid attenuated cell death in t-BHP-induced HepG2 liver cells and increased intracellular glutathione content, upregulated the activity of heme oxygenase-1, and also increased the translocation of Nrf2 into the nucleus and Nrf2 target gene expression in a dose-dependent manner. The exposure of chebulic acid activated the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases. The overall result is that chebulic acid has cytoprotective effect on t-BHP-induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cells through Nrf2-mediated antioxidant enzymes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn M-J, Kim CY, Lee JS, Kim TG, Kim SH, Lee C-K, Lee B-B, Shin C-G, Huh H, Kim J. Inhibition of HIV-1 integrase by galloyl glucoses from Terminalia chebula and flavonol glycoside gallates from Euphorbia pekinensis. Planta Med. 68: 457–459 (2002)
Apopa PL, He X, Ma Q. Phosphorylation of Nrf2 in the transcription activation domain by casein kinase 2 (CK2) is critical for the nuclear translocation and transcription activation function of Nrf2 in IMR‐32 neuroblastoma cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 22: 63–76 (2008)
Bains JS, Shaw CA. Neurodegenerative disorders in humans: the role of glutathione in oxidative stress-mediated neuronal death. Brain Res. Rev. 25: 335–358 (1997)
Chen C, Kong A-NT. Dietary chemopreventive compounds and ARE/EpRE signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 36: 1505–1516 (2004)
Cheng HY, Lin TC, Yu KH, Yang CM, Lin CC. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of Terminalia chebula. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 26: 1331–1335 (2003)
Cuadrado A, Rojo AI. Heme oxygenase-1 as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases and brain infections. Curr. Pharm. Des. 14: 429–442 (2008)
Droge W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol. Rev. 82: 47–95 (2002)
Hong F, Freeman ML, Liebler DC. Identification of sensor cysteines in human Keap1 modified by the cancer chemopreventive agent sulforaphane. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 18: 1917–1926 (2005)
Hu D, Yuan JM. Time-dependent sensitivity analysis of biological networks: Coupled MAPK and PI3K signal transduction pathways. J. Phys. Chem A. 110: 5361–5370 (2006)
Huang H-C, Nguyen T, Pickett CB. Regulation of the antioxidant response element by protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation of NF-E2-related factor 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97: 12475–12480 (2000)
Hwang YP, Choi JH, Choi JM, Chung YC, Jeong HG. Protective mechanisms of anthocyanins from purple sweet potato against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced hepatotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 49: 2081–2089 (2011)
Kaur S, Grover I, Singh M, Kaur S. Antimutagenicity of hydrolyzable tannins from Terminalia chebula in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 419: 169–179 (1998)
Kong A-NT, Owuor E, Yu R, Hebbar V, Chen C, Hu R, Mandlekar S. Induction of xenobiotic enzymes by the map kinase pathway and the antioxidant or electrophile response element (ARE/EpRE). Drug Metab. Rev. 33: 255–271 (2001)
Kovacic P, Jacintho JD. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis: Focus on oxidative stress and electron transfer. Curr. Med. Chem. 8: 773–796 (2001)
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J. Sounding the alarm: protein kinase cascades activated by stress and inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 24313–24316 (1996)
Lee HS, Jung SH, Yun BS, Lee KW. Isolation of chebulic acid from Terminalia chebula Retz. and its antioxidant effect in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch. Toxicol. 81: 211–218 (2007)
Liu XM, Peyton KJ, Shebib AR, Wang H, Korthuis RJ, Durante W. Activation of AMPK stimulates heme oxygenase-1 gene expression and human endothelial cell survival. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 300: H84–H93 (2011)
Malekzadeh F, Ehsanifar H, Shahamat M, Levin M, Colwell R. Antibacterial activity of black myrobalan (Terminalia chebula Retz) against Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 18: 85–88 (2001)
McMahon M, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Chanas SA, Henderson CJ, McLellan LI, Wolf CR, Cavin C, Hayes JD. The cap ‘n’ collar basic leucine zipper transcription factor Nrf2 (NF-E2 p45-related factor 2) controls both constitutive and inducible expression of intestinal detoxification and glutathione biosynthetic enzymes. Can. Res. 61: 3299–3307 (2001)
Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B. Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 582: 67–78 (1979)
Muriel P. Role of free radicals in liver diseases. Hepatol. Int. 3: 526–536 (2009)
Nguyen T, Yang CS, Pickett CB. The pathways and molecular mechanisms regulating Nrf2 activation in response to chemical stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 37: 433–441 (2004)
Otterbein LE, Choi AM. Heme oxygenase: colors of defense against cellular stress. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 279: L1029-L1037 (2000)
Perry LM, Metzger J. Medicinal plants of east and southeast Asia: attributed properties and uses. MIT press. 80–81 (1980)
Rojo AI, Sagarra MRd, Cuadrado A. GSK-3β down-regulates the transcription factor Nrf2 after oxidant damage: relevance to exposure of neuronal cells to oxidative stress. J. Neurochem. 105: 192–202 (2008)
Sabu M, Kuttan R. Anti-diabetic activity of medicinal plants and its relationship with their antioxidant property. J Ethnoparmacol. 81: 155–160 (2002)
Saleem A, Husheem M, Härkönen P, Pihlaja K. Inhibition of cancer cell growth by crude extract and the phenolics of Terminalia chebula retz. fruit. J Ethnoparmacol. 81: 327–336 (2002)
Surh YJ, Kundu JK, Na HK. Nrf2 as a master redox switch in turning on the cellular signaling involved in the induction of cytoprotective genes by some chemopreventive phytochemicals. Planta Med. 74: 1526–1539 (2008)
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MTD, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 39: 44–84 (2007)
Vonshak A, Barazani O, Sathiyamoorthy P, Shalev R, Vardy D, Golan‐Goldhirsh A. Screening South Indian medicinal plants for antifungal activity against cutaneous pathogens. Phytother Res. 17: 1123–1125 (2003)
Wild A, GIPP J, Mulcahy T. Overlapping antioxidant response element and PMA responseelement sequences mediate basal and β-naphthoflavone-induced expression of the human γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase catalytic subunit gene. Biochem. J. 332: 373–381 (1998)
Willis D, Moore A, Frederick R, Willoughby D. Heme oxygenase: a novel target for the modulation of inflammatory response. Nat. Med. 2: 87–93 (1996)
Yang JH, Shin BY, Han JY, Kim MG, Wi JE, Kim YW, Cho IJ, Kim SC, Shin SM, Ki SH. Isorhamnetin protects against oxidative stress by activating Nrf2 and inducing the expression of its target genes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 274: 293–301 (2014)
Yang S-Y, Kang JH, Seomun Y, Lee K-W. Caffeic acid induces glutathione synthesis through JNK/AP-1-mediated γ-glutamylcysteine ligase catalytic subunit induction in HepG2 and primary hepatocytes. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 24: 1845–1852 (2015)
Yang S-Y, Lee S, Pyo MC, Jeon H, Kim Y, Lee K-W. Improved physicochemical properties and hepatic protection of Maillard reaction products derived from fish protein hydrolysates and ribose. Food Chem. 221: 1979–1988 (2017)
Zipper LM, Mulcahy RT. Erk activation is required for Nrf2 nuclear localization during pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate induction of glutamate cysteine ligase modulatory gene expression in HepG2 cells. Toxicol. Sci. 73: 124–134 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Korea University Grant (K1617111). The authors also thank the Institute of Biomedical Science and Food Safety, CJ-Korea University Food Safety Hall (Seoul, South Korea) for providing the equipment and facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that are no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, HL., Yang, SY., Pyo, M.C. et al. Protective effects of chebulic acid from Terminalia chebula Retz. against t-BHP-induced oxidative stress by modulations of Nrf2 and its related enzymes in HepG2 cells. Food Sci Biotechnol 28, 555–562 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0477-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0477-z