Abstract
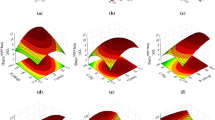
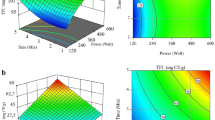
In this research, optimal conditions for extraction of caffeine and polyphenols were established from Iranian green tea leaves. In the first step, caffeine was extracted with efficacy about 86% versed to 4.5% of EGC + EGCG. The EGCG + EGC was extracted from partially decaffeinated green tea leaves through microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) and ultrasound-assisted extraction (USE) with efficiency levels of 95 and 85%, respectively. The best results for the MAE process were obtained with 7.8 min and three number of extraction cycles and for the USE process were as followed: time 57 min, temperature 65 °C, and the number of extraction cycles 3. The total phenol content values at the best conditions of MAE and the USE processes were 125 ± 5 and 96 ± 6 mg gallic acid/g DW. The 50% inhibition (IC50) on 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) were 56 and 66 mg/g of phenol for the MAE and USE processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoa C, Chena C, Wanasundara U, Shahidi F. Natural antioxidants from tea. Natural Antioxidants: Chemistry, Health Effects, and Applications: 213–223 (1997)
Finger A, Engelhardt UH, Wray V. Flavonol triglycosides containing galactose in tea. Phytochem. 30: 2057–2060 (1991)
Watson RR, Preedy VR. Bioactive foods and extracts: Cancer treatment and prevention. CRC Press (2010)
Choung MG, Hwang YS, Lee MS, Lee J, Kang ST, Jun TH. Comparison of extraction and isolation efficiency of catechins and caffeine from green tea leaves using different solvent systems. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 49: 1572–1578 (2014)
Vuong QV, Roach PD. Caffeine in green tea: its removal and isolation. Sep. Purif. Rev. 43: 155–174 (2014)
Ko M-J, Cheigh C-I, Chung M-S. Optimization of subcritical water extraction of flavanols from green tea leaves. J. Agric. Food. Chem 62: 6828–6833 (2014)
Gujar J, Wagh S, Gaikar V. Experimental and modeling studies on microwave-assisted extraction of thymol from seeds of Trachyspermum ammi (TA). Sep. Purif. Technol. 70: 257–264 (2010)
Knorr D, Zenker M, Heinz V, Lee D-U. Applications and potential of ultrasonics in food processing. Trends Food Sci. Technol 15: 261–266 (2004)
Both S, Chemat F, Strube J. Extraction of polyphenols from black tea–Conventional and ultrasound assisted extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem 21: 1030–1034 (2014)
Yolmeh M, Najafi MBH, Farhoosh R. Optimisation of ultrasound-assisted extraction of natural pigment from annatto seeds by response surface methodology (RSM). Food Chem. 155: 319–324 (2014)
Beringhs AO, Dalmina M, Creczynski-Pasa TB, Sonaglio D. Response Surface Methodology IV-Optimal design applied to the performance improvement of an RP-HPLC-UV method for the quantification of phenolic acids in Cecropia glaziovii products. Rev. bras. Farmacogn. 25: 513–521 (2015)
Labbé D, Tremblay A, Bazinet L. Effect of brewing temperature and duration on green tea catechin solubilization: Basis for production of EGC and EGCG-enriched fractions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 49: 1–9 (2006)
Zuo Y, Chen H, Deng Y. Simultaneous determination of catechins, caffeine and gallic acids in green, Oolong, black and pu-erh teas using HPLC with a photodiode array detector. Talanta 57: 307–316 (2002)
ISO 14502-1:2005. Determination of substances characteristic of green and black tea. Part 1: content of total polyphenols in tea. Colorimetric method using FolineCiocalteu reagent
ISO 10727:2002. Tea and instant tea in solid form - Determination of caffeine content – Method using high-performance liquid chromatography
ISO 14502-2:2005. Determination of substances characteristic of green and black tea—Part 2: Content of catechins in green tea—Method using high-performance liquid chromatography
Fenglin H, Ruili L, Liang M. Free radical scavenging activity of extracts prepared from fresh leaves of selected Chinese medicinal plants. Fitoterapia 75: 14–23 (2004)
Jones B, Goos P. I-optimal versus D-optimal split-plot response surface designs. J. QUAL. TECHNOL. 44: 85 (2012)
Suteerapataranon S, Butsoongnern J, Punturat P, Jorpalit W, Thanomsilp C. Caffeine in Chiang Rai tea infusions: Effects of tea variety, type, leaf form, and infusion conditions. Food Chem. 114: 1335–1338 (2009)
Liang H, Liang Y, Dong J, Lu J, Xu H, Wang H. Decaffeination of fresh green tea leaf (Camellia sinensis) by hot water treatment. Food Chem. 101: 1451–1456 (2007)
Bermejo DV, Luna P, Manic MS, Najdanovic-Visak V, Reglero G, Fornari T. Extraction of caffeine from natural matter using a bio-renewable agrochemical solvent. Food Bioprod. Process. 91: 303–309 (2013)
Sun Q-L, Hua S, Ye J-H, Lu J-L, Zheng X-Q, Liang Y-R. Decaffeination of green tea by supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Med. Plant Res. 4: 1161–1168 (2010)
Bermejo DV, Mendiola JA, Ibáñez E, Reglero G, Fornari T. Pressurized liquid extraction of caffeine and catechins from green tea leaves using ethyl lactate, water and ethyl lactate + water mixtures. Food Bioprod. 96: 106–112 (2015)
Li D-C, Jiang J-G. Optimization of the microwave-assisted extraction conditions of tea polyphenols from green tea. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 61: 837–845 (2010)
Quan PT, Hang T, Hai Ha N, De NX, Tuyen TN. Microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenols from fresh tea shoots. Sci. & Tech. Develop., 9(8), 69–75
Perva-Uzunalić A, Škerget M, Knez Ž, Weinreich B, Otto F, Grüner S. Extraction of active ingredients from green tea (Camellia sinensis): Extraction efficiency of major catechins and caffeine. Food Chem. 96: 597–605 (2006)
Xiao W, Han L, Shi B. Microwave-assisted extraction of flavonoids from Radix Astragali. Sep. Purif. Technol. 62: 614–618 (2008)
Chemat F, Rombaut N, Sicaire A-G, Meullemiestre A, Fabiano-Tixier A-S, Abert-Vian M. Ultrasound assisted extraction of food and natural products. Mechanisms, techniques, combinations, protocols and applications. A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 34: 540–560 (2017)
Choung M-G, Lee M-S. Optimal extraction conditions for simultaneous determination of catechins and caffeine in green tea leaves. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 20: 327–333 (2011)
Hitoshi K, Nobuyoshi M. Extraction of Catechins from Green Tea Using Ultrasound. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46: 4936 (2007)
Xia T, Shi S, Wan X. Impact of ultrasonic-assisted extraction on the chemical and sensory quality of tea infusion. J. Food Eng. 74: 557–560 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemzadeh-mohammadi, V., Zamani, B., Afsharpour, M. et al. Extraction of caffeine and catechins using microwave-assisted and ultrasonic extraction from green tea leaves: an optimization study by the IV-optimal design. Food Sci Biotechnol 26, 1281–1290 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0182-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0182-3