Abstract
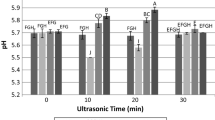
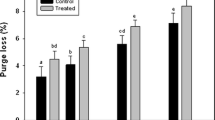
The objective of this study was to investigate the physicochemical and textural properties of heat-induced gels prepared with pork muscles irradiated with gamma rays, electron beams, and X-rays. Pork muscles were irradiated at 5 kGy using the different irradiation sources, and heat-induced gels were prepared from the irradiated pork muscles at a protein concentration of 5 mg/mL. Each irradiation treatment produced lower water-holding capacity, protein solubility, apparent viscosity, hardness, springiness, cohesiveness, gumminess, and chewiness than the control gel prepared with non-irradiated pork muscle (P < 0.05). In addition, gamma irradiation was more influential than electron or X-ray irradiation on the negative impacts on water-holding capacity and texture of heat-induced gels. Therefore, this study suggests that the irradiation source could be one of the significant factors affecting gelling properties of irradiated meat.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi YS, Kim HW, Hwang KE, Song DH, Jeong TJ, Seo KW, Kim YB, Kim CJ. Effects of gamma irradiation on physicochemical properties of heat-induced gel prepared with chicken salt-soluble proteins. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 106: 16–20 (2015).
CAC (Codex Alimentarius Commission). Codex general standard for irradiated foods. CODEX STAN 106-1983. Rev.1-2003 (2003).
Wang SF, Smith DM, Steffe JF. Effect of pH on the dynamic rhelogical properties of chicken breast salt-soluble protein during heat-induced gelation. Poult. Sci. 69: 2220–2227 (1990).
McCord A, Smyth AB, O’Neill EE. Heat-induced gelation properties of salt-soluble muscle proteins as affected by non-meat proteins. J. Food Sci. 63: 580–583 (1998).
Kocher PN, Foegeding EA. Microcentrifuge-based method for measuring water-holding of protein gels. J. Food Sci. 58: 1040–1046 (1993).
Joo ST, Kauffman RG, Kim BC, Park GB. The relationship of sarcoplasmic and myofibrillar protein solubility to colour and water-holding capacity in porcine longissimus muscle. Meat Sci. 52: 291–297 (1999).
Park SY, Wang SH, Chin KB, Kim YD. Rheological properties of the mixture and heat-induced gel prepared from pork salt soluble protein in combined with soluble chitooligosaccharide and chitosan. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 36: 594–597 (2004).
Bourne MC. Texture profile analysis. Food Technol. 32: 62–66 (1978).
SAS., 2011. SAS user’s guide: Basic statistical analysis. NC, USA: Statistical Analysis Systems Institute.
Liu R, Zhao SM, Xiong SB, Xie BJ, Qin LH. Role of secondary structures in the gelation of porcine myosin at different pH values. Meat Sci. 80: 632–639 (2008).
Ciesla K, Salmieri S, Lacroix M, Tien Le C. Gamma irradiation influence on physical properties of milk proteins. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 71: 93–97 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported High Value-added Food Technology Development Program (314068-3) by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (Republic of Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HW., Kim, Y.H.B., Hwang, KE. et al. Effects of gamma-ray, electron-beam, and X-ray irradiation on physicochemical properties of heat-induced gel prepared with salt-soluble pork protein. Food Sci Biotechnol 26, 955–958 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0147-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0147-6