Abstract
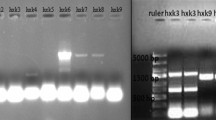
The SfLEU2 structural gene of LEU2 encoding β-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase was cloned from the amylolytic yeast Saccharomycopsis fibuligera isolated from Nuruk, a Korean traditional starter for rice wine production. Sequence analysis revealed the presence of an uninterrupted open-reading frame of 1,107 bp, including a stop codon, encoding a 368 amino acid residue. The deduced amino acid sequence of Leu2 in S. fibuligera was 76.4% homologous with Candida boidinii and Kluyveromyces marxianus sequences. The SfLEU2 gene complemented leu2Δ mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, suggesting that the gene encodes a functional LEU2 in S. fibuligera. The GenBank Accession No. for SfLEU2 is KR820563.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okamoto K, Nitta Y, Maekawa N, Yanase H. Direct ethanol production from starch, wheat bran and rice straw by the white rot fungus Trametes hirsuta. Enzyme Microb. Tech. 48: 273–277 (2011)
Rebros M, Rosenberg M, Grosova Z, Kristofikova L, Paluch M, Sipocz M. Ethanol production from starch hydrolyzates using Zymomonas mobilis and glucoamylase entrapped in polyvinylalcohol hydrogel. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 158: 561–570 (2009)
Bertoldo C, Antranikian G. Starch-hydrolyzing enzymes from thermophilic archaea and bacteria. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 6: 151–160 (2002)
Viktor MJ, Rose SH, van Zyl WH, Viljoen-Bloom M. Raw starch conversion by Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing Aspergillus tubingensis amylases. Biotechnol. Biofuels 6: 167 (2013)
van Zyl WH, Bloom M, Viktor MJ. Engineering yeasts for raw starch conversion. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 95: 1377–1388 (2012)
Choi DH, Park EH, Kim MD. Characterization of starch-utilizing yeast Saccharomycopsis fibuligera isolated from Nuruk. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 42: 407–412 (2014)
He Z, Zhang L, Mao Y, Gu J, Pan Q, Zhou S, Gao B, Wei D. Cloning of a novel thermostable glucoamylase from thermophilic fungus Rhizomucor pusillus and high-level co-expression with alpha-amylase in Pichia pastoris. BMC Biotechnol. 14: 114 (2014)
Kunze G, Meixner M, Steinborn G, Hecker M, Bode R, Samsonova IA, Birnbaum D, Hofemeister J. Expression in yeast of a Bacillus alpha-amylase gene by the ADH1 promoter. J. Biotechnol. 7: 33–48 (1988)
Saelim K, Dissara Y, Kittikun AH. Saccharification of cassava starch by Saccharomycopsis fibuligera YCY1 isolated from Loog-Pang (rice cake starter). Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 30: 65–71 (2008)
Valachova K, Horvathova V. Starch degradation by glucoamylase Glm from Saccharomycopsis fibuligera IFO 0111 in the presence and absence of a commercial pullulanase. Chem. Biodivers. 4: 874–880 (2007)
Eksteen JM, Van Rensburg P, Cordero Otero RR, Pretorius IS. Starch fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing the alpha-amylase and glucoamylase genes from Lipomyces kononenkoae and Saccharomycopsis fibuligera. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 84: 639–646 (2003)
Natalia D, Vidilaseris K, Ismaya WT, Puspasari F, Prawira I, Hasan K, Fibriansah G, Permentier HP, Nurachman Z, Subroto T, Dijkstra BW, Soemitro S. Effect of introducing a disulphide bond between the A and C domains on the activity and stability of Saccharomycopsis fibuligera R64 a-amylase. J. Biotechnol. 195: 8–14 (2015)
Vertes AA, Inui M, Yukawa H. Technological options for biological fuel ethanol. J. Mol. Microb. Biotech. 15: 16–30 (2008)
Sambrook J, Russell DW. Molecular Cloning. Vol I, pp. 1.31–1.162. In: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd ed. Russell DW (ed). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, NY, USA (2011)
Andreadis A, Hsu YP, Hermodson M, Kohlhaw G, Schimmel P. Yeast LEU2. Repression of mRNA levels by leucine and primary structure of the gene product. J. Biol. Chem. 259: 8059–8062 (1984)
De la Rosa JM, Perez JA, Gutierrez F, Gonzalez JM, Ruiz T, Rodriguez L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the LEU2 homologue gene from Pichia anomala. Yeast 18: 1441–1448 (2001)
Turakainen H, Korhola M. Cloning, sequencing and application of the LEU2 gene from the sour dough yeast Candida milleri. Yeast 22: 805–812 (2005)
Marti-Renom MA, Madhusudhan MS, Sali A. Alignment of protein sequences by their profiles. Protein Sci. 13: 1071–1087 (2004)
Yang Z. PAML: A program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 13: 555–556 (1997)
Parsons SJ, Burns RO. ²-Isopropylmalate dehydrogenase (Salmonella typhimurium). Methods Enzymol. 17: 793–799 (1970)
Boneau CA. The effects of violations of assumptions underlying the t-test. Psychol. Bull. 57: 49–64 (1960)
Friden P, Schimmel P. LEU3 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae activates multiple genes for branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis by binding to a common decanucleotide core sequence. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8: 2690–2697 (1988)
Wan Y, Wang X, Huang Y, Qiu D, Jiang L. Identification and characterization of cDNA sequences encoding the HIS3 and LEU2 genes of the fungus Alternaria tenuissima. J. Genet. Genomics 35: 251–256 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, EH., Yeo, SH. & Kim, MD. Cloning of the LEU2 gene from the amylolytic yeast Saccharomycopsis fibuligera . Food Sci Biotechnol 24, 2151–2154 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0286-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0286-6