Abstract
Objective
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is associated with a significant risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, especially in the development of premature atherosclerosis. Specific prediction models for premature atherosclerosis in SLE patients are still limited. The objective of this study was to establish a predictive model for premature atherosclerosis in SLE.
Method
The study collected clinical and laboratory data from 148 SLE patients under the age of 55, between January 2021 and June 2023. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator logistic regression model was utilized to identify potentially relevant features. Subsequently, a nomogram was developed using multivariable logistic analysis. The performance of the nomogram was evaluated through a receiver-operating characteristic curve, calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results
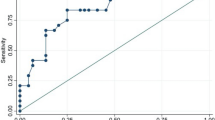
A total of 148 SLE patients who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were enrolled in the study, of whom 53 patients (35.81%) met the definition of premature atherosclerosis. Hypertension, antiphospholipid syndrome, azathioprine use, duration of glucocorticoid, and age of patients were included in the multivariable regression. The nomogram, based on the non-overfitting multivariable model, was internally validated and demonstrated sufficient clinical utility for assessing the risk of premature atherosclerosis (area under curve: 0.867).
Conclusions
The comprehensive nomogram constructed in this study serves as a useful and convenient tool for evaluating the risk of premature atherosclerosis in SLE patients. It is helpful for clinicians to early identify SLE patients with premature atherosclerosis and facilitates the implementation of more effective preventive measures.
Key Points • SLE patients are at a significantly higher risk of developing premature atherosclerosis compared to the general population, and this risk persists even in cases with low disease activity. Traditional models used to evaluate and predict premature atherosclerosis in SLE patients often underestimate the risk. • This study establishes a comprehensive and visually orientated predictive model of premature atherosclerosis in SLE patients, based on clinical characteristics. • The scoring system allows for convenient and effective prediction of individual incidence of premature atherosclerosis, and could provide valuable information for identification and making further intervention decision. |



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available upon reasonable request by any qualified researchers who engage in rigorous, independent scientific research, and will be provided following review and approval of a research proposal and Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP) and execution of a Data Sharing Agreement (DSA). All data relevant to the study are included in the article.
References
Tsokos GC (2020) Autoimmunity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Immunol 21(6):605–614
Frostegård J (2023) Systemic lupus erythematosus and cardiovascular disease. J Intern Med 293:48–62
Bello N, Meyers KJ, Workman J, Hartley L, McMahon M (2023) Cardiovascular events and risk in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Lupus 32(3):325–341
Taylor T, Anastasiou C, Ja C, Rush S, Trupin L, Dall'Era M et al (2023) Causes of death among individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus by race and ethnicity: a population-based study. Arthritis Care Res 75(1):61–68
Björkegren JLM, Lusis AJ (2022) Atherosclerosis: recent developments. Cell 185(10):1630–1645
Crooijmans J, Singh S, Naqshband M, Bruikman CS, Pinto-Sietsma S-J (2023) Premature atherosclerosis: an analysis over 39 years in the Netherlands. Implications for young individuals in high-risk families. Atherosclerosis 384:117267
Lee MT, Mahtta D, Ramsey DJ, Liu J, Misra A, Nasir K et al (2021) Sex-related disparities in cardiovascular health care among patients with premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. JAMA Cardiol 6(7):782–790
Appleton BD, Major AS (2021) The latest in systemic lupus erythematosus-accelerated atherosclerosis: related mechanisms inform assessment and therapy. Curr Opin Rheumatol 33(2):211–218
Kravvariti E, Konstantonis G, Sfikakis PP, Tektonidou MG (2018) Progression of subclinical atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus versus rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of low disease activity. Rheumatology (Oxford) 57(12):2158–2166
Papazoglou N, Kravvariti E, Konstantonis G, Sfikakis PP, Tektonidou MG (2024) The impact of traditional cardiovascular risk factor control on 7-year follow-up atherosclerosis progression in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 63(1):50–57
Tselios K, Gladman DD, Sheane BJ, Su J, Urowitz M (2019) All-cause, cause-specific and age-specific standardised mortality ratios of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in Ontario, Canada over 43 years (1971-2013). Ann Rheum Dis 78(6):802–806
Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, Buroker AB, Goldberger ZD, Hahn EJ et al (2019) 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 140(11):e596–e646
Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, Albus C, Brotons C, Catapano AL et al (2016) 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts) Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur Heart J 37(29):2315–2381
Esdaile JM, Abrahamowicz M, Grodzicky T, Li Y, Panaritis C, du Berger R et al (2001) Traditional Framingham risk factors fail to fully account for accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 44(10):2331–2337
Drosos GC, Konstantonis G, Sfikakis PP, Tektonidou MG (2021) Underperformance of clinical risk scores in identifying vascular ultrasound-based high cardiovascular risk in systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Prev Cardiol 28(3):346–352
McMahon M, Skaggs BJ, Grossman JM, Sahakian L, Fitzgerald J, Wong WK et al (2014) A panel of biomarkers is associated with increased risk of the presence and progression of atherosclerosis in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(1):130–139
Xing H, Pang H, Du T, Yang X, Zhang J, Li M, Zhang S (2021) Establishing a risk prediction model for atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol 12:622216
Liu C, Zhou Y, Zhou Y, Tang X, Tang L, Wang J (2023) Identification of crucial genes for predicting the risk of atherosclerosis with system lupus erythematosus based on comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and machine learning. Comput Biol Med 152:106388
Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, Brinks R, Mosca M, Ramsey-Goldman R et al (2019) 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol 71(9):1400–1412
Petri M, Orbai A-M, Alarcón GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR et al (2012) Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64(8):2677–2686
Tsutsumi A, Ichikawa K, Atsumi T, Matsuura E, Koike T, Krilis SA (1998) Use of various methods for anticardiolipin detection in the updated American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus: comment on the letter by Hochberg. Arthritis Rheum 41(7):1326–1327
Gladman DD, Ibañez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29(2):288–291
Libby P, Buring JE, Badimon L, Hansson GK, Deanfield J, Bittencourt MS et al (2019) Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5(1):56
Corrales A, González-Juanatey C, Peiró ME, Blanco R, Llorca J, González-Gay MA (2014) Carotid ultrasound is useful for the cardiovascular risk stratification of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results of a population-based study. Ann Rheum Dis 73(4):722–727
Touboul PJ, Hennerici MG, Meairs S, Adams H, Amarenco P, Bornstein N et al (2007) Mannheim carotid intima-media thickness consensus (2004-2006). An update on behalf of the Advisory Board of the 3rd and 4th Watching the Risk Symposium, 13th and 15th European Stroke Conferences, Mannheim, Germany, 2004, and Brussels, Belgium, 2006. Cerebrovasc Dis 23(1):75–80
Sauerbrei W, Royston P, Binder H (2007) Selection of important variables and determination of functional form for continuous predictors in multivariable model building. Stat Med 26(30):5512–5528
Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, DeMatteo RP (2015) Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol 16(4):e173–ee80
Barbhaiya M, Feldman CH, Chen SK, Guan H, Fischer MA, Everett BM, Costenbader KH (2020) Comparative risks of cardiovascular disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, diabetes mellitus, and in general medicaid recipients. Arthritis Care Res 72(10):1431–1439
Reiss AB, Jacob B, Ahmed S, Carsons SE, DeLeon J (2021) Understanding accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: toward better treatment and prevention. Inflammation 44(5):1663–1682
Roman MJ, Shanker B-A, Davis A, Lockshin MD, Sammaritano L, Simantov R et al (2003) Prevalence and correlates of accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 349(25):2399–2406
Kay SD, Poulsen MK, Diederichsen ACP, Voss A (2016) Coronary, carotid, and lower-extremity atherosclerosis and their interrelationship in Danish patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 43(2):315–322
Frostegård J (2023) Systemic lupus erythematosus and cardiovascular disease. J Intern Med 293(1):48–62
Wu G-C, Liu H-R, Leng R-X, Li X-P, Li X-M, Pan H-F, Ye D-Q (2016) Subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev 15(1):22–37
Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, Buroker AB, Goldberger ZD, Hahn EJ et al (2019) 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation 140(11):e563–ee95
Munguia-Realpozo P, Mendoza-Pinto C, Sierra Benito C, Escarcega RO, Garcia-Carrasco M, Mendez Martinez S et al (2019) Systemic lupus erythematosus and hypertension. Autoimmun Rev 18(10):102371
McMahon M, Skaggs BJ, Sahakian L, Grossman J, FitzGerald J, Ragavendra N et al (2011) High plasma leptin levels confer increased risk of atherosclerosis in women with systemic lupus erythematosus, and are associated with inflammatory oxidised lipids. Ann Rheum Dis 70(9):1619–1624
Rees F, Doherty M, Grainge M, Lanyon P, Davenport G, Zhang W (2016) Burden of comorbidity in systemic lupus erythematosus in the UK, 1999-2012. Arthritis Care Res 68(6):819–827
Evangelatos G, Kravvariti E, Konstantonis G, Tentolouris N, Sfikakis PP, Tektonidou MG (2022) Atherosclerosis progression in antiphospholipid syndrome is comparable to diabetes mellitus: a 3 year prospective study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 61(8):3408–3413
Cervera R, Serrano R, Pons-Estel GJ, Ceberio-Hualde L, Shoenfeld Y, de Ramón E et al (2015) Morbidity and mortality in the antiphospholipid syndrome during a 10-year period: a multicentre prospective study of 1000 patients. Ann Rheum Dis 74(6):1011–1018
Bettiol A, Emmi G, Finocchi M, Silvestri E, Urban ML, Mattioli I et al (2020) Obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome is not associated with an increased risk of subclinical atherosclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 59(12):3709–3716
Selmi C, De Santis M, Battezzati PM, Generali E, Lari SA, Ceribelli A et al (2020) Anti-phospholipid antibody prevalence and association with subclinical atherosclerosis and atherothrombosis in the general population. Int J Cardiol 300:209–213
Tektonidou MG (2022) Cardiovascular disease risk in antiphospholipid syndrome: thrombo-inflammation and atherothrombosis. J Autoimmun 128:102813
Ruiz-Irastorza G, Bertsias G (2020) Treating systemic lupus erythematosus in the 21st century: new drugs and new perspectives on old drugs. Rheumatology (Oxford) 59(Suppl5):v69–v81
Apostolopoulos D, Kandane-Rathnayake R, Raghunath S, Hoi A, Nikpour M, Morand EF (2016) Independent association of glucocorticoids with damage accrual in SLE. Lupus Sci Med 3(1):e000157
Merashli M, Bucci T, Arcaro A, Gentile F, Ames PRJ (2023) Subclinical atherosclerosis in Behcet’s disease and its inverse relation to azathioprine use: an updated meta-analysis. Clin Exp Med 23(7):3431–3442
de Melo Bisneto AV, Fernandes AS, VdS VS, Véras JH, ETS S, da Silva Santos AF et al (2021) Anti-angiogenic activity of azathioprine. Microvasc Res 138:104234
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge all the patients who participated in our study.
Funding
The study was supported by grants from the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7242160) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (92374101, 81871290).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yin Su and Yuan An contributed to the conception and design of this study. Ruyu Liang, Haojie Xu, and Ranran Yao participated in data collection and analysis. Wenwen Pei, Ziye Wang, Renge Liang, Xiao Han, and Yunshan Zhou helped the date collection. Ruyu Liang and Haojie Xu drafted the manuscript and Ruyu Liang contributed to image processing and interpreted the data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript and consented to publish this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Declaration of generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process
During the preparation of this work, the authors used ChatGPT 4.0 in order to polish the language of this article. After using this tool, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary file 1
(DOCX 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, R., Xu, H., Yao, R. et al. A predictive model for premature atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus based on clinical characteristics. Clin Rheumatol 43, 1541–1550 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-024-06934-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-024-06934-3