Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the eight-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Methods
The survey was conducted with a consecutive sampling of 158 Chinese SLE patients attending public hospitals from January to March 2021. We used the translated Chinese version of the MMAS-8 to collect related data. Reliability, item, and factor analyses were used to test the reliability and validity of the MMAS-8 scale in the selected patients. The internal consistency reliability was evaluated using Cronbach’s α coefficient. Test–retest reliability was assessed using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) in a subset of 30 participants. Construct validity was evaluated using confirmatory factor analysis and correlations between the Self-efficacy for Appropriate Medication Use Scale (SEAMS) and related measures.
Results
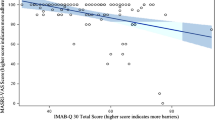
The internal consistency reliability of the Chinese version of the MMAS-8 was high (Cronbach’s α = 0.817), and the test–retest reliability was excellent (intraclass correlation = 0.947; P < 0.001). There were significant differences in the F test and t test between the two extreme groups before and after the ranking of 27% of the questionnaire scores (P < 0.001). The Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) value of construct validity was 0.860. The spherical test value of Bartlettgers was 417.8822. Factor analysis yielded three components that accounted for 69.375% of the total variance. Exploratory factor analysis identified three dimensions of the Chinese version of the MMAS-8. In terms of criterion validity, the correlation of the MMAS-8 score in SEAMS indicated that the convergent validity was good (r = 0.926; P < 0.001).
Conclusions
This study shows that the Chinese version of the Medication Adherence Scale-8 is a reliable and valid tool for assessing medication adherence in Chinese SLE patients.
Key Points • Many factors affect medication adherence in SLE patients. • Many questionnaires measure medication adherence levels. • There is a lack of reliable validation of medication adherence questionnaires specifically for SLE patients. |
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carter EE, Barr SG, Clarke AE (2016) The global burden of SLE: prevalence, health disparities and socioeconomic impact. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12:605–620
Li MT, Zhao Y, Zhang ZY et al (2020) 2020 Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Immunol Res 1:5–23
Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Alunno A et al (2019) 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 78:736–745
Xie X, Yang H, Nie A et al (2018) Predictors of medication nonadherence in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in Sichuan: a cross-sectional study. Patient Prefer Adherence 12:1505–1511
Feldman CH, Costenbader KH, Solomon DH et al (2019) Area-level predictors of medication nonadherence among US Medicaid beneficiaries with lupus: a multilevel study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 71:903–913
Amalia R, Sasongko H, Kundarto W et al (2019) The analysis of the factors affecting medication adherence in patient with SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus) at Yayasan Tittari Griya Kupu Solo. Indian J Public Health Res Dev 10:672–676
Morisky DE, Green LW, Levine DM (1986) Concurrent and predictive validity of a self-reported measure of medication adherence. Med Care 24:67–74
Morisky DE, Ang A, Krousel-Wood M et al (2008) Predictive validity of a medication adherence measure in an outpatient setting. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 10:348–354
Si ZX, Guo LX, Zhou M et al (2012) Reliability and validity of the revised Morisky Drug Compliance scale in patients with anticoagulant therapy. J Nurs Sci 27:23–26
Xu WH, Wang Q, Liang WX (2007) Reliability and validity of Morisky questionnaire in measurement of the compliance with hypertensive medications. Chin J Prev Control Chronic Dis 5:424–426
Zhang SY, Bai LQ, Tan HZ et al (2010) Application of the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale on pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Chin J Antituberculosis 32:527–530
Wu F, Zhao JX, Wang TS et al (2018) Analysis of reliability and validity of the Chinese version Morisky Medication Adherence Scale-8 in assessing medication compliance of the patients with rheumatoid arthritis. China Pharm 29:263–268
Wong YJ, Zhao YM, Liu WJ et al (2018) Reliability and validity of Chinese version of 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale in patients with type 2 diabetes. Chin J Clin (Electronic Edition) 12:445–450
Wang H, Le Z, Zhe L et al (2018) Predicting medication nonadherence risk in a Chinese inflammatory rheumatic disease population: development and assessment of a new predictive nomogram. Patient Prefer Adher 12:1757–1765
Zhang L, Lu GH, Ye S et al (2017) Treatment adherence and disease burden of individuals with rheumatic diseases admitted as outpatients to a large rheumatology center in Shanghai. China Patient Prefer Adherence 11:1591–1601
Okello S, Nasasira B, Muiru ANW et al (2016) Validity and reliability of a self-reported measure of antihypertensive medication adherence in Uganda. PLoS ONE 11:e158499
Laghousi D, Rezaie F, Alizadeh M et al (2021) The eight-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale: validation of its Persian version in diabetic adults. Caspian J Intern Med 12:77
Martinez-Perez P, Orozco-Beltrán D, Pomares-Gomez F et al (2021) Validation and psychometric properties of the 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) in type 2 diabetes patients in Spain. Aten Prim 53:101942
Arnet I, Metaxas C, Walter PN et al (2015) The 8-item M orisky M edication A dherence S cale translated in G erman and validated against objective and subjective polypharmacy adherence measures in cardiovascular patients. J Eval Clin Pract 21:271–277
De Las CC, Peñate W (2015) Psychometric properties of the eight-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) in a psychiatric outpatient setting. Int J Clin Hlth Psyc 15:121–129
Plakas S, Mastrogiannis D, Mantzorou M et al (2016) Validation of the 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale in chronically ill ambulatory patients in rural Greece. Open J Nurs 6:158
Moharamzad Y, Saadat H, Shahraki BN et al (2015) Validation of the Persian version of the 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) in Iranian hypertensive patients. Global J Health Sci 7:173
Wong MC, Wu CH, Wang HH et al (2015) Association between the 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) score and glycaemic control among Chinese diabetes patients. J Clin Pharmacol 55:279–287
Tan C, Teng GG, Chong KJ et al (2016) Utility of the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale in gout: a prospective study. Patient Prefer Adher 10:2449
Xu M, Markström U, Lyu J et al (2017) Detection of low adherence in rural tuberculosis patients in China: application of Morisky Medication Adherence Scale. Int J Env Res Pub He 14:248
Yang A, Wang B, Zhu G et al (2014) Validation of Chinese version of the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale in patients with epilepsy. Seizure 23:295–299
Yan J, You LM, Yang Q et al (2014) Translation and validation of a C hinese version of the 8-item M orisky Medication Adherence Scale in myocardial infarction patients. J Eval Clin Pract 20:311–317
Funding
This manuscript was supported by a project grant from the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (1908085MH294) and a grant from the Seedling cultivation programme of the School of Nursing, Anhui Medical University (hlqm2021008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.L.S and G.C.W conceived the study. P.L. S, Z.Z.W, and G.C.W designed the study. P.L. S and L.W conducted the questionnaire investigation. P.L.S and G.C.W analysis analysed the data. P.L. S, R.C.G, and Z.G.W interpreted the data. P.L.S and G.C.W wrote the draft of the manuscript. G.C.W critically revised the manuscript. All authors approved the submission of the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Pei-Li Shi and Zhen-Zhen Wu contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, PL., Wu, ZZ., Wu, L. et al. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the eight-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 41, 2713–2720 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-022-06195-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-022-06195-y