Abstract
Objective
The novel inflammatory markers C-reactive protein to albumin ratio (CAR), neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were associated with the disease activity of many autoimmune diseases. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association of these new inflammatory indexes with relapsing polychondritis disease activity index (RPDAI).
Methods
The data of relapsing polychondritis (RP) patients hospitalized between 2004 and 2020 at Peking Union Medical College Hospital were collected. One of the exclusive criteria was that RP patients overlapped with other diseases. Another was the RP patients with incomplete data. A total of 170 RP patients and 170 healthy controls (HCs) were included. The association of new inflammatory makers with RPDAI was assessed by Spearman’s correlation analysis.
Results
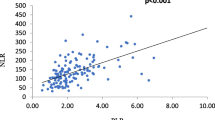
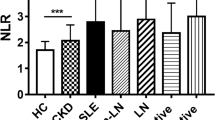
Compared to HCs, the CAR, NLR, and PLR were significantly higher in RP patients (both p < 0.001). The CAR, NLR, PLR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and neutrophil counts in peripheral blood positively correlated with RPDAI. Blood albumin, lymphocyte count, hemoglobin (Hb) negatively correlated with RPDAI. The association of CAR, NLR, and PLR with RPDAI was demonstrated by Spearman’s correlation analysis.
Conclusion
The novel inflammatory markers CAR, NLR and PLR were associated with RPDAI.
Key Points • This is the first research to explore the association of CAR, NLR, and PLR with disease activity in patients with RP • CAR, NLR, and PLR are positively correlated with RPDAI • CAR, NLR, and PLR might be the potential predictors of disease activity in RP |

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The readers can access the data supporting the conclusions of the study from the article.
References
Chopra R, Chaudhary N, Kay J (2013) Relapsing polychondritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 39:263–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2013.03.002
Hazra N, Dregan A, Charlton J, Gulliford MC, D’Cruz DP (2015) Incidence and mortality of relapsing polychondritis in the UK: a population-based cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 54:2181–2187. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kev240
Rednic S, Damian L, Talarico R, Scire CA, Tobias A, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Launay D, Mathian A, Mattews L, Ponte C, Toniati P, Bombardieri S, Frank C, Schneider M, Smith V, Cutolo M, Mosca M, Arnaud L (2018) Relapsing polychondritis: state of the art on clinical practice guidelines. RMD Open 4:e788. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000788
Arnaud L, Devilliers H, Peng SL, Mathian A, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Buckner J, Dagna L, Michet C, Sharma A, Cervera R, Haroche J, Papo T, D’Cruz D, Arlet P, Zwerina J, Belot A, Suzuki N, Harle JR, Moots R, Jayne D, Hachulla E, Marie I, Tanaka T, Lebovics R, Scott D, Kucharz EJ, Birchall M, Kong KO, Gorochov G, Amoura Z (2012) The Relapsing Polychondritis Disease Activity Index: development of a disease activity score for relapsing polychondritis. Autoimmun REV 12:204–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2012.06.005
Yang WM, Zhang WH, Ying HQ, Xu YM, Zhang J, Min QH, Huang B, Lin J, Chen JJ, Wang XZ (2018) Two new inflammatory markers associated with disease activity score-28 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: albumin to fibrinogen ratio and C-reactive protein to albumin ratio. Int Immunopharmacol 62:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.07.007
Chen Q, Chen DY, Xu XZ, Liu YY, Yin TT, Li D (2019) Platelet/lymphocyte, lymphocyte/monocyte, and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratios as biomarkers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Med Sci Monit 25:6474–6481. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.916583
Wu Y, Chen Y, Yang X, Chen L, Yang Y (2016) Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were associated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Immunopharmacol 36:94–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.04.006
Qin B, Ma N, Tang Q, Wei T, Yang M, Fu H, Hu Z, Liang Y, Yang Z, Zhong R (2016) Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were useful markers in assessment of inflammatory response and disease activity in SLE patients. Mod Rheumatol 26:372–376. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2015.1091136
Soliman WM, Sherif NM, Ghanima IM, El-Badawy MA (2020) Neutrophil to lymphocyte and platelet to lymphocyte ratios in systemic lupus erythematosus: Relation with disease activity and lupus nephritis. Reumatol Clin 16:255–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reuma.2018.07.008
Lee YH, Song GG (2018) Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, mean platelet volume and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in Behcet’s disease and their correlation with disease activity: a meta-analysis. Int J Rheum Dis 21:2180–2187. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.13404
Dion J, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Sene D, Cohen-Bittan J, Leroux G, Dion C, Frances C, Piette JC (2016) Relapsing polychondritis can be characterized by three different clinical phenotypes: analysis of a recent series of 142 patients. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:2992–3001. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39790
Horvath A, Pall N, Molnar K, Kovats T, Surjan G, Vicsek T, Pollner P (2016) A nationwide study of the epidemiology of relapsing polychondritis. Clin Epidemiol 8:211–230. https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S91439
Pallo P, Levy-Neto M, Pereira R, Shinjo SK (2017) Relapsing polychondritis: prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and its risk factors, and general disease features according to gender. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed 57:338–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbre.2017.02.003
McAdam LP, O’Hanlan MA, Bluestone R, Pearson CM (1976) Relapsing polychondritis: prospective study of 23 patients and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 55:193–215
Damiani JM, Levine HL (1979) Relapsing polychondritis—report of ten cases. Laryngoscope 89:929–946
Bruegel M, Nagel D, Funk M, Fuhrmann P, Zander J, Teupser D (2015) Comparison of five automated hematology analyzers in a university hospital setting: Abbott Cell-Dyn Sapphire, Beckman Coulter DxH 800, Siemens Advia 2120i, Sysmex XE-5000, and Sysmex XN-2000. Clin Chem Lab Med 53:1057–1071. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2014-0945
Schultze HE, Schwick G (1959) Quantitative immunological determination of blood proteins. Clin Chim Acta 4:15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(59)90075-0
Doumas BT, Watson WA, Biggs HG (1971) Albumin standards and the measurement of serum albumin with bromcresol green. Clin Chim Acta 31:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(71)90365-2
(1993) ICSH recommendations for measurement of erythrocyte sedimentation rate. International Council for Standardization in Haematology (Expert Panel on Blood Rheology) J Clin Pathol 46:198–203. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.46.3.198
Clauss A (1957) Rapid physiological coagulation method in determination of fibrinogen. Acta Haematol 17:237–246. https://doi.org/10.1159/000205234
Ferrada MA, Grayson PC, Banerjee S, Sikora KA, Colbert RA, Sinaii N, Katz JD (2018) Patient perception of disease-related symptoms and complications in relapsing polychondritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 70:1124–1131. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.23492
Yayla ME, Ilgen U, Okatan IE, UsluYurteri E, Torgutalp M, Kelesoglu DA, Aydemir GE, Sezer S, Turgay TM, Kinikli G, Ates A (2020) Association of simple hematological parameters with disease manifestations, activity, and severity in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 39:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04685-0
Seringec AN, Yildirim CG, Gogebakan H, Acipayam C (2019) The C-reactive protein/albumin ratio and complete blood count parameters as indicators of disease activity in patients with Takayasu arteritis. Med Sci Monit 25:1401–1409. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.912495
Stabler T, Piette JC, Chevalier X, Marini-Portugal A, Kraus VB (2004) Serum cytokine profiles in relapsing polychondritis suggest monocyte/macrophage activation. Arthritis Rheum 50:3663–3667. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.20613
Wu Y, Potempa LA, El KD, Filep JG (2015) C-reactive protein and inflammation: conformational changes affect function. Biol Chem 396:1181–1197. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2015-0149
Cronkite DA, Strutt TM (2018) The regulation of inflammation by innate and adaptive lymphocytes. J Immunol Res 2018:1467538. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1467538
Couldwell G, Machlus KR (2019) Modulation of megakaryopoiesis and platelet production during inflammation. Thromb Res 179:114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2019.05.008
Don BR, Kaysen G (2004) Serum albumin: relationship to inflammation and nutrition. Semin Dial 17:432–437. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0894-0959.2004.17603.x
Zeb A, Khurshid S, Bano S, Rasheed U, Zammurrad S, Khan MS, Aziz W, Tahir S (2019) The role of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as markers of disease activity in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Cureus 11:e6025. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.6025
Hu ZD, Sun Y, Guo J, Huang YL, Qin BD, Gao Q, Qin Q, Deng AM, Zhong RQ (2014) Red blood cell distribution width and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio are positively correlated with disease activity in primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin Biochem 47:287–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2014.08.022
Jung JY, Lee E, Suh CH, Kim HA (2019) Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio are associated with disease activity in polymyalgia rheumatica. J Clin Lab Anal 33:e23000. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.23000
Yang W, Wang X, Zhang W, Ying H, Xu Y, Zhang J, Min Q, Chen J (2017) Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio are 2 new inflammatory markers associated with pulmonary involvement and disease activity in patients with dermatomyositis. Clin Chim Acta 465:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2016.12.007
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 81671614, the website: www.nsfc.gov.cn/]; Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences(CIFMS)[grant number 2017-I2M-3–001]; and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant number No. 2016YFC0901500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Zhao, M., Li, H. et al. Three new inflammatory markers C reactive protein to albumin ratio, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, and platelet to lymphocyte ratio correlated with relapsing polychondritis disease activity index. Clin Rheumatol 40, 4685–4691 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05827-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05827-z