Abstract
Introduction/objectives
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) may coexist and carry a higher risk for future comorbidities. Although 14-3-3η protein is recently a known diagnostic marker in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), its role has not been investigated in SLE. The aim of this study was to compare serum 14-3-3η protein level in SLE and RA patients and to examine its association with clinical and laboratory features in SLE patients.
Methods
Eighty-four SLE patients and 39 RA patients were included. Sociodemographic, SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI), and damage index were assessed for SLE patients. Data about secondary SS were collected. 14-3-3η was measured by ELISA; titres above 0.19 ng/ml were considered positive.
Results
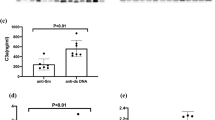
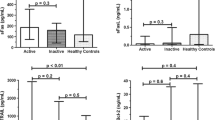
Serum 14-3-3η protein in SLE was significantly lower than in RA (0.37 ± 0.09 vs 1.5 ± 0.51; p < 0.001). 14-3-3η protein level was comparable between SLE patients with and without arthritis (0.29 ± 0.8 vs 0.15 ± 0.08 respectively; p = 0.20). Serum 14–3-3η protein level was higher in SLE with secondary SS features compared to those without (0.22 ± 0.10 IU/ml vs 0.11 ± 0.04 IU/ml; respectively, p < 0.001). There were no differences in 14–3-3η positivity for other lupus criteria or correlation of 14–3-3η titer with SLEDAI. 14–3-3η protein at 1.11 ng/mL yield a secondary SS diagnostic accuracy of 71%.
Conclusions
Serum 14–3-3η protein level is high in SLE-associated SS. The 14–3-3η protein level was able to distinguish patients with secondary SS among patients with SLE. Studying the role of 14–3-3η protein in Sjögren’s syndrome would be considered in further larger scale studies to confirm the impact of any association.
Key Points • Serum 14-3-3η protein level is significantly higher in systemic lupus patients with secondary Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) in comparison to those without. • Serum 14-3-3η protein can be used as a useful marker to distinguish patients with secondary SS among patients with systemic lupus. • 14-3-3η protein level shows no difference between systemic lupus patients with and without arthritis. |



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petri M (2002) Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 16:847–858
Mok CC, Lau CS (2003) Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Pathol 56:481–490. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.56.7.481
Aggarwal R, Anaya J-M, Koelsch KA, Kurien BT, Scofield RH (2015) Association between secondary and primary Sjögren’s syndrome in a large collection of lupus families. Autoimmune Dis 2015:298506. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/298506
Manganelli P, Fietta P (2003) Apoptosis and Sjogren syndrome. Semin Arthritis Rheum 33:49–65. https://doi.org/10.1053/sarh.2003.50019
Gheita TA, Bassyouni IH, Bassyouni RH (2012) Plasma concentrations of growth arrest specific protein 6 and the soluble form of its tyrosine kinase receptor Axl in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and Behcets disease. J Clin Immunol 32:1279–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9743-7
Aitken A (2006) 14-3-3 proteins: a historic overview. Semin Cancer Biol 16:162–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.03.005
Yang X, Lee WH, Sobott F, Papagrigoriou E, Robinson CV, Grossmann JG, Sundström M, Doyle DA, Elkins JM (2006) Structural basis for protein-protein interactions in the 14-3-3 protein family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:17237–17242. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605779103
Maksymowych WP, van der Heijde D, Allaart CF, Landewé R, Boire G, Tak PP, Gui Y, Ghahary A, Kilani R, Marotta A (2014) 14-3-3eta is a novel mediator associated with the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and joint damage. Arthritis Res Ther 16:R99. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4547
Kilani RT, Maksymowych WP, Aitken A, Boire G, St-Pierre Y, Li Y, Ghahary A (2007) Detection of high levels of 2 specific isoforms of 14-3-3 proteins in synovial fluid from patients with joint inflammation. J Rheumatol 34:1650–1657
Zeng T, Tan L (2018) 14-3-3eta protein: a promising biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis. Biomark Med 12:917–925. https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm-2017-0385
Guan S-Z, Yang Y-Q, Bai X, Wang Y, Feng KQ, Zhang HJ, Dong M, Yang HW, Li HQ (2019) Serum 14-3-3eta could improve the diagnostic rate of rheumatoid arthritis and correlates to disease activity. Ann Clin Lab Sci 49:57–62
Maksymowych WP, Naides SJ, Bykerk V, Siminovitch KA, van Schaardenburg D, Boers M, Landewé R, van der Heijde D, Tak PP, Genovese MC, Weinblatt ME, Keystone EC, Zhukov OS, Abolhosn RW, Popov JM, Britsemmer K, van Kuijk A, Marotta A (2014) Serum 14-3-3eta is a novel marker that complements current serological measurements to enhance detection of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 41:2104–2113. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.131446
van Schaardenburg D, Maksymowych WP, Boers M et al (2014) THU0244 14-3-3Eta is an independent predictor of radiographic changes in early RA and higher titres inform a higher likelihood of joint damage progression. Ann Rheum Dis 73:266 LP–266266
Dalrymple AM, Tuttle P IV, Feller L, Zhukov OS, Lagier RJ, Bridgforth R, Williams GJ, Popov JM, Naides SJMT (2017) 14-3-3η (eta) Protein in juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) patients. Arthritis Rheumatol 69
Marotta A, Kuijk AW, Maksymowych WP, Tak PP (2013) SAT0309 serum 14-3-3 ETA: an independent biomarker associated with joint damage in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 71:576 LP–576576. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-eular.3256
Hitchon C, Robinson D, El-Gabalawy H et al (2017) 215 active arthritis is associated with 14–3–beta titre in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci & Med 4:A99 LP–A99A99
Petri M, Orbai A-M, Alarcon GS et al (2012) Derivation and validation of the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64:2677–2686. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.34473
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO III, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JM, Hobbs K, Huizinga TW, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Ménard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PP, Upchurch KS, Vencovský J, Wolfe F, Hawker G (2010) 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581
Gladman DD, Ibañez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29:288–291
Gladman DD, Goldsmith CH, Urowitz MB, Bacon P, Fortin P, Ginzler E, Gordon C, Hanly JG, Isenberg DA, Petri M, Nived O, Snaith M, Sturfelt G (2000) The systemic lupus international collaborating clinics/American College of Rheumatology (SLICC/ACR) damage index for systemic lupus erythematosus international comparison. J Rheumatol 27:373–376
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, Daniels TE, Fox PC, Fox RI, Kassan SS, Pillemer SR, Talal N, Weisman MH, European Study Group on Classification Criteria for Sjögren’s Syndrome (2002) Classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis 61:554–558. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.61.6.554
Franceschini F, Cavazzana I (2005) Anti-Ro/SSA and La/SSB antibodies. Autoimmunity 38:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916930400022954
Cau Y, Valensin D, Mori M et al (2018) Structure, function, involvement in diseases and targeting of 14-3-3 proteins: an update. Curr Med Chem 25:5–21. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170426095015
Jia H, Liang Z, Zhang X, Wang J, Xu W, Qian H (2017) 14-3-3 proteins: an important regulator of autophagy in diseases. Am J Transl Res 9:4738–4746
Sreedhar R, Arumugam S, Thandavarayan RA, Giridharan VV, Karuppagounder V, Pitchaimani V, Afrin R, Miyashita S, Nomoto M, Harima M, Gurusamy N, Suzuki K, Watanabe K (2015) Myocardial 14-3-3eta protein protects against mitochondria mediated apoptosis. Cell Signal 27:770–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.12.021
Gheita TA, Kenawy SAB, El Sisi RW et al (2014) Subclinical reduced G6PD activity in rheumatoid arthritis and Sjogren’s syndrome patients: relation to clinical characteristics, disease activity and metabolic syndrome. Mod Rheumatol 24:612–617. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2013.851639
Scheinfeld N (2006) Sjögren syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus are distinct conditions. Dermatol Online J 12:4
Deutsch O, Krief G, Konttinen YT et al (2015) Identification of Sjogren’s syndrome oral fluid biomarker candidates following high-abundance protein depletion. Rheumatology (Oxford) 54:884–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keu405
Shovman O, Gilburd B, Watad A et al (2018) Decrease in 14-3-3eta protein levels is correlated with improvement in disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tofacitinib. Pharmacol Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.11.009
Maxwell SA, Li Z, Jaye D, Ballard S, Ferrell J, Fu H (2009) 14-3-3zeta mediates resistance of diffuse large B cell lymphoma to an anthracycline-based chemotherapeutic regimen. J Biol Chem 284:22379–22389. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.022418
Baer AN, Maynard JW, Shaikh F, Magder LS, Petri M (2010) Secondary Sjogren’s syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus defines a distinct disease subset. J Rheumatol 37:1143–1149. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.090804
van Beers-Tas MH, Marotta A, Boers M, Maksymowych WP, van Schaardenburg D (2016) A prospective cohort study of 14-3-3η in ACPA and/or RF-positive patients with arthralgia. Arthritis Res Ther 18:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-016-0975-4
Hammam N, Salah S, Marotta AFKE (2017) Evaluation of synovial fluid 14-3-3η protein as a marker of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 69
Shiboski SC, Shiboski CH, Criswell LA, Baer A, Challacombe S, Lanfranchi H, Schiødt M, Umehara H, Vivino F, Zhao Y, Dong Y, Greenspan D, Heidenreich AM, Helin P, Kirkham B, Kitagawa K, Larkin G, Li M, Lietman T, Lindegaard J, McNamara N, Sack K, Shirlaw P, Sugai S, Vollenweider C, Whitcher J, Wu A, Zhang S, Zhang W, Greenspan J, Daniels T, Sjögren’s International Collaborative Clinical Alliance (SICCA) Research Groups (2012) American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a data-driven, expert consensus approach in the Sjögren’s International Collaborative Clinical Alliance cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64:475–487
Al-Hashimi I, Khuder S, Haghighat N, Zipp M (2001) Frequency and predictive value of the clinical manifestations in Sjogren’s syndrome. J Oral Pathol Med 30:1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
The study conforms to the 1995 Helsinki declaration and was approved by Assiut Faculty of Medicine ethical committee. Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hammam, N., Gamal, N.M., Elzohri, M.H. et al. Serum 14-3-3η protein is associated with clinical and serologic features of Sjögren’s syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a cross-sectional analysis. Clin Rheumatol 39, 2603–2610 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05033-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05033-3