Abstract
Objective
miR-150-5p has been implicated in the regulation and onset of immune diseases. We investigated the effects of miR-150-5p on the functions of RA synovial fibroblasts (RASFs).
Method
The binding site between suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) and miR-150-5p was analyzed using European Bioinformatics Institute database, and the 3′ UTR of SOCS1 mRNA, including the binding site, was amplified and ligated to the 3′-end of LUC2 gene in the pmirGL0 dual-luciferase vector. The pmirGL0 vector and corresponding mimics were subsequently co-transfected into 293T cells to compare the relative fluorescence intensity of LUC2 between the miR-150-5p mimics and the negative control (NC) mimics groups. Further, the RASF cell line MH7A was transfected with miR-150-5p or NC mimics and subjected to flow cytometric analysis, cell counting kit-8 assay, western blot analysis, qPCR, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA) assay 48 h after transfection.
Results
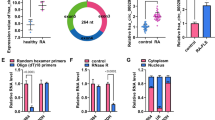
miR-150-5p mimics resulted in a lower cell apoptotic rate and proportion of cells in the S phase. Using a dual-luciferase reporter gene assay, we then found that SOCS1 is a potential target of miR-150-5p. Compared with NC mimics, miR-150-5p mimics significantly decreased the protein and mRNA expression levels of SOCS1. ELISA assay showed that miR-150-5p mimics increased interleukin-6 level in the cell culture medium but did not influence tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels.
Conclusions
Overall, the growth-promoting effect of miR-150-5p on MH7A cells may be attributed to the miR-150-5p-induced degradation of SOCS1 mRNA, suggesting a potential therapeutic target for RA.
Key Points • SOCS1 is a potential target of miR-150-5p. • miR-150-5p promoted the growth of RASF cell line MH7A. • miR-150-5p increased the secretion of IL-6 but did not significantly affect TNF-α levels in MH7A cells. |




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
16 January 2020
The first name of the co-author of the above article was presented incorrect in the published version. The author name “<Emphasis Type="Bold">Miangliang Qiu</Emphasis>” should read “<Emphasis Type="Bold">Mingliang Qiu</Emphasis>” as mentioned above.
References
Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL, Akl EA, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC, Vaysbrot E, McNaughton C, Osani M, Shmerling RH, Curtis JR, Furst DE, Parks D, Kavanaugh A, O’Dell J, King C, Leong A, Matteson EL, Schousboe JT, Drevlow B, Ginsberg S, Grober J, St.Clair EW, Tindall E, Miller AS, McAlindon T (2016) 2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 68:1–25
Lau CS, Chia F, Harrison A, Hsieh TY, Jain R, Jung SM, Kishimoto M, Kumar A, Leong KP, Li Z, Lichauco JJ, Louthrenoo W, Luo SF, Nash P, Ng CT, Park SH, Suryana BP, Suwannalai P, Wijaya LK, Yamamoto K, Yang Y, Yeap SS (2015) APLAR rheumatoid arthritis treatment recommendations. Int J Rheum Dis 18:685–713
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB (2016) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet (London, England) 388:2023–2038
Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet (London, England) 376:1094–1108
Sonkoly E, Pivarcsi A (2009) Advances in microRNAs: implications for immunity and inflammatory diseases. J Cell Mol Med 13:24–38
Chen Z, Wang H, Xia Y, Yan F, Lu Y (2018) Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal cell-derived miRNA-150-5p-expressing exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis mediated by the modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J Immunol 201:2472–2482
Zhou H, Hasni SA, Perez P, Tandon M, Jang SI, Zheng C, Kopp JB, Austin H 3rd, Balow JE, Alevizos I, Illei GG (2013) miR-150 promotes renal fibrosis in lupus nephritis by downregulating SOCS1. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:1073–1087
Starr R, Willson TA, Viney EM, Murray LJ, Rayner JR, Jenkins BJ, Gonda TJ, Alexander WS, Metcalf D, Nicola NA, Hilton DJ (1997) A family of cytokine-inducible inhibitors of signalling. Nature 387:917–921
Hilton DJ, Richardson RT, Alexander WS, Viney EM, Willson TA, Sprigg NS, Starr R, Nicholson SE, Metcalf D, Nicola NA (1998) Twenty proteins containing a C-terminal SOCS box form five structural classes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:114–119
Isomaki P, Alanara T, Isohanni P, Lagerstedt A, Korpela M, Moilanen T, Visakorpi T, Silvennoinen O (2007) The expression of SOCS is altered in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:1538–1546
de Hooge AS, van de Loo FA, Koenders MI, Bennink MB, Arntz OJ, Kolbe T, van den Berg WB (2004) Local activation of STAT-1 and STAT-3 in the inflamed synovium during zymosan-induced arthritis: exacerbation of joint inflammation in STAT-1 gene-knockout mice. Arthritis Rheum 50:2014–2023
Mor A, Abramson SB, Pillinger MH (2005) The fibroblast-like synovial cell in rheumatoid arthritis: a key player in inflammation and joint destruction. Clin Immunol 115:118–128
Chen Z, Wang H, Xia Y, Yan F, Lu Y (2018) RA. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal cell-derived miRNA-150-5p-expressing exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis mediated by the modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J Immunol 201:2472–2482
Niimoto T, Nakasa T, Ishikawa M, Okuhara A, Izumi B, Deie M, Suzuki O, Adachi N, Ochi M (2010) MicroRNA-146a expresses in interleukin-17 producing T cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 11:209
Churov AV, Oleinik EK, Knip M (2015) MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: altered expression and diagnostic potential. Autoimmun Rev 14:1029–1037
Ebrahimiyan H, Rezaei N, Vojdanian M, Aslani S, Jamshidi A, Mahmoudi M (2019) microRNA involvement in the regulation of survivin in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int J Rheum Dis 22:1107–1114
Su YJ, Tsai NW, Kung CT, Wang HC, Lin WC, Huang CC, Chang YT, Su CM, Chiang YF, Cheng BC, Lin YJ, Lu CH (2018) Investigation of MicroRNA in mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomed Res Int 2018:9026357
Abulaban KM, Fall N, Nunna R, Ying J, Devarajan P, Grom A, Bennett M, Ardoin SP, Brunner HI (2016) Relationship of cell-free urine MicroRNA with lupus nephritis in children. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J 14:4
Honda N, Jinnin M, Kira-Etoh T, Makino K, Kajihara I, Makino T, Fukushima S, Inoue Y, Okamoto Y, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, Ihn H (2013) miR-150 down-regulation contributes to the constitutive type I collagen overexpression in scleroderma dermal fibroblasts via the induction of integrin beta3. Am J Pathol 182:206–216
Perez-Sanchez C, Font-Ugalde P, Ruiz-Limon P, Lopez-Pedrera C, Castro-Villegas MC, Abalos-Aguilera MC, Barbarroja N, Arias-de la Rosa I, Lopez-Montilla MD, Escudero-Contreras A, Lopez-Medina C, Collantes-Estevez E, Jimenez-Gomez Y (2018) Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers of disease activity and structural damage in ankylosing spondylitis patients. Hum Mol Genet 27:875–890
Huang XL, Zhang L, Li JP, Wang YJ, Duan Y, Wang J (2015) MicroRNA-150: a potential regulator in pathogens infection and autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity 48:503–510
Zhou B, Wang S, Mayr C, Bartel DP, Lodish HF (2007) miR-150, a microRNA expressed in mature B and T cells, blocks early B cell development when expressed prematurely. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:7080–7085
Bezman NA, Chakraborty T, Bender T, Lanier LL (2011) miR-150 regulates the development of NK and iNKT cells. J Exp Med 208:2717–2731
Tsitsiou E, Lindsay MA (2009) microRNAs and the immune response. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:514–520
Bian Z, Li L, Cui J, Zhang H, Liu Y, Zhang CY, Zen K (2011) Role of miR-150-targeting c-Myb in colonic epithelial disruption during dextran sulphate sodium-induced murine experimental colitis and human ulcerative colitis. J Pathol 225:544–553
Ghisi M, Corradin A, Basso K, Frasson C, Serafin V, Mukherjee S, Mussolin L, Ruggero K, Bonanno L, Guffanti A, De Bellis G, Gerosa G, Stellin G, D’Agostino DM, Basso G, Bronte V, Indraccolo S, Amadori A, Zanovello P (2011) Modulation of microRNA expression in human T-cell development: targeting of NOTCH3 by miR-150. Blood 117:7053–7062
Wu Q, Jin H, Yang Z, Luo G, Lu Y, Li K, Ren G, Su T, Pan Y, Feng B, Xue Z, Wang X, Fan D (2010) MiR-150 promotes gastric cancer proliferation by negatively regulating the pro-apoptotic gene EGR2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 392:340–345
Laragione T, Gulko PS (2010) mTOR regulates the invasive properties of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med 16:352–358
Lin JT, Stein EA, Wong MT, Kalpathy KJ, Su LL, Utz PJ, Robinson WH, Fathman CG (2012) Differential mTOR and ERK pathway utilization by effector CD4 T cells suggests combinatorial drug therapy of arthritis. Clin Immunol 142:127–138
Rawlings JS, Rosler KM, Harrison DA (2004) The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Sci 117:1281–1283
Malemud CJ (2018) The role of the JAK/STAT signal pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 10:117–127
McGarry T, Orr C, Wade S, Biniecka M, Wade S, Gallagher L, Low C, Veale DJ, Fearon U (2018) JAK/STAT blockade alters synovial bioenergetics, mitochondrial function, and proinflammatory mediators in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ) 70:1959–1970
Mateen S, Zafar A, Moin S, Khan AQ, Zubair S (2016) Understanding the role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chim Acta 455:161–171
Asquith DL, McInnes IB (2007) Emerging cytokine targets in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 19:246–251
Malemud CJ (2017) Negative regulators of JAK/STAT signaling in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci 18
Aittomaki S, Pesu M (2014) Therapeutic targeting of the Jak/STAT pathway. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 114:18–23
Aaronson DS, Horvath CM (2002) A road map for those who don’t know JAK-STAT. Science 296:1653–1655
Xiong H, Du W, Zhang YJ, Hong J, Su WY, Tang JT, Wang YC, Lu R, Fang JY (2012) Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, suppresses JAK2/STAT3 signaling via inducing the promoter-associated histone acetylation of SOCS1 and SOCS3 in human colorectal cancer cells. Mol Carcinog 51:174–184
Tamiya T, Kashiwagi I, Takahashi R, Yasukawa H, Yoshimura A (2011) Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins and JAK/STAT pathways: regulation of T-cell inflammation by SOCS1 and SOCS3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:980–985
Chinen T, Komai K, Muto G, Morita R, Inoue N, Yoshida H, Sekiya T, Yoshida R, Nakamura K, Takayanagi R, Yoshimura A (2011) Prostaglandin E2 and SOCS1 have a role in intestinal immune tolerance. Nat Commun 2:190
Mori T, Miyamoto T, Yoshida H, Asakawa M, Kawasumi M, Kobayashi T, Morioka H, Chiba K, Toyama Y, Yoshimura A (2011) IL-1beta and TNFalpha-initiated IL-6-STAT3 pathway is critical in mediating inflammatory cytokines and RANKL expression in inflammatory arthritis. Int Immunol 23:701–712
Hammond SM (2015) An overview of microRNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 87:3–14
Li YT, Chen SY, Wang CR, Liu MF, Lin CC, Jou IM, Shiau AL, Wu CL (2012) Brief report: amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by lentivirus-mediated silencing of microRNA-223. Arthritis Rheum 64:3240–3245
Tao Y, Wang Z, Wang L, Shi J, Guo X, Zhou W, Wu X, Liu Y, Zhang W, Yang H, Shi Q, Xu Y, Geng D (2017) Downregulation of miR-106b attenuates inflammatory responses and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 56:1804–1813
Dang Q, Yang F, Lei H, Liu X, Yan M, Huang H, Fan X, Li Y (2017) Inhibition of microRNA-34a ameliorates murine collagen-induced arthritis. Exp Ther Med 14:1633–1639
Peng JS, Chen SY, Wu CL, Chong HE, Ding YC, Shiau AL, Wang CR (2016) Amelioration of experimental autoimmune arthritis through targeting of synovial fibroblasts by Intraarticular delivery of microRNAs 140-3p and 140-5p. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ) 68:370–381
Nakasa T, Shibuya H, Nagata Y, Niimoto T, Ochi M (2011) The inhibitory effect of microRNA-146a expression on bone destruction in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 63:1582–1590
Wu J, Fan W, Ma L, Geng X (2018) miR-708-5p promotes fibroblast-like synoviocytes’ cell apoptosis and ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by the inhibition of Wnt3a/beta-catenin pathway. Drug Des Dev Ther 12:3439–3447
Funding
This study was partially supported by a grant from the project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO.21605075) and the project of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (NO.20181BAB203020, NO.20192BBGL70024). The funder had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised: The first name of the co-author of the above article was presented incorrect in the published version. The author name “Miangliang Qiu” should read “Mingliang Qiu” and is now presented correctly in this article.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, M., Mo, L., Li, J. et al. Effects of miR-150-5p on the growth and SOCS1 expression of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Clin Rheumatol 39, 909–917 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04894-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04894-7