Abstract
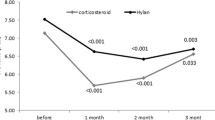
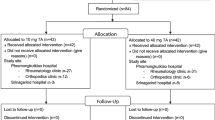
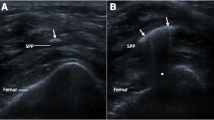
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic multifactorial disease characterized by progressive joint degeneration. The purpose of this study was to compare the effects of ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection with oxygen–ozone injection in patients with knee OA. This double-blind randomized clinical trial was performed on 62 patients with knee OA. The patients were randomly divided into two groups. In the first group 40 mg triamcinolone (1 cc) and in the second group 10 cc (15 μg/ml) oxygen–ozone (O2–O3) were injected into the knee joint under ultrasound guidance. Outcome measures included the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis (WOMAC), knee flexion range of motion (ROM), effusion in ultrasound images of the suprapatellar recess, and visual analog scale (VAS), which were evaluated before injection, 1 week, 1 month, and 3 months after the treatment. Sixty-two patients (10 men and 52 women) were enrolled with mean age of 57.9 years. VAS improved in both groups (steroid P value = 0.001, oxygen–ozone P value > 0.001). The improvements seen in VAS and WOMAC scores 3 months after treatment were in favor of the oxygen–ozone group when compared to the steroid group (P = 0.041 vs P = 0.19). There was no significant difference between the two groups in ROM and joint effusion seen under ultrasound (ROM p = 0.880, effusion p = 0.362). However, in the oxygen–ozone-receiving group, joint effusion was decreased significantly (p < 0.001). Both steroid and oxygen–ozone injections are effective in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Our study showed that the effects of oxygen–ozone injection last longer than those of steroid injection to the knee joint.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hawamdeh ZM, Al-Ajlouni JM (2013) The clinical pattern of knee osteoarthritis in Jordan: a hospital based study. Int J Med Sci 10(6):790. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.5140
Gupta S, Hawker G, Laporte A, Croxford R, Coyte P (2005) The economic burden of disabling hip and knee osteoarthritis (OA) from the perspective of individuals living with this condition. Rheumatology 44(12):1531–1537. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kei049
Li Y, Wei X, Zhou J, Wei L (2013) The age-related changes in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/916530
Samson DJ, Grant MD, Ratko TA, Bonnell CJ, Ziegler KM, Aronson N (2007) Treatment of primary and secondary osteoarthritis of the knee. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep) 157(157):1–157
Peat G, McCarney R, Croft P (2001) Knee pain and osteoarthritis in older adults: a review of community burden and current use of primary health care. Ann Rheum Dis 60(2):91–97. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.60.2.91
Felson DT (2005) The sources of pain in knee osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 17(5):624–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2013.02.546
Shengelia R, Parker SJ, Ballin M, George T, Reid MC (2013) Complementary therapies for osteoarthritis: are they effective? Pain Manag Nurs 14(4):e274–e288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmn.2012.01.001
Buckwalter JA, Stanish WD, Rosier RN, Schenck Jr RC, Dennis DA, Coutts RD (2001) The increasing need for nonoperative treatment of patients with osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 385:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200104000-00008
Braun HJ, Wilcox-Fogel N, Kim HJ, Pouliot MA, Harris AH, Dragoo JL (2012) The effect of local anesthetic and corticosteroid combinations on chondrocyte viability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(9):1689–1695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-011-1728-1
Matzkin EG, Curry EJ, Kong Q, Rogers MJ, Henry M, Smith EL (2017) Efficacy and treatment response of intra-articular corticosteroid injections in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. JAAOS—J Am Acad Orthop Surg 25(10):703–714. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-16-00541
Desai A, Ramankutty S, Board T, Raut V (2009) Does intraarticular steroid infiltration increase the rate of infection in subsequent total knee replacements? Knee 16(4):262–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2008.12.002
Jones AC, Pattrick M, Doherty S, Doherty M (1995) Intra-articular hyaluronic acid compared to intra-articular triamcinolone hexacetonide in inflammatory knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 3(4):269–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1063-4584(05)80018-4
Al-Jaziri AA, Mahmoodi SM (2008) Painkilling effect of ozone-oxygen injection on spine and joint osteoarthritis. Saudi Med J 29(4):553–557
Mishra SK, Pramanik R, Das P, Das PP, Palit AK, Roy J et al (2011) Role of intra-articular ozone in osteo-arthritis of knee for functional and symptomatic improvement. Ind J Phys Med Rehabil 22(2):65–69
Andreula CF, Simonetti L, De Santis F, Agati R, Ricci R, Leonardi M (2003) Minimally invasive oxygen-ozone therapy for lumbar disk herniation. Am J Neuroradiol 24(5):996–1000
Bonetti M, Fontana A, Martinelli F, Andreula C.(2011) Oxygen–ozone therapy for degenerative spine disease in the elderly: a prospective study. Advances in minimally invasive surgery and therapy for spine and nerves: Springer p. 137–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-211-99370-5_21
Apuzzo D, Giotti C, Pasqualetti P, Ferrazza P, Soldati P, Zucco GM (2014) An observational retrospective/horizontal study to compare oxygen-ozone therapy and/or global postural re-education in complicated chronic low back pain. Funct Neurol 29(1):31. https://doi.org/10.11138/FNeur/2014.29.1.031
Bianchi S, Zamorani MP. (2007)US-guided interventional procedures. Ultrasound of the musculoskeletal system. Springer; :891–917. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28163-4_18
Eftekhar-Sadat B, Niknejad-Hosseyni SH, Babaei-Ghazani A, Toopchizadeh V, Sadeghi H (2015) Reliability and validity of Persian version of Western Ontario and McMaster universities osteoarthritis index in knee osteoarthritis. J Anal Res Clin Med 3:170–177. https://doi.org/10.15171/jarcm.2015.027
Eftekharsadat B, Babaei-Ghazani A, Habibzadeh A, Kolahi B (2015) Efficacy of action potential simulation and interferential therapy in the rehabilitation of patients with knee osteoarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskel Dis 7(3):67–75. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759720X15575724
Hochberg MC, Altman RD, April KT, Benkhalti M, Guyatt G, McGowan J, Towheed T, Welch V, Wells G, Tugwell P, American College of Rheumatology (2012) American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64(4):465–474. Review. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.21596
Hashemi M, Jalili P, Mennati S, Koosha A, Rohanifar R, Madadi F, Razavi SS, Taheri F (2015) The effects of prolotherapy with hypertonic dextrose versus prolozone (intraarticular ozone) in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine 5(5):e27585. https://doi.org/10.5812/aapm.27585
Giombini A, Menotti F, Di Cesare A, Giovannangeli F, Rizzo M, Moffa S et al (2016) Comparison between intrarticular injection of hyaluronic acid, oxygen ozone, and the combination of both in the treatment of knee osteoarthrosis. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 30(2):621–625. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179185
Duymus TM, Mutlu S, Dernek B, Komur B, Aydogmus S, Kesiktas FN (2017) Choice of intra-articular injection in treatment of knee osteoarthritis: platelet-rich plasma, hyaluronic acid or ozone options. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25(2):485–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4110-5
Raeissadat SA, Rayegani SM, Forogh B, Hassan Abadi P, Moridnia M, Rahimi Dehgolan S (2018) Intra-articular ozone or hyaluronic acid injection: which one is superior in patients with knee osteoarthritis? A 6-month randomized clinical trial. J Pain Res 11:111–117. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S142755
Giurazza F, Guarnieri G, Murphy KJ, Muto M (2017) Intradiscal O2O3: rationale, injection technique, short- and long-term outcomes for the treatment of low back pain due to disc herniation. Can Assoc Radiol J 68(2):171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carj.2016.12.007
Jüni P, Hari R, Rutjes AW, Fischer R, Silletta MG, Reichenbach S et al (2015) Intra-articular corticosteroid for knee osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (10). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005328.pub3
Maricar N, Parkes MJ, Callaghan MJ, Hutchinson CE, Gait AD, Hodgson R, Felson DT, O’Neill TW (2017) Structural predictors of response to intra-articular steroid injection in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 19(1):88. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-017-1292-2
Faúndez J, Cotoras P, Irarrázaval S (2016) Are intraarticular steroids effective for knee osteoarthritis? Medwave 16(Suppl5):e6599. https://doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2016.6599
Fatimah N, Salim B, Nasim A (2016) Predictors of response to intra-articular steroid injections in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee joint. Clin Rheumatol 35(10):2541–2547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3365-z
Lemont H, Ammirati KM, Usen N (2003) Plantar fasciitis: a degenerative process (fasciosis) without inflammation. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 93(3):234–237. https://doi.org/10.7547/87507315-93-3-234
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by the Vice-chancellor for Research, IUMS (Iran University of Medical Sciences), Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babaei-Ghazani, A., Najarzadeh, S., Mansoori, K. et al. The effects of ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection compared to oxygen–ozone (O2–O3) injection in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rheumatol 37, 2517–2527 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4147-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4147-6