Abstract
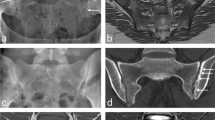
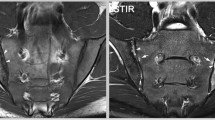
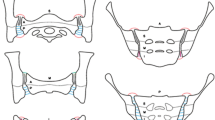
Plain radiography remains the benchmark for diagnostic evaluation of spondyloarthritis although MRI has much great sensitivity because it can detect a variety of inflammatory lesions as well as fat metaplasia. So, it is the imaging modality of choice when pelvic radiographs are equivocal and especially when important treatment decisions have to be made. Appropriate imaging includes the use of T1-weighted and short tau inversion recovery sequences of the sacroiliac joint in the tilted coronal plane. If there is localized spinal symptomatology, sagittal scans of the spine may also be helpful. However, routine spinal imaging is not recommended. Current consensus designates a positive MRI for classification purposes as requiring the presence of two definite subchondral inflammatory lesions on a single coronal slice or the presence of one such lesion on two consecutive coronal slices. However, such inflammatory lesions can occur in healthy individuals and in those with nonspecific back pain. Erosions are more specific, and their presence can enhance confidence in the diagnosis. MRI, together with CRP, can be helpful in selecting which patients without radiographic sacroiliitis are most likely to respond to tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapy. The role of MRI in monitoring of patients with SpA remains unclear although it may be helpful in excluding other sources of back pain. A major unanswered question is whether MRI may be useful in predicting relapse following withdrawal of TNFi in patients who have achieved sustained remission.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ryan LM, Carrera GF, Lightfoot RW Jr, Hoffman RG, Kozin F (1983) The radiographic diagnosis of sacroiliitis: a comparison of different views with computed tomograms of the sacroiliac joint. Arthritis Rheumatism 26:760–3
Mandl P, Navarro-Compán V, Terslev L, Aegerter P, van der Heijde D, D’Agostino MA, et al (2015) EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in the diagnosis and management of spondyloarthritis in clinical practice. Ann Rheum Dis 74(7):1327–39
Madsen KB, Egund N, Jurik AG (2010) Grading of inflammatory disease activity in the sacroiliac joints with magnetic resonance imaging: comparison between short-tau inversion recovery and gadolinium contrast-enhanced sequences. J Rheumatol 37:393–400
De Hooge M, van den Berg R, Navarro-Compan V, van Gaalen F, van der Heijde D, Huizinga T et al (2013) Magnetic resonance imaging of the sacroiliac joints in the early detection of spondyloarthritis: no added value of gadolinium compared with short tau inversion recovery sequence. Rheumatology 52:1220–4
Weiss PF, Xiao R, Biko DM, Johnson AM, Chauvin NA (2015) Detection of inflammatory sacroiliitis in children with magnetic resonance imaging: is gadolinium-contrast enhancement necessary? Arthritis Rheum 67:2250–6
Weber U, Maksymowych WP, Chan SM, Rufibach K, Pedersen SJ, Zhao Z et al (2015) Does evaluation of the ligamentous compartment enhance diagnostic utility of sacroiliac joint MRI in axial spondyloarthritis? Arthritis Res Ther 17:246
Weber U, Zubler V, Zhao Z, Lambert RG, Chan SM, Pedersen SJ et al (2015) Does spinal MRI add incremental diagnostic value to MRI of the sacroiliac joints alone in non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis? Ann Rheum Dis 74:985–92
Blachier M, Coutanceau B, Dougados M, Saraux A, Bastuji-Garin S, Ferkal S et al (2013) Does the site of magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities match the site of recent-onset inflammatory back pain? The DESIR cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 72:979–85
Rennie WJ, Dhillon SS, Conner-Spady B, Maksymowych WP, Lambert RGW (2009) MRI assessment of spinal inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis: standard clinical protocols may omit inflammatory lesions in thoracic vertebrae. Arthritis Rheum 61:1187–1193
Bollow M, Hermann KG, Biedermann T, Sieper J, Schontube M, Braun J (2005) Very early spondyloarthritis: where the inflammation in the sacroiliac joints starts. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1644–6
Maksymowych WP (2012) MRI and x-ray in axial spondyloarthritis: the relationship between inflammatory and structural changes. Arthritis Res Ther 14:207
Weber U, Pedersen SJ, Zubler V, Rufibach K, Chan SM, Lambert RG et al (2014) Fat infiltration on magnetic resonance imaging of the sacroiliac joints has limited diagnostic utility in nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. J Rheumatol 41:75–83
Weber U, Pedersen SJ, Ostergaard M, Rufibach K, Lambert R, Maksymowych WP (2012) Can erosions on MRI of the sacroiliac joints be reliably detected in patients with ankylosing spondylitis? A cross-sectional study. Arthritis Res Ther 14:R124
Pedersen SJ, Wichuk S, Chiowchanwisawakit P, Lambert RG, Maksymowych WP (2014) Tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapy but not standard therapy is associated with resolution of erosion in the sacroiliac joints of patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 16:R100
Maksymowych WP, Wichuk S, Chiowchanwisawakit P, Lambert RG, Pedersen SJ (2014) Fat metaplasia and backfill are key intermediaries in the development of sacroiliac joint ankylosis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 66:2958–67
Weber U, Lambert RG, Ostergaard M, Hodler J, Pedersen SJ, Maksymowych WP (2010) The diagnostic utility of MRI in spondyloarthritis: an international multicentre evaluation of 187 subjects (The MORPHO study). Arthritis Rheum 62:3048–58
Weber U, Ostergaard M, Lambert RG, Pedersen SJ, Chan SM, Zubler V et al (2015) Candidate lesion-based criteria for defining a positive sacroiliac joint MRI in two cohorts of patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 74(1976–82):2015
Rudwaleit M, Jurik AG, Hermann KGA, Landewé R, van der Heijde D, Baraliakos X et al (2009) Defining active sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: a consensual approach by the ASAS/OMERACT MRI Group. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1520–7
Lambert RGW, Bakker PAC, van der Heijde D, Weber U, Rudwaleit R, Hermann K-GA, et al (2016) Defining active sacroiliitis on MRI for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: update by the ASAS MRI working group. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208642
Gong Y, Zheng N, Chen SB, Xiao ZY, Wu MY, Liu Y et al (2012) Ten years’ experience with needle biopsy in the early diagnosis of sacroiliitis. Arthritis Rheum 64:1399–406
Bennett AN, McGonagle D, O’Connor P, Hensor EM, Sivera F, Coates LC et al (2008) Severity of baseline magnetic resonance imaging-evident sacroiliitis and HLA-B27 status in early inflammatory back pain predict radiographically evident ankylosing spondylitis at eight years. Arthritis Rheum 58:3413–8
Braun J, Landewe R, Hermann K-GA, Han J, Yan S, Williamson P et al (2006) Major reduction in spinal inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after treatment with infliximab. Arthritis Rheum 54:1646–1652
Lambert RGW, Salonen D, Rahman P, Inman RD, Wong RL, Einstein SG et al (2007) Adalimumab significantly reduces both spinal and sacroiliac joint inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 56:4005–14
van den Berg R, de Hooge M, Bakker PAC, van Gaalen F, Navarro-Compan V, Fagerli KM et al (2015) Metric Properties of the SPARCC Score of the Sacroiliac Joints - Data from Baseline, 3-month, and 12-month Followup in the SPACE Cohort. J Rheumatol 42:1186–93
Jarrett SJ, Sivera F, Cawkwell LS, Marzo-Ortega H, McGonagle D, Hensor E et al (2009) MRI and clinical findings in patients with ankylosing spondylitis eligible for anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy after a short course of etoricoxib. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1466–9 [Erratum appears in Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70: 1519]
Arkas G, Jans L, Cypers H, Van Praet L, Carron P, Elewaut D et al (2016) Arthritis Rheum 68:672–8
de Bruin F, ter Horst S, Bloem HL, van den Berg R, de Hooge M, van Gaalen F et al (2015) Prevalence of degenerative changes of the spine on magnetic resonance images and radiographs in patients aged 16–45 years with chronic back pain of short duration in the Spondyloarthritis Caught Early (SPACE) cohort. Rheumatology 55:56–65
Hermann KGA, Baraliakos X, van der Heijde DMFM, Jurik AG, Landewe R, Marzo-Ortega H et al (2012) Descriptions of spinal MRI lesions and definition of a positive MRI of the spine in axial spondyloarthritis: a consensual approach by the ASAS/OMERACT MRI study group. Ann Rheum Dis 71:1278–88
Bennett AN, Rehman A, Hensor EMA, Marzo-Ortega H, Emery P, McGonagle D (2009) Evaluation of the diagnostic utility of spinal magnetic resonance imaging in axial spondylarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 60:1331–41 [Erratum appears in Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Oct;62(10):3005]
Weber U, Zhao ZS, Rufiback K, Zubler V, Lambert R, Chan SM et al (2015) Diagnostic Utility of Candidate Definitions for Demonstrating Axial Spondyloarthritis on Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Spine. Arthritis Rheum 67:924–933
Vastesaeger N, van der Heijde D, Inman RD, Wang Y, Deodhar A, Hsu B et al (2011) Predicting the outcome of ankylosing spondylitis therapy [published erratum appears in Ann Rheum Dis 2012; 71: 1434]. Ann Rheum Dis 70:973–81
Rudwaleit M, Claudepierre P, Wordsworth P, Cortina EL, Sieper J, Kron M et al (2009) Effectiveness, safety and predictors of good clinical response in 1250 patients treated with adalimumab for active ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 36:801–8
Molto A, Paternotte S, Claudepierre P, Breban M, Dougados M (2014) Effectiveness of tumor necrosis factor alpha blockers in early axial spondyloarthritis: data from the DESIR cohort. Arthritis Rheum 66:1734–44
Sieper J, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, Mease PJ, Maksymowych WP, Brown MA et al (2013) Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: results of a randomised placebo-controlled trial (ABILITY-1). Ann Rheum Dis 72:815–22
Dougados M, van der Heijde D, Sieper J, Braun J, Maksymowych WP, Citera G et al (2014) Symptomatic efficacy of etanercept and its effects on objective signs of inflammation in early non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 66(1):2091–102
Sieper J, van der Heijde D, Dougados M, Maksymowych WP, Scott BB, Boice JA et al (2015) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, sixteen-week study of subcutaneous golimumab in patients with active nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 67:2702–12
Landewe R, Braun J, Deodhar A, Dougados M, Maksymowych WP, Mease PJ et al (2014) Efficacy of certolizumab pegol on signs and symptoms of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis: 24-week results of a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled Phase 3 study. Ann Rheum Dis 73(1):39–47
Maksymowych WP, Dhillon SS, Park R, Salonen D, Inman RD, Lambert RGW (2007) Validation of the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) MRI Spinal Inflammation Index: is it necessary to score the entire spine? Arthritis Rheum 57:501–7
Machado P, Landewe RBM, Braun J, Baraliakos X, Hermann KGA, Hsu B et al (2012) MRI inflammation and its relation with measures of clinical disease activity and different treatment responses in patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor. Ann Rheum Dis 71:2002–5
Weis A, Song I, Haibel H, Listing J, Sieper J (2014) Good correlation between changes in objective and subjective signs of inflammation in patients with short- but not long duration of axial spondyloarthritis treated with tumor necrosis factor-blockers. Arthritis Res Ther 16(R35):2014
Nguyen C, Bendeddouche I, Sanchez K, Jousse M, Papelard A, Feydy A et al (2010) Assessment of ankylosing spondylitis criteria in patients with chronic low back pain and vertebral endplate Modic I signal changes. J Rheumatol 37:2334–2339
Maksymowych WP, Wichuk S, Jones H, Szumski A, Marshall L, Bukowski J et al (2015) Ankylosing spondylitis disease activity score more closely reflects MRI parameters of sacroiliitis than the bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis. J Rheumatol 42:7 (abstract)
Maksymowych WP, Østergaard M, Chiowchanwisawakit P, Pedersen SJ, Lambert RGW (2009) Atlas of magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in the spine in spondyloarthritis: definitions, reliability, training, and conceptual framework. Introduction: a report from the Canada (SPARCC)-Denmark International Spondyloarthritis Working Group. J Rheumatol 36(suppl 84):1–2
Lambert RGW, Pedersen SJ, Maksymowych WP, Chiowchanwisawakit P, Østergaard M (2009) Active inflammatory lesions detected by magnetic resonance imaging in the spine of patients with spondyloarthritis – definitions, assessment system, and reference image set. J Rheumatol 36(suppl 84):3–17
Østergaard M, Maksymowych WP, Pedersen SJ, Chiowchanwisawakit P, Lambert RGW (2009) Structural lesions detected by magnetic resonance imaging in the spine of patients with spondyloarthritis – definitions, assessment system, and reference image set. J Rheumatol 36(suppl 84):18–34
Pedersen SJ, Østergaard M, Chiowchanwisawakit P, Lambert RGW, Maksymowych WP (2009) Validation of definitions for active inflammatory lesions detected by magnetic resonance imaging in the spine of patients with spondyloarthritis. J Rheumatol 36(suppl 84):35–38
Chiowchanwisawakit P, Østergaard M, Pedersen SJ, Lambert RGW, Conner-Spady B, Maksymowych WP (2009) Validation of definitions for structural lesions detected by magnetic resonance imaging in the spine of patients with spondyloarthritis. J Rheumatol 36(suppl 84):39–47
Maksymowych WP, Dhillon SS, Chiowchanwisawakit P, Pedersen SJ, Martinez B, Østergaard M et al (2009) Development and validation of web-based training modules for systematic evaluation of active inflammatory lesions in the spine and sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis. J Rheumatol 36(suppl 84):48–57
Mandl P, Navarro-Compán V, Terslev L, Aegerter P, van der Heijde D, D’Agostino MA et al (2015) EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in the diagnosis and management of spondyloarthritis in clinical practice. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1327–39
Sudol-Szopinska I, Jurik AG, Eshed I, Lennart J, Grainger A, Ostergaard M et al (2015) Recommendations of the ESSR arthritis subcommittee for the use of magnetic resonance imaging in musculoskeletal rheumatic diseases. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 19:396–411
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maksymowych, W.P. The role of MRI in the evaluation of spondyloarthritis: a clinician’s guide. Clin Rheumatol 35, 1447–1455 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3265-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3265-2