Abstract
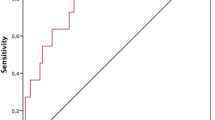
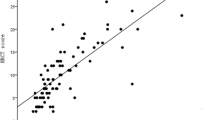
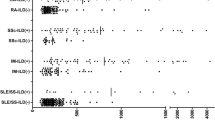
It was aimed to evaluate KL-6 glycoprotein levels to determine if it may be a diagnostic marker for the connective tissue diseases (CTDs) predicting CTD-related interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) (CTD-ILD) development and to examine if there was a difference between patients and healthy controls. The study included 113 patients with CTD (45 CTD without lung involvement, 68 CTD-ILD) and 45 healthy control subjects. KL-6 glycoprotein levels were analyzed with ELISA in patients and the control group. The relationship between KL-6 glycoprotein levels and CTD-ILD was assessed. In the comparison of all the groups in the study, significantly higher levels of KL-6 were determined in the CTD-ILD group than in either the CTD without pulmonary involvement group or the healthy control group (p < 0.008 and p < 0.001, respectively). There was no statistically significant difference between the KL-6 levels in the healthy control group and the CTD without pulmonary involvement group (p = 0.289). The KL-6 levels did not differ significantly according to the connective tissue diseases in the diagnostic groups (systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, mixed connective tissue disease, scleroderma, polymyositis/ dermatomyositis). In the healthy control group, there was a statistically significant difference between KL-6 levels in smokers and non-smokers. Smokers had significantly higher serum KL-6 levels compared with non-smokers (p < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference between smoking status (pack-year) and serum KL-6 levels. There was no statistically significant correlation between serum KL-6 levels and time since diagnosis of CTD and CTD-ILD. The level of KL-6 as a predictive factor could be used to identify the clinical development of ILD before it is detected on imaging modality. Further prospective clinical studies are needed to define whether levels of KL-6 might have prognostic value or might predict progressive ILD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olson AL, Brown KK, Fischer A (2012) Connective tissue disease-associated lung disease. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 32:513–536
Fischer A, Chartrand S (2015) Assessment and management of connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 22(32):2–21
Kohno N (1999) (1999) Serum marker KL-6/MUC1 for the diagnosis and management of interstitial pneumonitis. J Med Invest 46:151–158
Hu Y, Wang LS, Jin YP, et al. (2015) Serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 level as a diagnostic biomarker for interstitial lung disease in Chinese patients. Clin Respir J. doi: 10.1111/crj.12341. [Epub ahead of print]
Ishikawa N, Hattori N, Yokoyama A et al (2012) Utility of KL-6/MUC1 in the clinical management of interstitial lung diseases. Respir Inverstig 50:3–13
Bonella F, Costabel U (2014) Biomarkers in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 35:181–200
Kobayashi J, Kitamura S (1995) KL-6: a serum marker for interstitial pneumonia. Chest 108:311–315
Kobayashi J, Kitamura S (1996) Serum KL-6 for the evaluation of active pneumonitis in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest 109:1276–82
Yanaba K, Hasegawa M, Hamaguchi Y et al (2003) Longitudinal analysis of serum KL-6 levels in patients with systemic sclerosis: association with the activity of pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 21:429–436
Doishita S, Inokuma S, Asashima H et al (2011) Serum KL-6 level as an indicator of active or inactive interstitial pneumonitis associated with connective tissue diseases. Intern Med 50:2889–2892
Ohnishi H, Yokoyama A, Kondo K et al (2002) Comparative study of KL-6, surfactant protein-A, surfactant protein-D, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 as serum markers for interstitial lung diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:378–381
Yamane K, Ihn H, Kubo M et al (2000) Serum levels of KL-6 as a useful marker for evaluating pulmonary fibrosis in patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 27:930–934
Bonella F, Volpe A, Caramaschi P et al (2011) Surfactant protein D and KL-6 serum levels in systemic sclerosis: correlation with lung and systemic involvement. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 28:27–33
Ohshimo S, Yokoyama A, Hattori N et al (2005) KL-6, a human MUC1 mucin, promotes proliferation and survival of lung fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338:1845–1852
Ishikawa N, Mazur W, Toljamo T et al (2011) Ageing and long term smoking affects KL-6 levels in the lung, induced sputum and plasma. BMC Pulm Med 11:22
Ashida T, Higashishiba M, Sumimoto Y et al (2001) Serum KL-6 levels in patients with pulmonary complications after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Int J Hematol 74:464–468
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oguz, E.O., Kucuksahin, O., Turgay, M. et al. Association of serum KL-6 levels with interstitial lung disease in patients with connective tissue disease: a cross-sectional study. Clin Rheumatol 35, 663–666 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3167-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3167-8