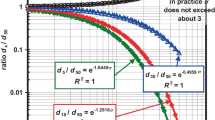
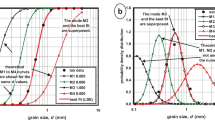
Abstract
Many models are available to fit the curve of a grain size distribution, GSD. The article lists 61 models and 33 comparative studies of models. Examples explain how to extract stratification data from split-spoon samples and how to verify whether a model respects the internal structure of the data. This extraction is essential to determine the field hydraulic properties and in situ behavior of soils. Many tools are available to assess the goodness-of-fit, GOF. This article proves that these tools are not independent. A first new equation is obtained, which links the RMSE (root mean squared error) and (1-R2), R2 being the coefficient of determination. A second new equation is obtained, which links the AIC (Akaike information criterion) and (1-R2) for a GSD. The two novel equations help to derive a new method to assess the GOF for GSDs. The distributions of (1-R2) values clearly classify fitting models as poor, fair, good, or very good. The author’s MDM (modal decomposition method) is the only one to rank very good for any soil. Its basic assumption is verified by individual sublayers, which provide a sound basis. Its explanations are correct for in situ permeability in stratified soils. Most models do not pay attention to the data’s internal structure and distribution of residuals. The MDM respects the internal structure and yields Gaussian residuals for a GSD, which may not be the case of other models. Clear graphs illustrate underfitting and overfitting, and clear rules are given to explain how to use the MDM and extract useful information from a GSD. Free pre-programmed Excel files are made available to readers.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used in this article were either provided in Tables for examples, or are the data that can be found in the cited references.
References
Afrasiabi F, Khodaverdiloo H, Asadzadeh F, van Genuchten MT (2019) Comparison of alternative soil particle-size distribution models and their correlation with soil physical attributes. J Hydrol Hydromech 67(2):179–190. https://doi.org/10.2478/johh-2018-0009
Akaike H (1973) Information theory and an extension of maximum likelihood principle. In: Petrov BN, Csàki F (eds) 2nd Int symp information theory. Akademia Kiado, Budapest, pp 267–281
Akaike H (1974) New look at statistical-model identification. IEEE Trans Automatic Control AC-9(6):716–723. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705
Almiron M, Lopes GB, Oliveira ALC, Medeiros AC, Frery AC (2010) On the numerical accu-racy of spreadsheets. J Stat Softw 34(4):1–29
Arya LM, Paris JF (1981) A physicoempirical model to predict the soil moisture characteristic from particle-size distribution and bulk density data. Soil Sci Soc Am J 45(6):1023–1030. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1981.0361599500450060004x
Ashley GM (1978) Interpretation of polymodal sediments. J. Geology 86(4):411–421. https://doi.org/10.1086/649710
Assouline S, Tessier D, Bruand A (1998) A conceptual model of the soil water retention curve. Water Res Res 34(2):223–231. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR03039
ASTM D6913/D6913M-17 (2017) Standard test methods for particle size distribution (gradation) of soils using sieve analysis. West Conshohocken, PA. https://doi.org/10.1520/D6913-17
ASTM D7928–17 (2017) Standard test method for particle-size distribution (gradation) of fine-grained soils using the sedimentation (hydrometer) analysis. West Conshohocken, PA. https://doi.org/10.1520/D7928-17
ASTM E2651 (2019) Standard Guide for powder particle Size Analysis. West Conshohocken, PA. https://doi.org/10.1520/E2651-19
Aubertin M, Bussière B, Chapuis RP (1996) Hydraulic conductivity of homogenized tailings from hard rock mines. Can Geotech J 33(3):470–482. https://doi.org/10.1139/t96-068
Bader H (1970) The hyperbolic distribution of particle sizes. J Geophy Res 75(15):2822–2830. https://doi.org/10.1029/JC075i015p02822
Bagarello V, Provenzano G, Sgroi A (2009) Fitting particle size distribution models to data from Burundian soils for the BEST procedure and other purposes. Biosystems Engng 104(3):435–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2009.07.008
Bagnold RA (1954) The physics of blown sand and desert dunes. Methuen, London
Bagnold RA, Barndorff-Nielsen O (1980) The pattern of nature size distributions. Sedimentology 27(21):199–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.1980.tb01170.x
Bah AR, Kravchuk O, Kirchhof G (2009) Fitting performance of particle–size distribution models on data derived by conventional and laser–diffraction techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73(4):1101–1107. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2007.0433
Baptiste N, Chapuis RP (2015) What maximum permeability can be measured with a monitoring Well? Eng Geol 184:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.11.006
Barndorff-Nielsen O (1977) Exponentially decreasing distributions for the logarithm of particle size. Proc Royal Society A353(1674):401–419. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1977.0041
Bayat H, Rastgou M, Zadeh MM, Vereecken H (2015) Particle size distribution models, their characteristics and fitting capability. J Hydrology 529:872–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.08.067
Bayat H, Rastgou M, Nemes A, Mansourizadeh M, Zamani P (2017) Mathematical models for soil particle-size distribution and their overall and fraction-wise fitting to measurements. Eur J Soil Science 68:345–364. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12423
Bennett JG (1936) Broken coal. J Institute Fuel 10(49):22–39
Bird N, Perrier E, Rieu M (2000) The water retention function for a model of soil structure with pore and solid fractal distributions. Eur J Soil Science 51(1):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.2000.00278.x
Birmili W, Wiedensohler A, Heintzenberg J, Lehmann K (2001) Atmospheric particle number size distribution in Central Europe: statistical relations to air masses and meteorology. J Geophys Res 106(D23):32005–32018. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD000220
Bittelli M, Campbell GS, Flury M (1999) Characterization of particle-size distribution in soils with a fragmentation model. Soil Sci Soc Am J 63(4):782–788. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1999.634782x
Botula YD, Cornelis WM, Baert G, Mafuka P, van Ranst E (2013) Particle size distribution models for soils of the humid tropics. J Soils Sediments 13(4l):686–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-012-0635-5
Buchan GD (1989) Applicability of the simple lognormal model to particle-size distribution in soils. Soil Sci 147(3):155–161. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-198903000-00001
Buchan GD, Grewal KS, Robson AB (1993) Improved models of particle-size distribution: an illustration of model comparison techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57(4):901–908. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1993.03615995005700040004x
Caputo F, Vogel R, Savage J, Vella G, Law A, Della Camera G, Hannon G, Peacock B, Mehn D, Ponti J, Geiss O, Aubert D, Prina-Mello A, Calzolai L (2021) Measuring particle size distribution and mass concentration of nanoplastics and microplastics: Addressing some analytical challenges in the sub-micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 588:401–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.12.039
Chapuis RP (1995) Controlling the quality of ground water parameters: some examples. Can Geotech J 36(1):39–51. https://doi.org/10.1139/t95-014
Chapuis RP (1999) Borehole variable-head permeability tests in compacted clay liners and covers. Can Geotech J 32(1):172–177. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-36-1-39
Chapuis RP (2004a) Predicting the saturated hydraulic conductivity of sand and gravel using effecttive diameter and void ratio. Can Geotech J 41(5):787–795. https://doi.org/10.1139/T04-022
Chapuis RP (2004b) Permeability tests in rigid-wall permeameters: determining the degree of saturation, its evolution, and its influence on test results. Geotech Test J 27(3):304–313. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ10905
Chapuis RP (2010) Class Action—Residents of Shannon—Expert Report on Groundwater Conditions (in French), for FARC, Justice Quebec, p 156
Chapuis RP (2012a) Predicting the saturated hydraulic conductivity of soils: a review. Bull Eng Geol Environ 71(3):401–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-012-0418-7
Chapuis RP (2012b) Estimating the in situ porosity of sandy soils sampled in boreholes. Eng Geol 141–142:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.04.015
Chapuis RP (2013a) Permeability scale effects in sandy aquifers: a few case studies. In: Delage P, Desrues J, Frank R, Puech A, Schlosser F (eds) Challenges and innovations in geotechnics: Proc 18th Int Conf on Soil Mech and Geotech Eng, Paris, vol 1. Presses des Ponts. Paris, pp 507–510
Chapuis RP (2013b) Full-scale evaluation of the performance of three compacted clay liners. Geotech Test J 36(4):575–583. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20120198
Chapuis RP (2015) Overdamped slug tests in aquifers: the three diagnostic graphs for a user-independent interpretation. Geotech Test J 38(4):474–489. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20140250
Chapuis RP (2016) Extracting information from grain size distribution curves. Geotics Editions. Montreal, p 197
Chapuis RP (2019a) Tracer tests in stratified alluvial aquifers: predictions of effective porosity and longitudinal dispersivity versus field values. Geotech Test J 42(2):407–432. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20170344
Chapuis RP (2019b) Disagreeing evaluations for slug tests in monitoring wells: importance of standards. Geotech Test J 42(5):1246–1273. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20160046
Chapuis RP (2020) Modal decomposition method (MDM) for a grain size distribution (GSD). Scholars Portal Dataverse. https://doi.org/10.5683/SP2/0DPZT1
Chapuis RP (2021a) Analyzing grain size distributions with the modal decomposition method: literature review and procedures. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80(9):6649–6666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02328-w
Chapuis RP (2021b) Analyzing grain size distributions with the modal decomposition method: potential for future research in engineering geology. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80(9):6667–6676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02341-z
Chapuis RP (2021c) Evaluating at three scales the hydraulic conductivity in an unconfined and stratified alluvial aquifer. Geotech Test J 44(4):948–970. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20180170
Chapuis RP (2022) The physical reasons to have underdamped or oscillating variable-head (slug) tests: a review and a clarification. Geotech Test J 45(1):244–279. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20210065
Chapuis RP (2023a) How to correctly interpret strange data for field permeability (slug) tests in monitoring wells or between packers. Geotech Test J 46(1):132–152. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20220017
Chapuis RP (2023b) Recent and new information from the slug test data of Ferris and Knowles (1954). Geotech Test J 46(4): in print. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20220167
Chapuis RP (2023c) Specific storage or elastic modulus of solid matrix in aquifers and aquitards – Results from slug tests: A review and a clarification. Geotech Test J 4x(x): in print. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20230383
Chapuis RP, Légaré PP (1992) A simple method for determining the surface area of fine aggregates and fillers in bituminous mixtures. ASTM STP 1147, Meininger RC, Ed, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, pp 177–186. https://doi.org/10.1520/STP24217S
Chapuis RP, Aubertin M (2003) On the use of the Kozeny-Carman equation to predict the hydraulic conductivity of soils. Can Geotech J 40(3):616–628. https://doi.org/10.1139/t03-013
Chapuis RP, Saucier A (2020) Assessing internal erosion with the modal decomposition of grain size distribution curves. Acta Geotech 15(6):1595–1605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-019-00865-z
Chapuis RP, Baass K, Davenne L (1989) Granular soils in rigid-wall permeameters: method for determining the degree of saturation. Can Geotech J 26(1):71–79. https://doi.org/10.1139/t89-008
Chapuis RP, Contant A, Baass K (1996) Migration of fines in 0–20 mm crushed base during placement, compaction, and seepage under laboratory conditions. Can Geotech J 33(1):168–176. https://doi.org/10.1139/t96-032
Chapuis RP, Dallaire V, Saucier A (2014) Getting information from modal decomposition of grain size distribution curves. Geotech Test J 37(2):282–295. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20120218
Chapuis RP, Masse I, Madinier B, Duhaime F (2015a) Water retention curves of coarse soils without organic matter: improved data for improved predictions. Geotech Test J 38(3):325–337. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20130154
Chapuis RP, Weber S, Duhaime F (2015b) Permeability tests results with packed spheres and non-plastic soils. Geotech Test J 38(6):950–964. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20140124
Chapuis RP, Gatien T, Marron JC (2020) How to improve the quality of laboratory permeability tests in rigid-wall permeameters: a review. Geotech Test J 43(4):1037–1056. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20180350
Chapuis RP, Marefat V, Zhang L (2021) Using public well databanks to improve field investiga-tions for excavations. Geotech Test J 44(6):1898–1919. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20200202
Chapuis RP, Marefat V, Zhang L (2022) Barometric fluctuations and duration of variable-head (slug) field permeability tests. Geotech Test J 45(3):530–547. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20200287
Cherevko S, Chung CH (2011) Direct electrodeposition of nanoporous gold with controlled multimodal pore size distribution. Electrochem Commun 13(1):16–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2010.11.001
Cho EJ, Holback H, Liu KC, Abouelmagd SA, Park J, Yeo Y (2013) Nanoparticle characteri-zation: state of the art, challenges, and emerging technologies. Mol Pharmac 10(6):2093–2110. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp300697h
Christiansen C, Blaesild P, Dalsgaard K (1984) Re-interpreting ‘segmented’ grain-size distributions. Geol Magazine 121(1):47–51. https://doi.org/10.1017/S001675680002793X
Colorado-Arango L, Menéndez-Aguado JM, Osorio-Correa A (2021) Particle size distribution models for metallurgical coke grinding products. Metals 11(8):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081288
Curray JR (1960) Tracing sediment masses by grain size modes. Report of the 21st Session Norden, Int Geol Congress, Copenhagen, Int Ass Sedimentology, pp 119–130
da Silva EM, Lima JEFW, Rodrigues LN, de Azevedo JA (2004) Comparação de modelos matemáticos para o traçado de curvas granulométricas. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 39(4):363–370. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2004000400010
Dallavale JM, Orr C, Blocker HG (1951) Fitting bimodal particle size distribution curves: comparison of methods. Indust Eng Chemistry 43(6):1377–1380
Danaei M, Dehghankhold M, Ataei S, Davarani FH, Javanmard R, Dokhani A, Khorasani S, Mozafari MR (2018) Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 10(2):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020057
Dietze E, Hartmann K, Diekmann B, Imker J, Lehmkuhl F, Opitz S, Stauch G, Wünnemann B, Borchers A (2012) An end-member algorithm for deciphering modern detrital processes from lake sediments of lake Donggi Cona, NE Tibetan Plateau, China. Sedim Geol 243:169–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2011.09.014
Dietze M, Schulte P, Dietze E (2022) Application of end-member modelling to grain-size data: constraints and limitations. Sedimentology 69(2):845–863. https://doi.org/10.1111/sed.12929
Ding Y, Erlebacher J (2003) Nanoporous metals with controlled multimodal pore size distribution. J Am Chem Soc 125(26):7772–7773. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja035318g
Dunbar CA, Hickey AJ (2000) Evaluation of probability density functions to approximate particle size distributions of representative pharmaceutical aerosols. J Aerosol Sci 31(7):813–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-8502(99)00557-1
Esmaeelnejad L, Siavashi F, Seyedmohammadi J, Shabanpour M (2016) The best mathematical models describing particle size distribution of soils. Model Earth Systems Environ 2(4):166–1 to 11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0220-9
Folk RL, Ward WC (1957) Brazos River Bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters. J Sedim Petrol 27(1):3–26. https://doi.org/10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Fooladmand HR, Mansuri M (2013) Comparison of two models for estimating the soil particle-size distribution curve based on soil textural data. Arch Agro Soil Sci 59(1):83–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2011.604775
Fredlund MD, Xing AQ, Huang SY (1994) Predicting the permeability function for unsaturated soils using the soil water characteristic curve. Can Geotech J 31(4):533–546. https://doi.org/10.1139/t94-062
Fredlund MD, Fredlund D, Wilson GW (2000) An equation to represent grain-size distribution. Can Geotech J 37(4):817–827. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-37-4-817
Fredlund MD, Wilson GW, Fredlund DG (2002) Use of grain-size distribution for the estimation of the soil–water characteristic curve. Can Geotech J 39(5):1103–1117. https://doi.org/10.1139/t02-049
Fylstra D, Lasdon L, Watson J, Warren A (1998) Design and use of the Microsoft Excel Solver. Interfaces 28(5):29–55. https://doi.org/10.1287/inte.28.5.29
Gimenez D, Rawls W, Pachepsky Y, Watt J (2001) Prediction of a pore distribution factor from soil textural and mechanical parameters. Soil Sci 166(2):79–88. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-200102000-00001
Gonzalez-Tello P, Camacho F, Vicaria JM, Gonzalez PA (2008) A Modified Nukiyama-Tanasawa distribution function and a Rosin-Rammler model for the particle-size-distribution analysis. Powder Technol 186(3):278–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2007.12.011
Güney M, Chapuis RP, Zagury G (2016) Lung bioaccessibility of contaminants in particulate matter of geological origin. Environ Sci Pollution Res 23(24):24422–24434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6623-3
Güney M, Bourges CMJ, Chapuis RP, Zagury G (2017) Lung bioaccessibility of As, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn in fine fraction (< 20 μm) from contaminated soils and mine tailings. Sci Total Environ 579:378–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.086
Han H, Wang PF, Li YJ, Liu RH, Tian C (2020) Effect of water supply pressure on atomization characteristics and dust-reduction efficiency of internal mixing air atomizing nozzle. Advanced Powder Technol 31(1):252–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2019.10.017
Harris C (1968) The application of size distribution equations to multi-event comminution processes. Trans Inst Mining Metallurgy London 241:343–358
van Hateren JA, Prins MA, van Balen RT (2018) On the genetically meaningful decomposition of grain-size distributions: a comparison of different end-member modelling algorithms. Sedim Geol 375(SI - Nov):49–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2017.12.003
Haverkamp RT, Parlange JY (1986) Predicting the water-retention curve from particle-size distribution: 1. Sandy soils without organic matter. Soil Sci 142:325–339. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-198612000-00001
Hazen A (1892) Some physical properties of sand and gravel, with special reference to their use in filtration, Massachusetts state board of health, 24th annual report. Massachusetts Department of Public Health, Boston, pp 539–556
Hwang SI (2004) Effect of texture on the performance of soil particle-size distribution models. Geoderma 123:363–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.03.003
Hwang SI, Powers SE (2003) Using particle-size distribution models to estimate soil hydraulic properties. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67(4):1103–1112. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2003.1103
Hwang SI, Lee KP, Lee DS, Powers SE (2002) Models for estimating soil particle-size distributions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66(4):1143–1150. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2002.1143
Inman DL (1952) Measures for describing the size distribution of sediments. J Sedim Petrol 22(3):125–145. https://doi.org/10.1306/D42694DB-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
ISO 13320 (2020) Particle size analysis - laser diffraction methods - part 1: General principles. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, p 59
Jaky J (1944) Soil mechanics. Egyetemi Nyomda, Budapest (in Hungarian)
Johnson NL (1949) Systems of frequency curves generated by methods of translation. Biometrika 36(1–2):149–176. https://doi.org/10.2307/2332539
Jones SB (2012) Grain size distribution with geomorphology on gypsum dunes in the White Sands Erg, White Sands National Monument, New Mexico. MSc thesis, University of Texas at El Paso, UMI Number: 1533231, 120 p
Kemmer G, Keller S (2010) Nonlinear least-squares data fitting in Excel spreadheets. Nat Protoc 5(2):267–281. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.182
Kok JF (2011) A scaling theory for the size distribution of emitted dust aerosols suggests climate models underestimate the size of the global dust cycle. Proc Nat Acad Science USA 108(3):1016–1021. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1014798108
Kolev B, Rousseva S, Dimitrov D (1996) Derivation of soil water capacity parameters from standard soil texture information for Bulgarian soils. Ecol Model 84(1–3):315–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3800(95)00134-4
Kolmogorov AN (1941) On the lognormal distribution of particle sizes during fragmentation (in Russian). Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 31(2):99–101
Kosugi K (1999) General model for unsaturated hydraulic conductivity for soils with lognormal pore-size distribution. Soil Sci Soc Am J 63(2):270–277. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1999.03615995006300020003x
Kravchenko A, Zhang R (1998) Estimating the soil water retention from particle-size distributions: a fractal approach. Soil Sci 163(3):171–179. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-199803000-00001
Krumbein WC (1938) Size frequency distribution of sediments and the normal phi curve. J Sedim Res 8(3):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1306/D4269008-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Kumar R, Thakur AK, Chaudhari P, Banerjee N (2022) Particle size reduction techniques of pharmaceutical compounds for the enhancement of their dissolution rate and bioavailability. J Pharmac Innov 17(2):333–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-020-09530-5
Lassabatere L, Angulo-Jaramillo R, Soria Ugalde J, Cuenca R, Braud I, Haverkamp R (2006) Beerkan estimation of soil transfer parameters through infiltration experiments – BEST. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70(2):521–532. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2005.0026
Leys J, McTainsh G, Koen T, Mooney B, Strong C (2005) Testing a statistical curve-fitting procedure for quantifying sediment populations within multi-modal particle-size distributions. Earth Surf Proc Land 30(5):579–590. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.1159
Li Y, Vanapalli SK (2022) Prediction of soil-water characteristics curves using two artificial intelligence (AI) models and AI aid design method for sands. Can Geotech J 59(1):129–143. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2020-0562
Li Y, Huang CM, Wang BL, Tian XF, Liu JJ (2017) A unified expression for grain size distribution of soils. Geoderma 288:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.11.011
Li M, Wu FW, Liu HB (2018) Estimation of soil particle size distribution - from Katchinski to USDA scheme. Adv Eng Res 120:940–946 (It has not a doi)
Li H, Li J, Bodycomb J, Patience GS (2019) Experimental methods in chemical engineering particle size distribution by laser diffraction – PSD. Can J Chem Eng 97(7):1974–1981. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.23480
Li WP, Li XX, Mei X, Zhang F, Xu JP, Liu CR, Wei CAY, Liu QS (2021) A review of current and emerging approaches for quaternary marine sediment dating. Science Total Environ 780:146522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146522
Lin YC, Mu GJ, Xu LS, Zhao X (2021) Grain size characteristics of the sand silt layers in the ancient delta of the dried Lop Nur Lake (East Tarim Basin) and their environmental implications. Arabian J Geosci 14(21):2229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08630-x
Liu Y, Sansalone JJ (2020) Physically-based particle size distribution models of urban water particulate matter. Water Air Soil Pollution 231(11):555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04925-z
Liu W, Chen WW, Bi J, Lin GC, Wu WJ, Su X (2017) Fitting performance of different models on loess particle size distribution curves. Advances Mat Sci Eng 2017:6295078. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6295078
Liu XM, Qu SZ, Chen RP, Chen S (2018) Development of a two-dimensional fractal model for analyzing the particle size distribution of geomaterials. J Materials Civil Eng 300(8):04018175. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002365
Liu Y, Liang SJ, Han ZY, Song JM, Wang QX (2018b) A novel model of calculating particle sizes in plasma rotating electrode process for superalloys. Powder Technol 336:406–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.06.002
Liu YM, Liu XX, Sun YB (2021) QGrain: An open-source and easy-to-use software for the comprehensive analysis of grain size distributions. Sedimen Geol 423:15980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2021.105980
Mandelbrot BB (1983) The Fractal Geometry of Nature. Macmillan, Freeman
McCullough BD (2008) Editorial: special section on Microsoft excel 2007. Comput Stat Data Anal 52(10):4568–4569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csda.2008.03.009
McCullough BD, Yalta AT (2013) Spreadsheets in the Cloud – Not ready yet. J Stat Softw 52(7):1–14. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v052.i07
Mélard G (2014) On the accuracy of statistical procedures in Microsoft Excel 2010. Comput Statistics 29(5):1095–1128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-014-0482-5
Melrose C (2014) Polymodal grain-size modes in Long Island sands, silts, and weathered bedrock. Master of Science, Geosciences, Stony Brook Univ, UMI Number: 1584360, 156 p
Menéndez-Aguado JM, Peña-Carpio E, Sierra C (2015) Particle size distribution fitting of surface detrital sediment using the Swebrec function. J Soils Sedim 15(9):2004–2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1156-9
Meskini-Vishkaee F, Davatgar N (2018) Evaluation of different predictor models for detailed soil particle-size distribution. Pedosphere 28(1):157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60422-3
Millan H, Gonzalez-Posada M, Aguilar M, Dominguez J, Cespedes L (2003) On the fractal scaling of soil data. Particle-Size Distributions Geoderma 117(1–2):117–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(03)00138-1
Molina-Gomez AM, Chapuis RP (2021) Internal erosion of a 0–5 mm crushed sand in a rigid wall-permeameter: experimental methods and results. Geotech Test J 44(6):1737–1753. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20190218
Nemes A, Wösten J, Lilly A, Oude Voshaar J (1999) Evaluation of different procedures to interpolate particle-size distributions to achieve compatibility within soil databases. Geoderma 90(3–4):187–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(99)00014-2
Nesbitt A, Breytenbach W (2006) A particle size distribution model for manufactured particulate solids of narrow and intermediate size ranges. Powder Technol 164:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2006.03.015
Norby RD (1981) Evaluation of Lake Michigan nearshore sediments for nourishment of Illinois beaches. — Champaign, IL. Illinois State Geol Survey, Environ Geol Notes 97 (April), 67 p
Ouchterlony F (2005) The Swebrec© function: linking fragmentation by blasting and brushing. Trans Inst Mining Metall: Section A 114(1):29–44. https://doi.org/10.1179/037178405X44539
Pang HL, Li FQ, Gao HS, Jia YX, Chen DB, Zhang XN (2022) Application of hierarchical clustering endmember modeling analysis for identification of sedimentary environment in the Houtao section of the Upper Yellow River. Water 14(7):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071025
Pasikatan MC, Milliken GA, Steele JL, Spillman CK, Haque E (2001) Modeling the size properties of first–break ground wheat. Trans ASAE 44(6):1727–1735. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.6985)@2001
Pässe T (1997) Grain size distribution expressed as tanh-functions. Sedimentology 44(6):1011–1014. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.1997.tb02175.x
Paterson GA, Heslop D (2015) New methods for unmixing sediment grain size data. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 16:4494–4506. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GC006070
Peleg M (2019) Beta distributions for particle size having a finite range and predetermined mode, mean or median. Powder Technol 356:790–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.09.015
Peng YJ, Xiao J, Nakamura T, Liu BL, Inouchi Y (2005) Holocene east Asian monsoonal precipitation pattern revealed by grain-size distribution of core sediments of Daihai Lake in Inner Mongolia of North-Central China. Earth Planet Sci Letters 233:467–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.022
Perrier E, Bird N (2002) Modelling soil fragmentation: the pore solid fractal approach. Soil Tillage Res 64(1–2):91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(01)00247-1
Perrier E, Bird N, Rieu M (1999) Generalizing the fractal model of soil structure: the pore–solid fractal approach. Geoderma 88(3–4):137–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(98)00102-5
Purkait B (2010) The use of grain-size distribution patterns to elucidate aeolian processes on a transverse dune of Thar Desert. India Earth Surf Proc Landforms 35(5):525–530. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.1939
Rao JP, Geckeler KE (2011) Polymer nanoparticles: preparation techniques and size-control parameters. Prog Polymer Sci 36(7):887–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.01.001
Rastgou M, Bayat H, Mansoorizadeh M (2021) Developing conceptual and empirical models for well- and gap-graded soil particle size distribution (PSD) curve. Arch Agro Soil Sci 67(13):1770–1782. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2020.1808626
Roman-Sanchez A, Temme A, Willgoose G, van den Berg D, Gura CM, Vanwalleghem T (2021) The fingerprints of weathering: grain size distribution changes along weathering sequences in different lithologies. Geoderma 383:114753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114753
Rosin P, Rammler E (1933) The laws governing the fineness of powdered coal. J Inst Fuel 7(July):29–36
Saygin SD, Erpul G (2019) Modeling aggregate size distribution of eroded sediment resulting from rain-splash and rain drop impacted flow processes. Int J Sedim Res 34(2):166–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2018.10.004
Schimmelmann A, Lange CB, Schieber J, Francus P, Ojala AEK, Zolitschka B (2016) Varves in marine sediments: a review. Earth Sci Rev 159(August):215–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.04.009
Schuhmann JR (1940) Principles of comminution, I-size distribution and surface calculations. Mining Technol 4(1):l–11
Shekunov BY, Chattopadhyay P, Tong HHY, Chow AHL (2007) Particle size analysis in pharmaceutics: principles, methods and applications. Pharmac Res 24(2):203–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9146-7
Shi JP, Khan AA, Harrison RM (1999) Measurements of ultrafine particle concentration and size distribution in the urban atmosphere. Science Total Environ 235(1–3):51–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00189-8
Skaggs TH, Arya LM, Shouse PJ, Mohanty BP (2001) Estimating particle-size distribution from limited soil texture data. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65(4):1038–1044. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2001.6541038x
Sklar LS, Riebe CS, Marshall JA, Genetti J, Leclere S, Lukens CL, Merces V (2017) The problem of predicting the size distribution of sediment supplied by hillslopes to rivers. Geomorphology 277:31–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.05.005
Smith L (1981) Spatial variability of flow parameters in a stratified sand. J Int Ass Math Geol 13(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01032006
Stanic F, Tchiguirinskaia I, Versini PA, Cui YJ, Delage P, Aimedieu P, Tarquis AM, Bornert M, Schertzer D (2021) A new multifractal-based grain size distribution model. Geoderma 404:115294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.115294
Stark WJ, Stoessel PR, Wohlleben W, Hafner A (2015) Industrial applications of nanoparticles. Chem Soc Reviews 44(16t):5793–5805. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00362d
Sun D, Bloemendal J, Rea DK, Vandenberghe J, Jiang F, An Z, Su R (2002) Grain-size distribution functions of polymodal sediments in hydraulic and aeolian environments, and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components. Sedim Geol 152(3–4):263–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00082-9
Swamee P, Ojha C (1991) Bed-load and suspended-load transport of nonuniform sediments. J Hydraul Eng, 117(6):774–787. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1991)
Takahashi T, Nakano K, Nira R, Kumagai E, Nishida M, Namikawa M (2020) Conversion of soil particle size distribution and tTexture classification from ISSS system to FAO/USDA system in Japanese paddy soils. Soil Sci Plant Nut 66(3):407–414. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2020.1763143
Tampieri F, Tomasi C (1976) Size distribution models of fog and cloud droplets in terms of the modified Gamma function. Tellus 28(4):333–347. https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusa.v28i4.10300
Tegen I, Lacis AA (1996) Modeling of particle size distribution and its influence on the radiative properties of mineral dust aerosol. J Geophys Res 101(D14):19237–19244. https://doi.org/10.1029/95JD03610
Teklay A, Haile M, Teferra A, Murray EJ (2014) Improved mathematical models for particle-size distribution data representation of tropical weathered residual soils. Zede J 32:1–21
Thompson J, Sattar AMA, Gharabaghi B, Warner RC (2016) Event-based total suspended sediment particle size distribution model. J Hydrol 536:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.02.056
Tian SM, Li ZW, Wang ZY, Jiang EH, Wang WL, Sun M (2021) Mineral composition and particle size distribution of river sediment and loess in the Middle and Lower Yellow River. Int J Sedim Res 36(3):392–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2020.07.008
Tong CX, Burton GJ, Zhang S, Sheng D (2018) A simple particle-size distribution model for granular materials. Can Geotech J 55(1):246–257. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2017-0098
Torre G, Gaiero DM, Cosentino NJ, Coppo R (2020) The paleoclimatic message from the polymodal grain-size distribution of late Pleistocene-early Holocene Pampean loess (Argentina). Aeolian Res 42:100563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeolia.2019.100563
Tyler SW, Wheatcraft SW (1992) Fractal scaling of soil particle-size distributions: analysis and limitations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56(2):362–369. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1992.03615995005600020005x
Udden JA (1914) Mechanical composition of clastic sediments. Bull Geol Soc Am 25(1):655–744. https://doi.org/10.1130/GSAB-25-655
Ulusoy U, Igathinathane C (2016) Particle size distribution modeling of milled coals by dynamic image analysis and mechanical sieving. Fuel Process Technol 143:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.11.007
Vandenberghe J (2013) Grain Size of Fine-Grained Windblown Sediment: A Powerful Proxy for Process Identification. Earth-Sci Rev 121(June):18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.03.001
Vandenberghe J, Sun Y, Wang X, Abels HA, Liu X (2018) Grain-size characterization of reworked fine-grained aeolian deposits. Earth-Science Review 177:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.11.005
Vaz CMP, Ferreira EJ, Durand Posadas A (2020) Evaluation of models for fitting soil particle-size distribution using UNSODA and a Brazilian dataset. Geoderma Reg 21:e00273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2020.e00273
Vipulanandan C, Ozgurel HG (2009) Simplified relationships for particle-size distribution and permeation groutability limits for soils. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 135(9):1190–1197. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000064
Visher GS (1969) Grain Size Distributions and Depositional Processes. J Sedim Res 39(3):1074–1106
Wang WP, Liu JL, Zhao BZ, Zhang JB, Li XP, Yan YF (2015) Critical evaluation of particle size distribution models using soil data obtained with a laser diffraction method. PLoS ONE 10(4):e0125048. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125048
Wang XJ, Bolan N, Tsang DCW, Sarkar B, Bradney L, Li Y (2021) A review of microplastics aggregation in aquatic environment: influence factors, analytical methods, and environmental implications. J Hazard Mat 402:123496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123496
Webster R (2001) Statistics to support soil research and their presentation. Eur J Soil Sci 52(2):331–340. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.2001.00383.x
Wei SG, Dai YJ, Garcia-Gutierrez C, Yuan H (2014) Particle-size distribution models for the conversion of Chinese data to FAO/USDA system. Scientific World J 2014(July):109310. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/109310
Weibull W (1951) A statistical distribution function of wide applicability. ASME J Appl Mech Trans Am Soc Mech Eng 18(September):293–297
Weltje GJ, Prins MA (2007) Genetically meaningful decomposition of grain-size distributions. Sedim Geol 202(3):409–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2007.03.007
Wentworth CK (1922) A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. J Geol 30(5):377–392. http://www.jstor.org/stable/30063207. Accessed 11 Aug 2023
Wu L, Krijgsman W, Liu J, Li C, Wang R, Xiao W (2020) CFLab: a MATLAB GUI program for decomposing sediment grain size distribution using Weibull functions. Sedim Geol 398:105590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2020.105590
Xiao J, Chang Z, Si B, Qin X, Itoh S, Lomtatidze Z (2009) Partitioning of the grain-size components of Dali Lake core sediments: evidence for lake-level changes during the Holocene. J Paleolimnology 42(2):249–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-008-9274-7
Yang X, Lee J, Barker DE, Wang X, Zhang Y (2012) Comparison of six particle size distribution models on the goodness-of-fit to particulate matter sampled from animal buildings. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 62(6):725–735. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2012.671148
Yong L, Chengmin H, Baoliang W, Xiafei T, Jingjing L (2017) A unified expression for grain size distribution of soils. Geoderma 288:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.11.0110016-7061
Yu AB (1994) Johnson’s SB distribution function as applied in the mathematical representation of particle size distributions. Part 1: Theoretical background and numerical simulation. Part Part Systems Charact 11(4):291–298. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.19940110404
Yuan R, Yang B, Liu YF, Huang LY (2019) Modified Gompertz sigmoidal model removing fine-ending of grain-size distribution. Open Geosci 11(1):29–36. https://doi.org/10.1515/geo-2019-0003
Zarczynski M, Szmanda J, Tylmann W (2019) Grain-size distribution and structural characteristics of varved sediments from Lake Zabinskie (Northeastern Poland). Quaternary 2(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat2010008
Zhang XN, Zhou AF, Wang X, Song M, Zhao YT, Xie HC, Russell JM, Chen FH (2018) Unmixing grain-size distributions in lake sediments: a new method of endmember modeling using hierarchical clustering. Quat Res 89(1):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1017/qua.2017.78
Zhang XD, Wang HM, Xu SM, Yang ZS, Zhang A (2020) A basic end-member model algorithm for grain-size data of marine sediments. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 236:106656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106656
Zhang S, Xu H, Lan JH, Goldsmith Y, Torfstein A, Zhang GL, Zhang J, Song YP, Zhou KE, Tan LC, Xu S, Xu XM, Enzel Y (2021) Dust storms in northern China during the last 500 years. Sci China-Earth Sci 64(5):813–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-020-9730-2
Zhao P, Shao MA, Horton R (2011) Performance of soil particle-size distribution models for describing deposited soils adjacent to constructed dams in the China loess plateau. Acta Geophys 59(1):124–138. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-010-0037-2
Zhou ZQ, Ranjith PG, Li SC (2016) Optimal model for particle size distribution of granular soil. Proc Inst Civil Eng Geotech Eng 169(1):73–82. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeen.15.00075
Zhu JG, Guo WL, Wen YF, Yin JH, Zhou C (2018) New gradation equation and applicability for particle-size distributions of various soils. Int J Geomech 18(2):04017155. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001082
Zhuang J, Jin Y, Miyazaki T (2001) Estimating water retention characteristic from soil particle-size distribution using a non-similar media concept. Soil Sci 166(5):308–321. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-200105000-00002
Zobeck TM, Gill TE, Popham TW (1999) A two-parameter Weibull function to describe airborne dust particle size distributions. Earth Surf Proc Landf 24(10):943–955. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9837(199909)24:10%3c943::AID-ESP30%3e3.0.CO;2-9
Zolitschka B, Francus P, Ojala AEK, Schimmelmann A (2015) Varves in lake sediments - a review. Quat Sci Reviews 117:1–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.03.019
Acknowledgements
The author thanks the anonymous reviewers and the Editor for their comments and suggestions.
Funding
This research was not supported by funding in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Free Excel files for the LSE (least square estimate) of the modal decomposition method (MDM) of any normalized distribution, are available from Scholars Portal Dataverse (Chapuis 2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chapuis, R.P. Fitting models for a grain size distribution: a review. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 427 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03444-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03444-5