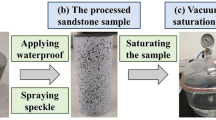
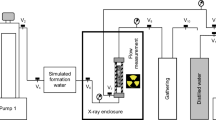
Abstract
The cyclic water intrusion and stresses lead to changes in the rock pores' microstructure, which affects the rock’s seepage characteristics. This study performs a three-dimensional reconstruction of the rock specimen using the Avizo software based on the results of multiple computed tomography (CT) tests conducted on sandstone subjected to varying numbers of cyclic water intrusions. In addition, a numerical model comprising pores and grain matrix is developed, based on which stress loading and seepage simulations are carried out. The results show that the mean outlet velocity, maximum seepage pressure, and permeability of the rock samples show an exponential increase with the number of cyclic water intrusions. Stress loading of the rock samples reveals that as the stress increases, the average exit velocity and permeability decrease. It is observed that the stress sensitivity index tends to increase and subsequently decrease with the number of water intrusion cycles at the same stress level when the stress sensitivity index is calculated under different water intrusion cycles. The relationship between effective stress, porosity, and stress sensitivity index is derived, and an effective linkage between permeability and macro-mechanical parameters considering stress sensitivity is achieved.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bustin AMM, Bustin RM (2012) Importance of rock properties on the producibility of gas shales. Int J Coal Geol 103:132–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2012.04.012
Cai PC, Que Y, Li X (2021) Numerical simulation of meso-seepage flow in undisturbed granite residual soil under confining pressure. J Fuzhou Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 49(03):400–406. https://doi.org/10.7631/issn.1000-2243.20265
Cheng YH (2021) Research on the anisotropic characteristics of gas microscopic seepage in coal pores based on X-ray μCT scanning. Mining Safety Environ Protect 48(04):12–17. https://doi.org/10.19835/j.issn.1008-4495.2021.04.003
Cui R, Feng QH, Chen HW et al (2019) Multiscale random pore network modeling of oil-water two-phase slip flow in shale matrix. J Pet Sci Eng 175:46–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.12.026
Cui X, Bustin RM (2005) Volumetric strain associated with methane desorption and its impact on coalbed gas production from deep coal seams. AAPG Bull 89(9):1181–1202. https://doi.org/10.1306/05110504114
David C, Wong TF, Zhu WL et al (1994) Laboratory measurement of compaction induced permeability change in porous rocks: implications for the generation and maintenance of pore pressure excess in the crust. Pure Appl Geophys 143(1/3):425–456. https://doi:linkspringer.53yu.com/article/, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00874337
Feng Q, Jin J, Zhang S et al (2022) Study on a damage model and uniaxial compression simulation method of frozen–thawed rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55:187–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02645-2
Huo RK, Qian MT, Li SG et al (2021) The seepage characteristics of sandstone subjected to acid corrosion. J Civil Environ Eng 1–10. https://doi.org/10.11835/j.issn.2096-6717.2020.077
Jabbari H, Zeng ZW, Ostadhassan M (2011) Impact of in-situ stress change on fracture conductivity in naturally fractured reservoirs: Bakken case study. ARMA 11–239:2011
Jiang H, Jiang A, Zhang F (2021) Experimental investigation on the evolution of damage and seepage characteristics for red sandstone under thermal–mechanical coupling conditions. Environ Earth Sci 80:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10121-x
Li CL (2006) Evaluation method for stress sensitivity of reservoir rock. Pet Geol Oilfield Develop Daqing 25(1):40–42
Liu WT, Du YH, Yu SJ et al (2021) Research on permeability and acoustic emission characteristics of karst collapsed column skeleton sandstone under triaxial compression. Chin J Rock Mechan Eng 40(08):1580–1590. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.1151
Liu Y, Wang CS, Sun QJ et al (2017) Digital core construction and seepage simulation of low permeability sandstone reservoir. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 24(06):817–821. https://doi.org/10.6056/dkyqt201706018
Lv ZX, Ji QQ, Ren WJ (2020) Experimental study and percolation analysis on seepage characteristics of fractured coal and sandstone based on real-time micro-CT. Geofluids 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8832946
Ranjith PG, Zhang CP, Zhang ZY (2019) Experimental study of fracturing behaviour in ultralow permeability formations: a comparison between CO2 and water fracturing. Eng Fract Mech 217:106541
Shen BT, Meng WH, Zhang SC et al (2021) Numerical simulation of hydro-mechanical-thermal coupling function in crack propagation of rock mass. Mining Res Develop 41(11):76–81. https://doi.org/10.13827/j.cnki.kyyk.2021.11.012
Song ZX, Zhang JW (2021) Progressive failure mechanical behaviour and response characteristics of sandstone under stress-seepage coupling. J Geophys Eng 18(2):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1093/jge/gxab008
Sun WB, Xue YC, Yin LM et al (2019) Experimental study on seepage characteristics of large size rock specimens under three-dimensional stress. Geomechan Eng 18(6):567–574. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2019.18.6.567
Yan M, Zhou M, Li SG et al (2021) Numerical investigation on the influence of micropore structure characteristics on gas seepage in coal with lattice Boltzmann method. Energy 230:120773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120773
Yang F, Wang H, Hang B et al (2019) Study on the stress sensitivity and seepage characteristics of tight sandstone based on CT scanning. J Geomechan 25(04):475–482
Yin Q, He LX, Jing HW et al (2018) Quantitative estimates of nonlinear flow characteristics of deformable rough-walled rock fractures with various lithologies. Processes 6(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6090149
Zhang PW, Hu LM, Jay NM et al (2020) Two-phase flow model based on 3D pore structure of geomaterials. Chin J Geotech Eng 42(01):37–45. https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE202001004
Zhao YX, Sun YF, Liu SM et al (2018) Pore structure characterization of coal by synchrotron radiation nano-CT. Fuel 215:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.11.014
Zhou G, Qiu L, Zhang W et al (2018) Simulation analysis on water’s micro seepage laws under different pressure gradients using computed tomography method. Adv Civil Eng 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3401341
Zhou G, Qiu L, Zhang W et al (2020a) Numerical simulation analysis of water injection seepage law in micro porous structure of coal. Tehnicki Vjesnik-Technical Gazette 27(2):458–466. https://doi.org/10.17559/TV-20180305040724
Zhou Z, Zhang J, Cai X et al (2020b) Permeability experiment of fractured rock with rough surfaces under different stress conditions. Geofluids 4342514:12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4342514
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China[Grant Number 51909149) and Shandong Key Laboratory of Civil Engineering Disaster Prevention and Mitigation[Grant Number CDPM2019ZR10].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Z., Pang, W., Mao, W. et al. Study on seepage characteristics and stress sensitivity of sandstone under cyclic water intrusion based on CT scanning technique. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 271 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03308-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03308-y