Abstract
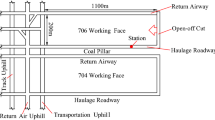
In order to provide a theoretical determination method for the fracture position of the main roof of the gob-side coal-rock roadway in a gently inclined coal seam (GCRGICS), a mechanical model of the overlying strata structure and a mechanical model of the coal rock body in the limit equilibrium zone were established based on the elastic–plastic limit equilibrium theory. The theoretical calculation formula of the fracture position of the main roof of the GCRGICS was derived. The fracture position of the main roof theory calculation and field test verification were carried out on 1511, 1509, and 151608 return airflow roadways with similar geological conditions in the Panjiang mining area of Guizhou Province. Combined with the similar simulation experimental results of the 1511 return airflow roadway, the differences between the similar simulation, field test and theoretical calculation results were all less than 1, which verified the practicality and reliability of the method. This method can be used to guide the reasonable width of coal pillar retention and the control of the surrounding rock in this type of roadway.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Ardehjani EA, Ataei M, Rafiee R (2020) Estimation of first and periodic roof weighting effect interval in mechanized longwall mining using numerical modelling. Int J Geomech 20(2):1–13
Bai JB (2006) Surrounding rock control of the gob-side roadway. China university of mining and technology press, Xuzhou, pp 19–28
Eremin M, Makarov P (2016) Estimation of general and set steps of roof caving in rock mass with excavations at mining. Numer Model Iop Conf 124:012051
Gao L, Liu PZ, Zhang PD, Wu GY, Kang XT (2022a) Influence of fracture types of main roof on the stability of surrounding rock of the gob-side coal-rock roadway in inclined coal seams and its engineering application. Coal Geol Explor 50(06):73–80
Gao L, Zhao SH, Huang XF, Ma ZQ, Kong DZ, Kang XT, Han S (2022b) Experimental study on surrounding rock characteristics of gateway in Panjiang mining area. J Guizhou Univ (Natural Sciences) 39(04):42–47
Gao L, Zhan XY, Zhang PD, Wen ZJ, Ma ZQ, Kong DZ, Kang XT, Han S (2022c) Study on the dip angle effect of asymmetric deformation and failure of the gob-side coal-rock roadway in gently inclined coal seam. Sustainability 14(12):1–15
Gu SC, Huang RB, Li JH, Su PL (2017) Stability analysis of un-mined coal pillars during the pressure adjustment prior to working face transfixion. J Min Saf Eng 34(01):60–66
He TJ (2000) The breaking place prediction of face end main roof flap top in the gob-side entry retaining. J China Coal Soc 2000(01):30–33
Hosseini N, Goshtasbi K, Oraee-Mirzamani B, Gholinejad M (2014) Calculation of periodic roof weighting interval in longwall mining using finite element method. Arabian J Geosci 7(5):1951–1956
Hou CJ, Ma NJ (1989) Stress in in-seam roadway sides and limit equilibrium zone. J China Coal Soc 04:21–29
Hou CJ (2013) Ground control of roadway. China university of mining and technology press, Xuzhou, pp 564–572
Huang WH, Zhang KM, Tang XY, Zhao ZG, Wan H (2010) Coking coals potential resources prediction in deep coal beds in Northern China. Energy Explor Exploit 28(4):313–324
Klishin VI, Yu Opruk G, Teleguz AS, Galkin AV (2018) Spectral acoustic and seismological monitoring of enclosing rock condition in the face area during roof softening by means of directional hydraulic fracturing (DHF). Earth and Environmental Science. In: International Scientific Conference Knowledge–based Technologies in Development and Utilization of Mineral Resources. Novokuznetsk: Siberian State Ind Univ, pp 1–7
Li YF, Hua XZ (2012) Mechanical analysis of stability of key blocks of overlying strata for gob-side entry retaining and calculating width of roadside backfill. Rock Soil Mech 33(04):1134–1140
Liu PZ, Gao L, Zhang PD, Wu GY, Wang C, Ma ZQ, Kong DZ, Kang XT (2022) Han S (2022) A case study on surrounding rock deformation control technology of gob-side coal-rock roadway in inclined coal seam of a mine in Guizhou. China Processes 15:1–16
Ma NJ, Hou CJ (1995) The underground pressure of sectional roadways and its control. Coal Industry Publishing House, Beijing, pp 62–66
Meng XJ (2020) Solid coal rib support technology of fully–mechanized mining along gob–side entry driving based on main roof fracture location. Coal Sci Technol 48(01):61–68
Mirenkov VE (2020) Influence of stresses and displacements in roof rocks on roof fracture in top coal caving. J Min Sci 56(2):203–208
Ning J, Xu G, Zhang CH, Sun ML (2020) Mechanical model and fracturing characteristics of multi-area supporting roof in fully mechanized mining working face. J China Coal Soc 45(10):3418–3426
Shi JJ, Ma NJ, Bai ZS (2013) Analysis on roof broken location of gateway retained along goaf and technology of roof support. Coal Sci Tech 41(07):35–37+42
Wang HS, Zhang DS (2006) Study on the mechanisms and aplications on controlling the creep failure in narrow side of gob–side entry. China university of mining and technology press, Xuzhou, pp 14–43
Wang ZQ, Guo L, Su ZH, Wang SS, Shen C (2020) Layout and combined support technology of alternate exterior stagger arrangement roadway and adjacent roadways in inclined and medium-thick coal seam. J China Coal Soc 45(02):542–555
Wu LX, Wang JZ, Guo ZC (2000) Foundation for Coal Pillar Design and Monitoring. China university of mining and technology press, Xuzhou, pp 85–96
Xie GX, Yang K, Liu QM (2006) Study on distribution laws of stress in inclined coal pillar for fully–mechanized top–coal caving face. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 03:545–549
Xu S, Gao L, Liu PZ, Zhang PD, Liu P, Ma ZQ, Kang XT, Wang YY (2022) Section shape optimization of gob-side coal-rock roadway in inclined coal seam. Coal Eng 54(08):122–128
Yang J, Wang HY, Wang YJ, Gao YB, Wang JW, Liu H (2019) Fracture characteristics of the roof in gob-side entry retaining with roof cutting and pressure release. J Min Saf Eng 36(06):1137–1144
Yin SF, Cheng GY, He FL, Shan Y (2016) An asymmetric support technique for fully-mechanized coal roadway nearby narrow pillar based on the fracture position analysis in basic roof. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 35(S1):3162–3174
Zha WH, Li X, Hua XZ, Wu TF, Yin SY (2014) Impact and application on narrow coal pillar for roadway protecting from fracture position of upper roof. J China Coal Soc 39(S2):332–338
Zhang PD, Gao L, Liu PZ, Kang XT, Ma ZQ, Wang YY, Liu P, Han S (2022a) Investigation of the bearing characteristics of bolts on a coal-rock combined anchor body under different pull-out rates. Energies 15(9):1–17
Zhang PD, Gao L, Liu PZ, Wang YY, Liu P, Kang XT (2022b) Study on the influence of borehole water content on bolt anchoring force in soft surrounding rock. Shock Vib 2022:2384626
Funding
This paper is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52004073 and No.52264008); Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Support Project (No. Qian Ke He Zhi Cheng [2021] General 400); Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Foundation (No. Qian Ke He Ji Chu [2020]1Y216); Guizhou Science and Technology Plan Project (Qianke Science Foundation [2020] 1Z047); The Scientific research project for talents introduction of Guizhou University (No. Gui Da Ren Ji He Zi (2020) No. 42), and The Cultivation project of Guizhou University (No. Gui Da Pei Yu [2019] No. 27); The Open Project Fund of Key Laboratory of Mining Disaster Prevention and Control (No. SMDPC202106) during the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, X., Gao, L., Liu, P. et al. Theoretical determination method and field verification of the fracture position of the main roof of the gob-side coal-rock roadway in gently inclined coal seam. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 209 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03249-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03249-6



