Abstract
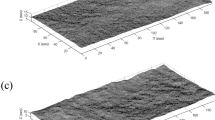
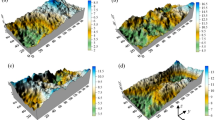
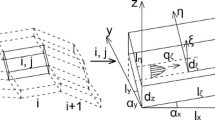
This paper experimentally evaluated the influences of the surface roughness and boundary load on the nonlinear flow behavior of real three-dimensional rock fractures. The rough fractures with various joint roughness coefficient (JRC) values in the range of 2.59 to 19.31 were generated with a fractal governing function, and the corresponding fractured granite specimens of a square plate shape in the size of 495 × 495 × 16 mm were manufactured. The fluid flow tests on these fractures were conducted with respect to various hydraulic pressures ranged from 0 to 0.6 MPa and various boundary loads ranged from 7 to 35 kN. The results show that Forchheimer’s law provides an excellent presentation of the relation between the hydraulic gradient and the flow rate, and both the linear and nonlinear fitting coefficients in the Forchheimer’s law show an increasing trend with both increases in the surface roughness and boundary load. The critical hydraulic gradient and critical Reynolds number decrease with the surface roughness. The critical hydraulic gradient increases more significantly under a small boundary load in the range of 7 to 14 kN than that under a high boundary load in the range of 21 to 35 kN. A cubic polynomial function is applied to analyze the transmissivity as a function of the hydraulic gradient, and the transmissivity shows a decreasing trend when the surface roughness and boundary load increase. The flow behavior is assessed by depicting the normalized transmissivity of the fractures based on the hydraulic gradient, and an increase in the surface roughness shifts the fitting curves downwards. The hydraulic aperture shows a hyperbolic decrease as the boundary load increased, and a power-law equation can be used to evaluate the variations in the nonlinear coefficient in terms of the hydraulic aperture.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- JRC:
-
Joint roughness coefficient
- u :
-
Flow velocity tensor
- P :
-
Hydraulic pressure
- ρ :
-
Fluid density
- Q :
-
Volume flow rate
- w :
-
Fracture width
- e h :
-
Hydraulic aperture
- J :
-
Hydraulic gradient
- a, b :
-
Linear and nonlinear coefficients in Forchheimer’s law
- E :
-
Judge parameter of fluid flow regime
- J c :
-
Critical hydraulic gradient
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- Re c :
-
Critical Reynolds number
- T :
-
Transmissivity
- T 0 :
-
Intrinsic transmissivity
- T/T0 :
-
Normalized transmissivity
- β :
-
Dimensionless coefficient
- D :
-
Fractal dimension
- xi, yi :
-
Coordinates of fracture profile
- M :
-
Number of sampling points
- F, Fx, Fy, Fz :
-
Boundary load
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- L :
-
Length of flow path
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration
- λ, m :
-
Regression coefficient
References
Andrade JSJ, Costa UMS, Almeida MP, Makse HA, Stanley HE (1999) Inertial effects on fluid flow through disordered porous media. Phys Rev Lett 82(26):5249–5252. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.82.5249
Bandis SC, Lumsden AC, Barton NR (1983) Fundamentals of rock joint deformation. Int J Rock Mech Min 20(6):249–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(83)90595-8
Bear J (1972) Dynamics of fluids in porous media, am. Elsevier, New York. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1973.03615995003700040004x
Berkowitz B (2002) Characterizing flow and transport in fractured geological media: a review. Adv Water Resour 25(8):861–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00042-8
Brush DJ, Thomson NR (2003) Fluid flow in synthetic rough-walled fractures: Navier-Stokes, Stokes, and local cubic law simulations. Water Resour Res 39(4):1037–1041. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002wr001346
Cai J, Yu B, Zou M, Mei M (2010) Fractal analysis of invasion depth of extraneous fluids in porous media. Chem Eng Sci 65(18):5178–5186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2010.06.013
Cao S, Yilmaz E, Xue G, Yilmaz E, Song W (2019) Loading rate effect on uniaxial compressive strength behavior and acoustic emission properties of cemented tailings backfill. Constr Build Mater 213(7):313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.082
Chen Y, Lian H, Liang W, Yang J, Nguyen VP, Bordas SPA (2019) The influence of fracture geometry variation on non-Darcy flow in fractures under confning stresses. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 113:59–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.11.017
Chen YF, Zhou JQ, Hu SH, Hu R, Zhou CB (2015) Evaluation of Forchheimer equation coefficients for non-Darcy flow in deformable rough-walled fractures. J Hydrol 529:993–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.09.021
Folch A, Menció A, Puig R, Soler A, Mas-Pla J (2011), “Groundwater development effects on different scale hydrogeological systems using head, hydrochemical and isotopic data and implications for water resources management: the Selva basin (NE Spain)”, J Hydrol, 403(1–2), 83–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.03.041
Huang YH, Yang SQ, Zhao J (2016) Three-dimensional numerical simulation on triaxial failure mechanical behavior of rock-like specimen containing two unparallel fissures. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(12):4711–4729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1081-2
Javadi M, Sharifzadeh M, Shahriar K, Mitani Y (2014) Critical Reynolds number for nonlinear flow through rough-walled fractures: the role of shear processes. Water Resour Res 50(2):1789–1804. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013wr014610
Ju Y, Zhang QG, Yang YM, Xie HP, Gao F, Wang HJ (2013) An experimental investigation on the mechanism of fluid flow through single rough fracture of rock. Sci China 56(8):2070–2080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-013-5274-6
Koyama T, Neretnieks I, Jing L (2008) A numerical study on differences in using Navier–Stokes and Reynolds equations for modeling the fluid flow and particle transport in single rock fractures with shear. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 45(7):1082–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.11.006
Lee SH, Lee KK, Yeo IW (2014) Assessment of the validity of Stokes and Reynolds equations for fluid flow through a rough-walled fracture with flow imaging. Geophys Res Lett 41:4578–4585. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014gl060481
Lee SH, Yeo IW, Lee KK, Detwiler RL (2015) Tail shortening with developing eddies in a rough-walled rock fracture. Geophys Res Lett 42(15):6340–6347. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL065116
Li B, Liu R, Jiang Y (2016a) Influences of hydraulic gradient, surface roughness, intersecting angle, and scale effect on nonlinear flow behavior at single fracture intersections. J Hydrol 538:440–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.04.053
Li SC, Wu J, Xu ZH, Li LP, Huang, X., Xue, Y.G., Wang, Z.C. (2016b), “Numerical analysis of water flow characteristics after inrushing from the tunnel floor in process of karst tunnel excavation”, Geomech. Eng., 10(4):471–526. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2016.10.4.471
Liu RC, Li B, Jiang YJ (2016) Critical hydraulic gradient for nonlinear flow through rock fracture networks: the roles of aperture, surface roughness, and number of interactions. Adv Water Resour 88:53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2015.12.002
Liu RC, Yu LY, Jiang YJ (2017) Quantitative estimates of normalized transmissivity and the onset of nonlinear fluid flow through rough rock fractures. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(4):1063–1071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1147-1
Ma D, Duan HY, Liu JF, Li XB, Zhou ZL (2019a) The role of gangue on the mitigation of mining-induced hazards and environmental pollution: an experimental investigation. Sci Total Environ 664:636–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.059
Ma D, Duan HY, Li XB, Li ZH, Zhou ZL, Li TB (2019b) Effects of seepage-induced erosion on nonlinear hydraulic properties of broken red sandstones. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 91:102993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2019.102993
Mandelbrot BB (1983) The fractal geometry of nature. New York: W H Freeman. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.13295
Min KB, Rutqvist J, Tsang CF, Jing L (2004) Stress-dependent permeability of fractured rock masses: a numerical study. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 41(7):1191–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.05.005
Olsson R, Barton N (2001) An improved model for hydromechanical coupling during shearing of rock joints. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 38(3):317–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(00)00079-4
Qian J, Zhan H, Chen Z, Ye H (2011) Experimental study of solute transport under non-Darcian flow in a single fracture. J Hydrol 339(3–4):246–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.01.003
Radilla G, Nowamooz A, Fourar M (2013) Modeling non-Darcian single- and two-phase flow in transparent replicas of rough-walled rock fractures. Transport. Porous. Med. 98(2):401–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0150-1
Ranjith PG, Darlington W (2007) Nonlinear single-phase flow in real rock joints. Water Resour Res 43(9):146–156. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006wr005457
Ranjith PG, Viete DR (2011) Applicability of the ‘cubic law’ for non-Darcian fracture flow. J Pet Sci Eng 78(2):321–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2011.07.015
Rong G, Yang J, Cheng L, Zhou CB (2016) Laboratory investigation of nonlinear flow characteristics in rough fractures during shear process. J Hydrol 541:1385–1394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.08.043
Rutqvist J, Stephansson O (2003) The role of hydromechanical coupling in fractured rock engineering. Hydrogeol J 11(1):7–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-002-0241-5
Shi XS, Zhao J (2020) Practical estimation of compression behavior of clayey/silty sands using equivalent void-ratio concept. J Geotech Geoenviron 146(6):04020046. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002267
Szulga J, Molz F (2001) The Weierstrass-Mandelbrot process revisited. J Stat Phys 104(5):1317–1348. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1010422315759
Tse R, Cruden DM (1979) Estimating joint roughness coefficients. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 16(5):303–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(79)90241-9
Wang M, Chen YF, Ma GW, Zhou JQ, Zhou CB (2016) Influence of surface roughness on nonlinear flow behaviors in 3D self-affine rough fractures: Lattice Boltzmann simulations. Adv Water Resour 96:373–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.08.006
Witherspoon PA, Wang JSY, Iwai K, Gale JE (1980) Validity of cubic law for fluid flow in a deformable rock fracture. Water Resour Res 16(6):1016–1024. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR016i006p01016
Xia CC, Gui Y, Wang W, Du SG (2014) Numerical method for estimating void spaces of rock joints and the evolution of void spaces under different contact states. J Geophys Eng 11(6):065004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-2132/11/6/065004
Xia CC, Qian X, Lin P, Xiao WM, Gui Y (2017) Experimental investigation of nonlinear flow characteristics of real rock joints under different contact conditions. J Hydraul Eng 143(3):04016090. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0001238
Xiong F, Jiang QH, Ye ZY, Zhang XB (2018) Nonlinear flow behavior through rough-walled rock fractures: the effect of contact area. Comput Geotech 102:179–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.06.006
Xiong XB, Li B, Jiang YJ, Koyama T, Zhang CH (2011) Experimental and numerical study of the geometrical and hydraulic characteristics of a single rock fracture during shear. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 48(8):1292–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.09.009
Yin Q, Jing HW, Liu RC, Ma GW, Yu LY, Su HJ (2018) Experimental study on stress-dependent nonlinear flow behavior and normalized transmissivity of real rock fracture networks. Geofluids. 8217921. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8217921
Yin Q, Liu RC, Jing HW, Su HJ, Yu LY, He LX (2019) Experimental study of nonlinear flow behaviors through fractured rock samples after high-temperature exposure. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(9):2963–2983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-1741-0
Yin Q, Ma GW, Jing HW, Su HJ, Liu RC (2017) Hydraulic properties of 3D rough-walled fractures during shearing: an experimental study. J Hydrol 555:169–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.10.019
Zeng ZW, Grigg R (2006) A criterion for non-Darcy flow in porous media. Transport. Porous. Med. 63(1):57–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-005-2720-3
Zhang L, Yu C, Sun JQ (2015) Generalized Weierstrass-Mandelbrot function model for actual stocks markets indexes with nonlinear characteristics. Fractals. 23(2):1550006. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X15500061
Zhang M, Prodanović M, Mirabolghasemi M, Zhao J (2019) 3D microscale flow simulation of shear-thinning fluids in a rough fracture. Transport Porous Med 128(1):243–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-019-01243-9
Zhang ZY, Nemcik J, Ma S (2013) Micro- and macro-behaviour of fluid flow through rock fractures: an experimental study. Hydrogeol J 21(8):1717–1729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-013-1033-9
Zhang ZY, Nemcik J (2013) Fluid flow regimes and nonlinear flow characteristics in deformable rock fractures. J Hydrol 477(1):139–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.024
Zhou JQ, Hu SH, Fang S, Chen YF, Zhou CB (2015) Nonlinear flow behavior at low Reynolds numbers through rough-walled fractures subjected to normal compressive loading. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 80:202–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.09.027
Zimmerman RW, Bodvarsson GS (1996) Hydraulic conductivity of rock fractures. Transport. Porous. Med. 23(1):1–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00145263
Zimmerman RW, AL-Yaarubi A, Pain CC, Grattoni CA (2004) Non-linear regimes of fluid flow in rock fractures. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 41(3):163–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.03.036
Zou L, Jing L, Cvetkovic V (2015) Roughness decomposition and nonlinear fluid flow in a single rock fracture. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 75:102–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.01.016
Zou LC, Jing L, Cvetkovic V (2017) Shear-enhanced nonlinear flow in rough-walled rock fractures. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 97:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.06.001
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51904290), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK20180663) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019 M661987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.Y. Wu and Q. Yin conceived and designed the experiments. J.Y. Wu and Q. Yin performed the experiments. J.Y. Wu, Q. Yin, and H.W. Jing analyzed the data. J.Y. Wu, Q. Yin, and H.W. Jing wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Yin, Q. & Jing, H. Surface roughness and boundary load effect on nonlinear flow behavior of fluid in real rock fractures. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79, 4917–4932 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01860-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01860-5