Abstract
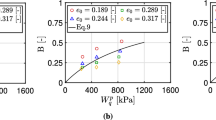
The deformation of rockfill materials is mostly caused by particle breakage and subsequent skeleton adjustment. To investigate the effect of size and strain rate on particle strength under seismic load, a series of single particle crushing tests with different sizes and loading rates were conducted. The results show that the particle strength increases with the loading rate, while the size effect on particle strength gradually weakens. Furthermore, within the framework of the weakest chain theory, the failure probability per unit volume and the spatial location distribution of microcracks are discussed, and a statistical model for quasi-static particle strength is established. The spatial location of microcracks follows a power law distribution, and there is a specific power exponent at different strain rates, so that the compound parameters of the particle volume and failure probability are gathered on a master curve determined by the weakest chain statistics. The strain rate effect reduces the failure probability per unit volume and makes the spatial location distribution of microcracks sparser.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arulrajah, A., Piratheepan, J., Disfani, M.M., Bo, M.W.: Geotechnical and geoenvironmental properties of recycled construction and demolition materials in pavement subbase applications. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 25(8), 1077–1088 (2013)
Cil, M.B., Sohn, C., Buscarnera, G.: DEM modeling of grain size effect in brittle granular soils. J. Eng. Mech. 146(3), 04019138 (2020)
Zhou, W., Wang, D., Ma, G., Cao, X., Hu, C., Wu, W.: Discrete element modeling of particle breakage considering different fragment replacement modes. Powder Technol. 360, 312–323 (2020)
Jia, Y., Xu, B., Chi, S., Xiang, B., Zhou, Y.: Research on the particle breakage of rockfill materials during triaxial tests. Int. J. Geomech. 17(10), 04017085 (2017)
Wang, J., Chi, S., Zhou, X., Shao, X.: Experimental and numerical investigation of the size effect of rockfill particles on crushing strength. Granul. Matter 25(4), 60 (2023)
Portnikov, D., Kalman, H.: Determination of elastic properties of particles using single particle compression test. Powder Technol. 268, 244–252 (2014)
Zhang, Y.D., Buscarnera, G., Einav, I.: Grain size dependence of yielding in granular soils interpreted using fracture mechanics, breakage mechanics and Weibull statistics. Geotechnique 66(2), 149–160 (2016)
Zhao, F., Chi, S.: Characteristics of particle breakage and constitutive model of coarse granular material incorporating gradation evolution. Geotechnique 73, 1–14 (2022)
Mao, H., Shen, C., Liu, S., Wang, L., Fu, Z.: Insight into the crushing strength of rockfill grains at different temperature and relative humidity conditions. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 56(9), 6529–6543 (2023)
Guo, Y., Chi, S., Mi, X., Yan, S.: Experimental investigation of statistical characteristics of elastic mechanical parameters and strength indexes of rockfill particles. Granul. Matter 25(2), 30 (2023)
Xiao, Y., Meng, M., Daouadji, A., Chen, Q., Wu, Z., Jiang, X.: Effects of particle size on crushing and deformation behaviors of rockfill materials. Geosci. Front. 11, 375–388 (2020)
Wong, T.-F., Wong, R.H.C., Chau, K.T., Tang, C.A.: Microcrack statistics, Weibull distribution and micromechanical modeling of compressive failure in rock. Mech. Mater. 38(7), 664–681 (2006)
Lei, W.-S., Zhang, P., Yu, Z., Qian, G.: Statistics of ceramic strength: use ordinary Weibull distribution function or Weibull statistical fracture theory? Ceram. Int. 46(13), 20751–20768 (2020)
Lei, W.-S., Yu, Z., Zhang, P., Qian, G.: Standardized Weibull statistics of ceramic strength. Ceram. Int. 47(4), 4972–4993 (2021)
Weibull, W.: A statistical distribution function of wide applicability. J. Appl. Mech. doi (1951). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4010337
Zhang, Q.B., Zhao, J.: A review of dynamic experimental techniques and mechanical behaviour of rock materials. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 47(4), 1411–1478 (2013)
Ma, L., Li, Z., Wang, M., Wei, H., Fan, P.: Effects of size and loading rate on the mechanical properties of single coral particles. Powder Technol. 342, 961–971 (2019)
Wang, X., Zhang, S., Wang, C., Song, R., Shang, C., Fang, X.: Experimental investigation of the size effect of layered roller compacted concrete (RCC) under high-strain-rate loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 165, 45–57 (2018)
Chen, X., Wu, S., Zhou, J.: Compressive strength of concrete cores under high strain rates. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 29(1), 06014005 (2015)
Qi, C., Wang, M., Bai, J., Wei, X., Wang, H.: Investigation into size and strain rate effects on the strength of rock-like materials. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 86, 132–140 (2016)
Li, X., Hong, L., Yin, T., Zhou, Z., Ye, Z.: Relationship between diameter of split Hopkinson pressure bar and minimum loading rate under rock failure. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 15, 218–223 (2008)
Jin, L., Yu, W., Du, X., Zhang, S., Li, D.: Meso-scale modelling of the size effect on dynamic compressive failure of concrete under different strain rates. Int. J. Impact Eng 125, 1–12 (2019)
McDowell, G.R., Amon, A.: The application of Weibull statistics to the fracture of soil particles. Soils Found. 40(5), 133–141 (2000)
Nakata, Y., Kato, Y., Hyodo, M., Hyde, A.F.L., Murata, H.: A probabilistic approach to sand particle crushing in the triaxial test. Geotechnique 49(5), 567–583 (1999)
Wei, X.X., Chau, K.T., Wong, R.H.C.: Theoretical and experimental validation of point load strength test for irregular lumps. J. Eng. Mech. 145(9), 04019065 (2019)
Yan, S., Chi, S., Shao, X., Guo, Y.: Effect of size and strain rate on particle strength and stress–strain properties of rockfill materials. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 162, 107422 (2022)
Batdorf: A statistical theory for the fracture of brittle structures subjected to nonuniform polyaxial stresses. J Appl Mech 41(2), 459–464 (1974)
Beremin, F.M., Pineau, A., Mudry, F., Devaux, J.C.: A local criterion for cleavage fracture of a nuclear pressure vessel steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 14(11), 2277–2287 (1983)
Griffith, A.A.: The phenomena of rupture and flow in solids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 221(580–593), 163–198 (1921)
Lei, W.-S.: A framework for statistical modelling of plastic yielding initiated cleavage fracture of structural steels. Philos. Mag. 96(35), 3586–3631 (2016)
Zhang, M., Lu, Y.J., Yang, Q.: Failure probability and strength size effect of quasi-brittle materials. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 29, 1782–1789 (2010)
Lei, W.S.: Evaluation of the basic formulations for the cumulative probability of brittle fracture with two different spatial distributions of microcracks. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 39(5), 611–623 (2016)
Lei, W.-S.: A generalized weakest-link model for size effect on strength of quasi-brittle materials. J. Mater. Sci. 53(2), 1227–1245 (2017)
Yu, Z., Lei, W.-S., Zhai, J.: A synchronized statistical characterization of size dependence and random variation of breakage strength of individual brittle particles. Powder Technol. 317, 329–338 (2017)
Meng, Q., Zhang, M., Han, L., Pu, H., Li, H.: Effects of size and strain rate on the mechanical behaviors of rock specimens under uniaxial compression. Arab. J. Geosci. 9(8), 527 (2016)
Liang, C.Y., Zhang, Q.B., Li, X., Xin, P.: The effect of specimen shape and strain rate on uniaxial compressive behavior of rock material. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 75(4), 1669–1681 (2015)
Li, H.B., Zhao, J., Li, T.J.: Micromechanical modelling of the mechanical properties of a granite under dynamic uniaxial compressive loads. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 37(6), 923–935 (2000)
Zhang, Q.B., Zhao, J.: Effect of loading rate on fracture toughness and failure micromechanisms in marble. Eng. Fract. Mech. 102, 288–309 (2013)
Qi, C., Wang, M., Bai, J., Li, K.: Mechanism underlying dynamic size effect on rock mass strength. Int. J. Impact Eng 68, 1–7 (2014)
Ovalle, C., Frossard, E., Dano, C., Hu, W., Maiolino, S., Hicher, P.: The effect of size on the strength of coarse rock aggregates and large rockfill samples through experimental data. Acta Mech. 225(8), 2199–2216 (2014)
Shao, X., Chi, S., Tao, Y., Zhou, X.: DEM simulation of the size effect on the wetting deformation of rockfill materials based on single-particle crushing tests. Comput. Geotech. 2020(123), 103429 (2020)
Cheng, J., Ma, G., Zhang, G., Chang, X., Zhou, W.: A theoretical model for evaluating the deterioration of mechanical properties of rockfill materials. Comput. Geotech. 163, 105757 (2023)
Huang, Q., Zhou, X., Liu, B.: Effect of realistic shape on grain crushing for rounded and angular granular materials. Comput. Geotech. 162, 105659 (2023)
Lim, W.L., McDowell, G.R., Collop, A.C.: The application of Weibull statistics to the strength of railway ballast. Granul. Matter 6(4), 229–237 (2004)
Ma, G., Wang, Y., Zhou, H., Lu, X., Zhou, W.: Morphology characteristics of the fragments produced by rock grain crushing. Int. J. Geomech. 22(4), 0422020 (2022)
Meng, M., Xiao, Y., Duan, X., Sun, Z., Du, L., Fan, H., Liu, H.: Crushing strength of artificial single-particle considering the effect of particle morphology. Acta Geotech. 17, 3909–3926 (2022)
Wang, Y., Ma, G., Mei, J., Zou, Y., Zhang, D., Zhou, W., Cao, X.: Machine learning reveals the influences of grain morphology on grain crushing strength. Acta Geotech. 16(11), 3617–3630 (2021)
Li, Z., Liu, B., Han, D., Xie, Y., Zhao, Y.: Study on the influence of microcracks of coarse aggregate with specific particle size on crushing strength. Comput. Part. Mech. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-023-00648-0
McDowell, G.R.: Statistics of soil particle strength. Geotechnique 51(10), 897–900 (2001)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial and technical support provided by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFB0201001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, S., Chi, S., Guo, Y. et al. Statistical evaluation of the effect of size and strain rate on particle strength of rockfill materials. Granular Matter 26, 51 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-024-01417-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-024-01417-3