Abstract
In this work, we analyse the physical consequences of capillary bridges coalescence between spherical particles agglomerates and more particularly the jump of the capillary force. By referring to Murase et al. (Adv Powder Technol 19(4):349–367, 2008) and Rynhart et al. (Res Lett Inf Math Sci 5:119–127, 2003) about bridges adhered to three particles, we analyse the effects of coalescense between three bridges with two grains and a bridge joining three grains. This monographic synthesis intends to explain analytically and geometrically the significant increase of the inter-particle force, a strengthening cohesion effect, experimentally observed, reported and still largely unelucidated to our knowledge in the literature.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The coefficient \(\sqrt{3}\) comes from the composition rule of the forces inclined of a \(\pi /3\) angle with respect to the vertical.
Independent of the coordinate system that is chosen.
This value corresponds to \(4\pi r \sin \pi /6\).
Whose vertex is the center of the upper sphere and the other direction given by the vertical.
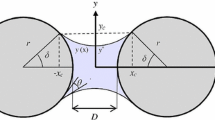
Characterized by the well-known relations \(s=0\) and \(y_{\delta }^{*}=r\sin \delta \ \sin \left( \delta +\theta \right) \).
By geometrical construction by dividing the major axis in three equal parts.
References
Aarts, D.G., Lekkerkerker, H.N., Guo, H., Wegdam, G.H., Bonn, D.: Hydrodynamics of droplet coalescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(16), 164503 (2005). http://eudml.org/doc/112068
Alberti, G., DeSimone, A.: Quasistatic evolution of sessile drops and contact angle hysteresis. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 202(1), 295–348 (2011)
do Carmo, M.P.: Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1976)
Decent, S.P., Sharpe, G., Shaw, A.J., Suckling, P.M.: The formation of a liquid bridge during the coalescence of drops. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 32(6), 717–738 (2006)
Delaunay, C.H.: Sur la surface de révolution dont la courbure moyenne est constante. J. Math. Pures Appl. 6, 309–314 (1841)
De Souza, E.J., Brinkmann, M., Mohrdieck, C., Arzt, E.: Enhancement of capillary forces by multiple liquid bridges. Langmuir 24(16), 8813–8820 (2008)
Eells, James: The surfaces of Delaunay. Math. Intell. 9(1), 53–57 (1987)
Eggers, J., Lister, J.R., Stone, H.A.: Coalescence of liquid drops. J. Fluid Mech. 401, 293–310 (1999)
Gagneux, G., Millet, O.: Analytic calculation of capillary bridges properties deduced as an inverse problem from experimental data. Transp. Porous Media (2014). doi:10.1007/s11242-014-0363-y
Gagneux, G., Millet, O.: Discrete mechanics of capillary bridges. Iste-Wiley Publ., Discrete Granular Mechanics Series (in preparation)
Gras, J.-P..: Approche micromécanique de la capillarité dans les milieux granulaires : rétention d’eau et comportement mécanique. Ph.D. Thesis University of Montpellier 2 (2011)
Hueckel, T., Mielniczuk, B., El Youssoufi, M.S.: Micro-scale study of rupture in desiccating granular media, Geotechnical Special Publication GSP 231, Geo-Congress 2013, San Diego, USA, 3–7 Mar. 2013, pp. 808-817 (2013). doi:10.1061/9780784412787.082
Murase, K., Mochida, T., Sagawa, Y., Sugama, H.: Estimation on the strength of a liquid bridge adhered to three spheres. Adv. Powder Technol. 19(4), 349–367 (2008)
Murase, K., Mochida, T., Sugama, H.: Experimental and numerical studies on liquid bridge formed among three spheres. Granul. Matter 6(2–3), 111–119 (2004)
Nase, S.T., Vargas, W.L., Abatan, A.A., McCarthy, J.J.: Discrete characterization tools for cohesive granular material. Powder Technol. 116(2), 214–223 (2001)
Rynhart, P.R., McLachlan, R., Jones, J.R., McKibbin, R.: Solution of the Young–Laplace equation for three particles. Res. Lett. Inf. Math. Sci. 5, 119–127 (2003)
Rynhart, P., McKibbin, R., McLachlan, R., Jones, J.R.: Mathematical modelling of granulation: static and dynamic liquid bridges. Res. Lett. Inf. Math. Sci. 3, 199–212 (2002)
Sanchez-Palencia, E., Millet, O., Béchet, F.: Thin Elastic Shells. Computing and Asymptotics. Lecture Notes in Applied and Computational Mechanics. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Shikhmurzaev, Y.D.: Coalescence and capillary breakup of liquid volumes. Phys. Fluids 12, 2386–2396 (2000)
Simons, S.J.R., Fairbrother, R.J.: Direct observations of liquid binder–particle interactions: the role of wetting behaviour in agglomerate growth. Powder Technol. 110(1), 44–58 (2000)
Sprittles, J.E., Shikhmurzaev, Y.D.: Coalescence of liquid drops: different models versus experiment. Phys. Fluids 24, 122105–122131 (2012)
Wu, M., Cubaud, T., Ho, C.M.: Scaling law in liquid drop coalescence driven by surface tension. Phys. Fluids 16, L51 (2004)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge J.P. Gras for allowing to reproduce at Sect. 2 experimental data from his Ph.D. Thesis and Prof. N.-P. Kruyt for personal discussions about this paper to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gagneux, G., Millet, O. An analytical framework for evaluating the cohesion effects of coalescence between capillary bridges. Granular Matter 18, 16 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-016-0613-5
Received:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-016-0613-5