Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study is to evaluate the potential effect of varicocele in the hormonal and clinical profile of adolescents.
Methods
Twenty adolescents at Tanner stage 4–5 with left varicocele were studied and compared with a control group of 20 healthy adolescents. All patients underwent ultrasonographic testicular volumetry as well as hormonal evaluation of inhibin B, testosterone, baseline and gonadotropin-releasing hormone stimulated, follicle-stimulating hormone as well as luteinizing hormone. Statistical analysis was performed using the student’s t test with p value <0.05 taken as statistical significant.
Results
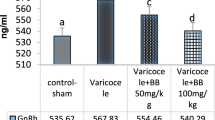
Patients with varicocele showed reduced levels of inhibin B compared to controls and a significant reduction in the testicular volume on the affected side. The response of luteinizing hormone to gonadotropin-releasing hormone stimulation was significantly higher in the varicocele group compared to the control group. Furthermore a significant inverse relationship of inhibin B compared to follicle-stimulating hormone was noted.
Conclusion
Serum inhibin B levels could represent a useful marker of Sertoli cell damage caused by varicocele.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbay E, Cayan S, Doruk E, Duce MN, Bozlu M (2000) The prevalence of varicocele and varicocele-related testicular atrophy in Turkish children and adolescents. BJU Int 86:490–493
Camoglio FS, Cervellione RM, Dipaola G, Balducci T, Giacomello L, Zanatta C, Forestieri C, Chironi C (2001) Idiopathic varicocele in children. Epidemiological study and surgical approach. Minerva Urol Nefrol 53:189–193
Al-Abbadi K, Smadi SA (2000) Genital abnormalities and groin hernias in elementary-school children in Aqaba:an epidemiological study. East Mediter Health J 6:293–298
Hwang Y, Park SW (2009) Epidemiologic study of the prevalence and awareness of cryptorchidism, hydrocele, and varicocele in elementary schools in Gwangju. Korean J Urol 50:278–281
Belloli G, D’Agostino S, Pesce C, Fantuz E (1993) Varicocele in childhood and adolescence and other testicular anomalies: an epidemiological study. Pediatr Med Chir 15:159–162
Skoog SJ, Roberts KP, Goldstein M, Pryor JL (1997) The adolescent varicocele: what’s new with an old problem in young parients? Pediatrics 100:112–121
Male infertility best practice policy committee of the American Urological Association (2004) Report on varicocele and infertility. Fertil Steril 82(Suppl):S1 42–S145
Kass EJ, Freitas JE, Salisz JA, Steinert BW (1993) Pituitary gonadal dysfunction in adolescents with varicocele. Urology 42:179–181
Romeo C, Arrigo T, Impellizzeri P, Manganaro A, Antonuccio P, Di Pasquale G, Messina MF, Marseglia L, Formica I, Zuccarello B (2007) Altered serum inhibin B levels in adolescents with varicocele. J Ped Surg 42:390–394
Dubin L, Amelar RD (1970) Varicocele size and results of varicocele in selected subfertile men with varicocele. Fertil Steril 21:606–609
Marshall WA, Tanner JM (1970) Variations of pubertal changes in boys. Arch Dis Child 45:13–23
Trigo RV, Bergada I, Rey R, Ballerini MG, Bedecarras P, Bergada C, Gottlieb S, Campo S (2004) Altered serum profile of inhibin B, pro-alphaC and anti-mullerian hormone in prepubertal and pubertal boys with varicocele. Clin Endocrinol 60:758–764
Burger HG (1992) Inhibin. Reprod Med Rev 1:1–20
McLachan RI, Matsumoto AM, Burger HG, De Kretser DM, Bremner WJ (1988) Relative roles of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone in the control of inhibin secretion in normal men. J Clin Investig 82:880–884
Sharpe RM, Kerr JB, Maddocks S (1988) Evidence for a role of the Leydig cells in control of the intratesticular secretion of inhibin. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2–3:243–247
Andersson AM, Juul A, Petersen JH, Muller J, Groome NP, Skakkebaek NE (1997) Serum inhibin B in healthy pubertal and adolescent boys: relation to age, stage of puberty, and folliclestimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, testosterone, and estradiol levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:3976–3981
Calsen E, Giwercman A, Skakkabaek NE, Keiding N (1992) Decreasing quality of semen. BMJ 305(6854):609–613
Illingworth PJ, Groome NP, Bryd W, Rainey WE, McNeilly AS, Mather JP, Bremner WJ (1996) Inhibin B: a likely candidate for the physiologically important form of inhibin in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:1321–1325
Ponchietti R, Raugai A, Grachi G (1987) Ultrastructural changes of Leydig cells in prepubertal varicocele. Acta Eur Fertil 18:347–348
Haans LC, Laven JS, Mali WP, Te Velde ER, Wensing CJ (1991) Testis volumes, semen quality, and hormonal patterns in adolescents with and without a varicocele. Fertil Steril 56:731–736
Steeno O, Knops J, Declerck L, Adimoelja A, Van de Voorde H (1976) Prevention of fertility disorders by detection and treatment of varicocele at school and college age. Andrologia 8:47–53
Lyon RP, Marshall S, Scott MP (1982) Varicocele in childhood and adolescence: implication in adult fertility. Urology 19:641–644
Paduch DA, Niedzielski J (1997) Repair versus observation in adolescent varicocele: a prospective study. J Urol 158:1128–1132
Sayfan J, Siplovich L, Koltun L, Benyamin N (1997) Varicocele treatment in pubertal boys prevents testicular growth arrest. J Urol 157:1456–1457
Guarino N, Tadini B, Bianchi M (2003) The adolescent varicocele: the crucial role of hormonal tests in selecting patients with testicular dysfunction. J Pediatr Surg 38:120–123
Liu MJ, Wang EH (2014) Impact of varicocele on semen quality and inhibin B concentration in serum and seminal plasma. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue 20:44–47
Romeo C, Arrigo T, Impellizzeri P, Manganaro A, Antonuccio P, Di Pasquale G, Messina MF, Marseglia L, Formica I, Zuccarello B (2007) Altered serum inhibin B levels in adolescents with varicocele. J Ped Surg 42:390–394
Hayes FJ, Hall JE, Boepple PA, Crowley WF (1998) Clinical review 96: differential control of gonadotropin secretion in the human: endocrine role of inhibin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:1835–1841
Foresta C, Bettella A, Rossato M, La Scala G, De Paoli M, Plebani M (1999) Inhibin B plasma concentration in oligozoospermic subjects before and after therapy with follicle stimulating hormone. Hum Reprod 14:906–912
Castro-Magana M, Angulo M, Canas A, Uy J (1990) Leydig cell function in adodescent boys with varicoceles. Arch Androl 24:73–79
Anyfantakis D, Symvoulakis EK, Barbounakis E, Kastanakis M, Athanasakis E, Blevrakis E, Kastanakis S (2014) A fatal case of seronegative, late-onset systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with motor sensory axonal polyneuropathy. Mod Rheumatol 24:858–861
Anyfantakis D, Symvoulakis EK (2011) Medical decision and patient’s preference: ‘much ethics’ and more trust always needed. Int J Med Sci 8:351–352
Schiff J, Kelly C, Goldstein M, Schlegel P, Poppas D (2005) Managing varicoceles in children: results with microsurgical varicocelectomy. BJU Int 95:399–402
Haddad NG, Houk CP, Lee PA (2014) Varicocele: a dilemma in adolescent males. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 2:274–283
Diamond DA, Gargollo PC, Caldamone AA (2011) Current management principles for adolescent varicocele. Fert Steril 96:1294–1298
Waalkes R, Manea IF, Nijman JM (2012) Varicocele in adolescents: a review and guideline for the daily practice. Arch Esp Urol 65:859–871
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blevrakis, E., Chatzidarellis, E., Anyfantakis, D. et al. Impact of varicocele on biological markers of gonadal function. Hernia 20, 435–439 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-015-1361-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-015-1361-x