Abstract
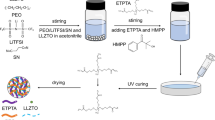
Due to their higher safety, stability and energy density, all-solid-state batteries will be promising candidates for the next generation of lithium battery systems. The acquisition of high-performance solid-state electrolytes is pivotal in the actualization of all-solid-state batteries. By uniformly dispersing nanoscale Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 (LATP) powders into polyethylene oxide (PEO)-LiClO4 at varying mass ratios, a composite electrolyte membrane of approximately 50 μm thickness was prepared using the casting method. Subsequent characterization of these materials, accomplished through X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and cyclic charge–discharge tests, unveiled intriguing findings. Although the beneficial effect of LATP on the conductivity of PEO is somewhat limited, it demonstrates a capability to reduce the interface impedance between polyethylene oxide and lithium metal, thereby enhancing interface stability. This research provides constructive insights and prompts for designing composite electrolytes for future all-solid-state batteries.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time due to legal or ethical reasons.
References
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414(6861):359–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/35104644
Whittingham MS (2004) Lithium batteries and cathode materials. Chem Rev 104(10):4271–4301. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr020731c
Nitta N, Wu F, Lee JT, Yushin G (2015) Li-ion battery materials: present and future. Mater Today 18(5):252–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2014.10.040
Liu K, Liu Y, Lin D, Pei A, Cui Y (2018) Materials for lithium-ion battery safety. Sci Adv 4(6):eaas9820. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aas9820
Li W, Dahn JR, Wainwright DS (1994) Rechargeable lithium batteries with aqueous-electrolytes. Science 264(5162):1115–1118. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.264.5162.1115
Manthiram A, Yu X, Wang S (2017) Lithium battery chemistries enabled by solid-state electrolytes. Nat Rev Mater 2(4):16103. https://doi.org/10.1038/natrevmats.2016.103
Zhang Y, Zuo TT, Popovic J, Lim K, Yin YX, Maier J, Guo YG (2020) Towards better Li metal anodes: challenges and strategies. Mater Today 33:56–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2019.09.018
Placke T, Kloepsch R, Duehnen S, Winter M (2017) Lithium ion, lithium metal, and alternative rechargeable battery technologies: the odyssey for high energy density. J Solid State Electr 21(7):1939–1964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3610-7
Zhao Y, Zheng K, Sun X (2018) Addressing interfacial issues in liquid-based and solid-state batteries by atomic and molecular layer deposition. Joule 2(12):2583–2604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2018.11.012
Goodenough JB (2013) Evolution of strategies for modern rechargeable batteries. Accounts Chem Res 46(5):1053–1061. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar2002705
Famprikis T, Canepa P, Dawson JA, Islam MS, Masquelier C (2019) Fundamentals of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for batteries. Nat Mater 18(12):1278–1291. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-019-0431-3
Sun C, Liu J, Gong Y, Wilkinson DP, Zhang J (2017) Recent advances in all-solid-state rechargeable lithium batteries. Nano Energy 33:363–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.01.028
Gao Z, Sun H, Fu L, Ye F, Zhang Y, Luo W, Huang Y (2018) Promises, challenges, and recent progress of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Adv Mater 30(17):1705702. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201705702
Shea JJ, Luo C (2020) Organic electrode materials for metal ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Inter 12(5):5361–5380. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b20384
Dirican M, Yan C, Zhu P, Zhang X (2019) Composite solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Mater Sci Eng R 136:27–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2018.10.004
Zhao W, Yi J, He P, Zhou H (2019) Solid-state electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries: fundamentals, challenges and perspectives. Electrochem Energy R 2(4):574–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41918-019-00048-0
Wu P, Zhou W, Su X, Li J, Su M, Zhou X, Sheldon BW, Lu W (2023) Recent advances in conduction mechanisms, synthesis methods, and improvement strategies for Li1+xAlxTi2-x(PO4)3 solid electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Adv Energy Mater 13(4):2203440. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202203440
Huang Y, Jiang Y, Zhou YX, Hu ZW, Zhu XH (2019) Influence of liquid solutions on the ionic conductivity of Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 solid electrolytes. ChemElectroChem 6(24):6016–6026. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201901687
Liu Y, Sun Q, Zhao Y, Wang B, Kaghazchi P, Adair KR, Li R, Zhang C, Liu J, Kuo L, Hu Y, Sham T, Zhang L, Yang R, Lu S, Song X, Sun X (2018) Stabilizing the interface of NASICON solid electrolyte against Li metal with atomic layer deposition. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10(37):31240–31248. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b06366
Porz L, Swamy T, Sheldon BW, Rettenwander D, Froemling T, Thaman HL, Berendts S, Uecker R, Carter WC, Chiang Y (2017) Mechanism of lithium metal penetration through inorganic solid electrolytes. Adv Energy Mater 7(20):1701003. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201701003
Xue Z, He D, Xie X (2015) Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3(38):19218–19253. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta03471j
Yu X, Manthiram A (2021) A review of composite polymer-ceramic electrolytes for lithium batteries. Energy Storage Mater 34:282–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2020.10.006
Liu L, Zhang D, Yang T, Hu W, Meng X, Mo J, Hou W, Fan Q, Liu K, Jiang B, Chu L, Li M (2022) Flexible ion-conducting membranes with 3D continuous nanohybrid networks for high-performance solid-state metallic lithium batteries. J Energy Chem 75:360–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2022.08.036
Hu Q, Sun Z, Nie L, Chen S, Yu J, Liu W (2022) High-safety composite solid electrolyte based on inorganic matrix for solid-state lithium-metal batteries. Mater Today Energy 27:101052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2022.101052
Roman HE (1990) A continuum percolation model for dispersed ionic conductors. J Phys Condens Matter 2(17):3909–3917. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/2/17/002
Bonizzoni S, Ferrara C, Berbenni V, Anselmi-Tamburini U, Mustarelli P, Tealdi C (2019) NASICON-type polymer-in-ceramic composite electrolytes for lithium batteries. Phys Chem Chem Phys 21(11):6142–6149. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cp00405j
Zaman W, Hortance N, Dixit MB, De Andrade V, Hatzell KB (2019) Visualizing percolation and ion transport in hybrid solid electrolytes for Li-metal batteries. J Mater Chem A 7(41):23914–23921. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA05118J
Song X, Zhang H, Jiang D, Yang L, Zhang J, Yao M, Ji X, Wang G, Zhang S (2021) Enhanced transport and favorable distribution of Li-ion in a poly(ionic liquid) based electrolyte facilitated by Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 nanoparticles for highly-safe lithium metal batteries. Electrochim Acta 368:137581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.137581
Pan K, Zhang L, Qian W, Wu X, Dong K, Zhang H, Zhang S (2020) A flexible ceramic/polymer hybrid solid electrolyte for solid-state lithium metal batteries. Adv Mater 32(17):2000399. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202000399
Huang Y, Zhang Z, Gao H, Huang J, Li C (2020) Li1.5Al0.5Ti1.5(PO4)3 enhanced polyethylene oxide polymer electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Solid State Ion 356:115437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2020.115437
Ban X, Zhang W, Chen N, Sun C (2018) A high-performance and durable poly(ethylene oxide)-based composite solid electrolyte for all solid-state lithium battery. J Phys Chem C 122(18):9852–9858. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b02556
Méry A, Rousselot S, Lepage D, Aymé-Perrot D, Dollé M (2023) Limiting factors affecting the ionic conductivities of LATP/polymer hybrid electrolytes. Batteries 9(2):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9020087
Shen C, Huang Y, Yang J, Chen M, Liu Z (2021) Unraveling the mechanism of ion and electron migration in composite solid-state electrolyte using conductive atomic force microscopy. Energy Storage Mater 39:271–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.04.028
Zagórski J, Amo JM, Cordill MJ, Aguesse F, Buannic L, Llordés A (2019) Garnet-polymer composite electrolytes: new insights on local Li-ion dynamics and electrodeposition stability with Li metal anodes. ACS Appl Energy Mater 2(3):1734–1746. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.8b01850
Funding
This work was financially supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant Nos. 2020YFH0047 and 2022ZYD0016) and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qiaohong Yan: Investigation, Methodology, Data curation, Writing—original draft. Xing Cheng: Methodology, Data curation. Rentai Yan: Data curation. Xingrui Pu: Validation. Xiaohong Zhu: Supervision, Writing—review & editing, Resources, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not involve any experiments with human participants or animal subjects.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Q., Cheng, X., Yan, R. et al. An ameliorated interface between PEO electrolyte and Li anode by Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 nanoparticles. J Solid State Electrochem 28, 601–607 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-023-05712-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-023-05712-6