Abstract
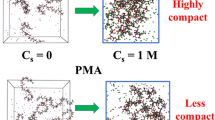
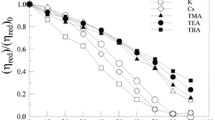
The intermolecular structure and solvation enthalpy of anionic polyelectrolyte atactic Na+-polyethacrylate (PEA) in aqueous solution, as a function of added salt concentration C s (dilute to concentrated) and valency (NaCl versus CaCl2), were investigated via molecular dynamics simulations with explicit-ion-solvent and atomistic polymer description. An increase in C s leads to a decrease in α, which stabilizes to a constant value beyond critical C s. A significant reduction in R g in the presence of CaCl2 salt was observed, due to ion bridging of PEA by Ca2+ ions, in agreement with results available in literature on other similar polycarboxylates. An increase in salt valency reduces the value of critical C s for the onset of stabilization of the overall size and shape of the polymer chain. The critical C s ratio for the divalent to monovalent salt case is in excellent agreement with results of Langevin dynamics studies on model systems available in the literature. PEA–water H-bond half-life increases with C s for CaCl2, but no appreciable effect is seen for NaCl. The hydration of PEA becomes stronger in the presence of divalent salt. The strength of H-bond interaction energy is greater for cations as compared to anions of the salt. The salt cation effect in displacing water molecules from the vicinity of PEA, with increase in C s, is greater for NaCl solution. The decrease in water coordination to PEA carboxylate groups, due to increased C s, is more pronounced in NaCl solution. The nature of the behavior of the solvation enthalpy of PEA and the type of intermolecular interactions contributing to it, is in agreement with experimental observations from the literature. The hydration enthalpy of PEA in divalent CaCl2 aqueous salt solution is more exothermic compared to monovalent NaCl salt solution, in agreement with experimental data. The solvation of PEA is thermodynamically more favorable in the case of CaCl2 solution. The exothermic solvation enthalpy, H-bond lifetime, number of H-bonds and H-bond interaction energy are greater in magnitude in CaCl2 aqueous solution.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobrynin AV (2008) Theory and simulations of charged polymers: from solution properties to polymeric nanomaterials. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 13(6):376–388
Dobrynin AV, Rubinstein M (2005) Theory of polyelectrolytes in solutions and at surfaces. Prog Polym Sci 30(11):1049–1118
Jiang H, Taranekar P, Reynolds JR, Schanze KS (2009) Conjugated polyelectrolytes: synthesis, photophysics, and applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 48(24):4300–4316
Coelho JF, Ferreira PC, Alves P, Cordeiro R, Fonseca AC, Góis JR, Gil MH (2010) Drug delivery systems: advanced technologies potentially applicable in personalized treatments. EPMA J 1(1):164–209
Zhuk A, Pavlukhina S, Sukhishvili SA (2009) Hydrogen-bonded layer-by-layer temperature-triggered release films. Langmuir 25(24):14025–14029
Seki K, Tirrell DA (1984) pH-dependent complexation of poly (acrylic acid) derivatives with phospholipid vesicle membranes. Macromolecules 17(9):1692–1698
You H, Tirrell DA (1991) Photoinduced, polyelectrolyte-driven release of contents of phosphatidylcholine bilayer vesicles. J Am Chem Soc 113(10):4022–4023
Thomas JL, You H, Tirrell DA (1995) Tuning the response of a pH-sensitive membrane switch. J Am Chem Soc 117(10):2949–2950
Linhardt JG, Thomas JL, Tirrell DA (1999) Free-radical synthesis of poly (2-ethylacrylic acid) fractions of low polydispersity: effects of molecular weight and polydispersity on the pH-dependent conformational transition in aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 32(13):4457–4459
Yessine MA, Leroux JC (2004) Membrane-destabilizing polyanions: interaction with lipid bilayers and endosomal escape of biomacromolecules. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56(7):999–1021
Sedlák M, Koňák C (2009) A new approach to polymer self-assembly into stable nanoparticles: poly (ethylacrylic acid) homopolymers. Macromolecules 42(19):7430–7438
Fichtner F, Schönert H (1977) Kooperative zustandsänderung von polyäthylacrylsäure in wäßriger lösung. Colloid Polym Sci 255(3):230–232
Joyce DE, Kurucsev T (1981) Hydrogen ion equilibria in poly (methacrylic acid) and poly (ethacrylic acid) solutions. Polymer 22(3):415–417
Sugai S, Nitta K, Ohno N, Nakano H (1983) Conformational studies on poly (ethacrylic acid) in aqueous salts by potentiometric, viscometric, optical and1H-NMR measurements. Colloid Polym Sci 261(2):159–165
Muroga Y, Iida S, Shimizu S, Ikake H, Kurita K (2004) Conformation of poly (sodium ethacrylate) in solution studied by small-angle X-ray scattering. Biophys Chem 110(1):49–58
Peljhan S, Zˇagar E, Cerkovnik J, Kogej K (2009) Strong intermolecular association between short poly (ethacrylic acid) chains in aqueous solutions. J Phys Chem B 113(8):2300–2309
Sappidi P, Sulatha MS, Natarajan U (2014) Conformations and hydration structure of hydrophobic polyelectrolyte atactic poly (ethacrylic acid) in dilute aqueous solution as a function of neutralisation. Mol Simul 40(4):295–305
Förster S, Schmidt M, Antonietti M (1990) Static and dynamic light scattering by aqueous polyelectrolyte solutions: effect of molecular weight, charge density and added salt. Polymer 31(5):781–792
Murayama Y, Sakamaki Y, Sano M (2003) Elastic response of single DNA molecules exhibits a reentrant collapsing transition. Phys Rev Lett 90(1):018102
Roiter Y, Trotsenko O, Tokarev V, Minko S (2010) Single molecule experiments visualizing adsorbed polyelectrolyte molecules in the full range of mono-and divalent counterion concentrations. J Am Chem Soc 132(39):13660–13662
Beer M, Schmidt M, Muthukumar M (1997) The electrostatic expansion of linear polyelectrolytes: Effects of gegenions, co-ions, and hydrophobicity. Macromolecules 30(26):8375–8385
Sarraguça JMG, Skepö M, Pais AACC, Linse P (2003) Structure of polyelectrolytes in 3: 1 salt solutions. J Chem Phys 119(23):12621–12628
Wei YF, Hsiao PY (2007) Role of chain stiffness on the conformation of single polyelectrolytes in salt solutions. J Chem Phys 127(6):064901
Wei YF, Hsiao PY (2010) Effect of chain stiffness onion distributions around a polyelectrolyte in multivalent salt solutions. J Chem Phys 132(2):024905
Hsiao PY, Luijten E (2006) Salt-induced collapse and reexpansion of highly charged flexible polyelectrolytes. Phys Rev Lett 97(14):148301
Liu S, Ghosh K, Muthukumar M (2003) Polyelectrolyte solutions with added salt: a simulation study. J Chem Phys 119(3):1813–1823
Carrillo JMY, Dobrynin AV (2011) Polyelectrolytes in salt solutions: molecular dynamics simulations. Macromolecules 44(14):5798–5816
Schweins R, Hollmann J, Huber K (2003) Dilute solution behaviour of sodium polyacrylate chains in aqueous NaCl solutions. Polymer 44(23):7131–7141
Schweins R, Lindner P, Huber K (2003) Calcium induced shrinking of NaPA chains: a SANS investigation of single chain behavior. Macromolecules 36(25):9564–9573
Luo Z, Wang X, Zhang G (2012) Ion-specific effect on dynamics of polyelectrolyte chains. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14(19):6812–6816
Lobaskin V, Qamhieh K (2003) Effective macroion charge and stability of highly asymmetric electrolytes at various salt conditions. J Phys Chem B 107(32):8022–8029
Pozar J, Bohinc K, Vlachy V, Kovacevic D (2011) Ion-specific and charge effects in counterion binding to poly (styrenesulfonate) anions. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13(34):15610–15618
Daoust H, Chabot MA (1980) Effect of cation size and of the presence of hydrophobic groups on heats of dilution of aqueous solutions of alkali metal and tetramethylammonium salts of the polyacrylic series. Macromolecules 13(3):616–619
Burba CM, Carter SM, Meyer KJ, Rice CV (2008) Salt effects on poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) phase transition thermodynamics from NMR spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 112(34):10399–10404
Ghosh T, Kalra A, Garde S (2005) On the salt-induced stabilization of pair and many-body hydrophobic interactions. J Phys Chem B 109(1):642–651
Ben-Naim A, Yaacobi M (1974) Effects of solutes on the strength of hydrophobic interaction and its temperature dependence. J Phys Chem 78(2):170–175
Athawale MV, Sarupria S, Garde S (2008) Enthalpy-entropy contributions to salt and osmolyte effects on molecular-scale hydrophobic hydration and interactions. J Phys Chem B 112(18):5661–5670
Accelrys Software (2007) Materials studio modeling environment, release 5.0. Accelrys Software, San Diego
Suter UW, Flory PJ (1975) Conformational energy and configurational statistics of polypropylene. Macromolecules 8(6):765–776
Rapold RF, Suter UW (1994) Conformational characteristics of polystyrene. Macromol Theory Simul 3(1):1–17
Suter UW (1981) Epimerization of vinyl polymers to stereochemical equilibrium. 1. Theory. Macromolecules 14(3):523–528
Oostenbrink C, Villa A, Mark AE, Van Gunsteren WF (2004) A biomolecular force field based on the free enthalpy of hydration and solvation: the GROMOS force‐field parameter sets 53A5 and 53A6. J Comput Chem 25(13):1656–1676
Berendsen H J, Postma JP, Van Gunsteren WF, Hermans J (1981) Interaction models for water in relation to protein hydration. In: Pullman B (ed) Intermolecular forces. Reidel, Dordracht, pp 331–342
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79(2):926–935
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1993) Particle mesh Ewald: an N log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98(12):10089–10092
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103(19):8577–8593
Hess B, Bekker H, Berendsen HJ, Fraaije JG (1997) LINCS: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 18(12):1463–1472
Berendsen HJ, Postma JV, Van Gunsteren WF, DiNola ARHJ, Haak JR (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81(8):3684–3690
Eslami H, Mozaffari F, Moghadasi J, Müller-Plathe F (2008) Molecular dynamics simulation of confined fluids in isosurface-isothermal-isobaric ensemble. J Chem Phys 129(19):194702
Basconi JE, Shirts MR (2013) Effects of temperature control algorithms on transport properties and kinetics in molecular dynamics simulations. J Chem Theory Comput 9(7):2887–2899
Hess B, Kutzner C, Van Der Spoel D, Lindahl E (2008) GROMACS 4: algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4(3):435–447
Miyamoto S, Kollman PA (1992) SETTLE: an analytical version of the SHAKE and RATTLE algorithm for rigid water models. J Comput Chem 13(8):952–962
Schweins R, Huber K (2001) Collapse of sodium polyacrylate chains in calcium salt solutions. Eur Phys J E 5(1):117–126
Molnar F, Rieger J (2005) Like-charge attraction” between anionic polyelectrolytes: molecular dynamics simulations. Langmuir 21(2):786–789
Bulo RE, Donadio D, Laio A, Molnar F, Rieger J, Parrinello M (2007) “Site Binding” of Ca2+ ions to polyacrylates in water: a molecular dynamics study of coiling and aggregation. Macromolecules 40(9):3437–3442
Neuman RC Jr, Woolfenden WR, Jonas V (1969) Effect of hydrogen bonding on the barrier to rotation about amide bonds. J Phys Chem 73(10):3177–3180
Sharp KA, Madan B, Manas E, Vanderkooi JM (2001) Water structure changes induced by hydrophobic and polar solutes revealed by simulations and infrared spectroscopy. J Chem Phys 114(4):1791–1796
Luzar A (2000) Resolving the hydrogen bond dynamics conundrum. J Chem Phys 113(23):10663–10675
Luzar A, Chandler D (1996) Hydrogen-bond kinetics in liquid water. Nature 379(6560):55–57
van der Spoel D, van Maaren PJ, Larsson P, Tîmneanu N (2006) Thermodynamics of hydrogen bonding in hydrophilic and hydrophobic media. J Phys Chem B 110(9):4393–4398
Powell DH, Barnes AC, Enderby JE, Neilson GW, Salmon PS (1988) The hydration structure around chloride ions in aqueous solution. Faraday Discuss Chem Soc 85:137–146
Collins KD, Neilson GW, Enderby JE (2007) Ions in water: characterizing the forces that control chemical processes and biological structure. Biophys Chem 128(2):95–104
Thomas AS, Elcock AH (2007) Molecular dynamics simulations of hydrophobic associations in aqueous salt solutions indicate a connection between water hydrogen bonding and the Hofmeister effect. J Am Chem Soc 129(48):14887–14898
Lyubartsev AP, Laaksonen A (1996) Concentration effects in aqueous NaCl solutions. A molecular dynamics simulation. J Phys Chem 100(40):16410–16418
Perera L, Berkowitz ML (1991) Many‐body effects in molecular dynamics simulations of Na+ (H2O) n and Cl–(H2O) n clusters. J Chem Phys 95(3):1954–1963
Megyes T, Bako I, Balint S, Grosz T, Radnai T (2006) Ion pairing in aqueous calcium chloride solution: Molecular dynamics simulation and diffraction studies. J Mol Liq 129(1):63–74
Bruni F, Imberti S, Mancinelli R, Ricci MA (2012) Aqueous solutions of divalent chlorides: ions hydration shell and water structure. J Chem Phys 136(6):064520
Hess B, van der Vegt NF (2006) Hydration thermodynamic properties of amino acid analogues: a systematic comparison of biomolecular force fields and water models. J Phys Chem B 110(35):17616–17626
Sinn CG, Dimova R, Antonietti M (2004) Isothermal titration calorimetry of the polyelectrolyte/water interaction and binding of Ca2+: effects determining the quality of polymeric scale inhibitors. Macromolecules 37(9):3444–3450
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the availability of the Virgo supercomputing cluster at the Indian Institute of Technology Madras, on which most of the simulations were carried out. The structural and dynamic analysis as well some of the preparatory NVT and NPT simulations were carried out on individual Linux workstations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 158 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sappidi, P., Natarajan, U. Effect of salt valency and concentration on structure and thermodynamic behavior of anionic polyelectrolyte Na+-polyethacrylate aqueous solution. J Mol Model 22, 274 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-016-3144-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-016-3144-4