Abstract
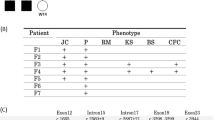
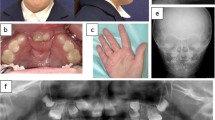
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS) is a rare autosomal dominant disease characterized by the development of multiple jaw keratocysts and basal cell carcinomas (BCC) and accompanied by diverse phenotypes. The establishment of diagnosis lies on the identification of a heterozygous germline pathogenic variant in the patched homolog 1 gene (PTCH1). PTCH1 has alternative splicing and selective initial coding exon, leading to three types of encoding proteins (PTCHL, PTCHM and PTCHS). The expression of each protein in NBCCS remains ambiguous, especially the importance of the first two exons in translation. Here, we report a Chinese NBCCS family of a novel PTCH1 heterozygous mutation (IVS 2, c.394+1G>T, g.10652G>T) identified by genomic sequencing and reverse-transcription-PCR as aberrant splicing. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of NBCCS with a splicing site mutation in intron 2 resulting in exon 2 skipping. Our finding suggests that exon 2 plays an important role in the development of NBCCS and further speculates that the role of longer isoforms PTCHL and PTCHM is crucial in NBCCS, while that of short isoform PTCHS might be dispensable.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gorlin RJ (1987) Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore) 66(2):98–113
Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J et al (1996) Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science 272(5268):1668–1671
Shimokawa T, Svard J, Heby-Henricson K, Teglund S, Toftgard R, Zaphiropoulos PG (2007) Distinct roles of first exon variants of the tumor-suppressor patched1 in Hedgehog signaling. Oncogene 26(34):4889–4896. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210301
Evans DG, Ladusans EJ, Rimmer S, Burnell LD, Thakker N, Farndon PA (1993) Complications of the naevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome: results of a population based study. J Med Genet 30(6):460–464
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S et al (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17(5):405–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.30
Gielen R, Reinders M, Koillinen HK, Paulussen ADC, Mosterd K, van Geel M (2018) PTCH1 isoform 1b is the major transcript in the development of basal cell nevus syndrome. J Hum Genet 63(9):965–969. https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-018-0485-0
Nagao K, Toyoda M, Takeuchi-Inoue K, Fujii K, Yamada M, Miyashita T (2005) Identification and characterization of multiple isoforms of a murine and human tumor suppressor, patched, having distinct first exons. Genomics 85(4):462–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2004.11.014
Suzuki M, Hatsuse H, Nagao K et al (2012) Selective haploinsufficiency of longer isoforms of PTCH1 protein can cause nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. J Hum Genet 57(7):422–426. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.45
Savino M, d'Apolito M, Formica V et al (2004) Spectrum of PTCH mutations in Italian nevoid basal cell-carcinoma syndrome patients: identification of thirteen novel alleles. Hum Mutat 24(5):441. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.9289
Kato C, Fujii K, Arai Y et al (2017) Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome caused by splicing mutations in the PTCH1 gene. Fam Cancer 16(1):131–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10689-016-9924-2
Acknowledgements
We thank all the subjects for participating in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Zhang, G., Shi, M. et al. A novel splicing mutation of PTCH1 in a Chinese family with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Med Mol Morphol 52, 235–237 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-019-00222-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-019-00222-9