Abstract
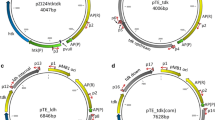
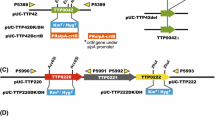
We constructed a new Thermus thermophilus cloning vector which enables the colour selection of cloned DNA inserts in the T. thermophilus HB27 host strain (β-gal−) on growth plates containing 3,4-cyclohexenoesculetin β-d-galactopyranoside (S-gal) in the medium. This vector harbors a modified β-galactosidase gene (TTP0042 of T. thermophilus HB27) with 12 unique restriction enzyme sites (Acc65I, AvrII, BlpI, BssHII, EcoRI, EcoRV, HindIII, NruI, SalI, SpeI, SphI and XbaI) as multiple cloning sites under the control of the T. thermophilus slpA promoter. This host–vector system facilitates cloning procedures in T. thermophilus HB27.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- bp:
-
Base pair
- MCS:
-
Multiple cloning sites
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
References
Angelov A, Li H, Geissler A, Leis B, Liebl W (2013) Toxicity of indoxyl derivative accumulation in bacteria and its use as a new counterselection principle. Syst Appl Microbiol 3:585–592
Aoki K, Itoh T (2007) Characterization of the ColE2-like replicon of plasmid pTT8 for Thermus thermophilus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 353:1028–1033
Casadaban M, Chou J, Cohen SN (1980) In-vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active β-galactosidase segment to amino terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol 143:971–980
Cava F, Hidalgo A, Berenguer J (2009) Thermus thermophilus as biological model. Extremophiles 13:213–231
de Grado M, Castan P, Berenguer J (1999) A high-transformation-efficiency cloning vector for Thermus thermophilus. Plasmid 42:241–245
Fujita A, Misumi Y, Koyama Y (2012) Two versatile vectors for Thermus thermophilus–Escherichia coli containing multiple cloning sites, lacZα gene and kanamycin or hygromycin resistance marker. Plasmid 67:272–275
Fujita A, Misumi Y, Honda S, Sato T, Koyama Y (2013) Construction of new cloning vectors that employ the phytoene synthase encoding gene for color screening of cloned DNA inserts in Thermus thermophilus. Gene 527:655–662
Fujita A, Sato T, Koyama Y, Misumi Y (2015) A reporter gene system for the precise measurement of promoter activity in Thermus thermophilus HB27. Extremophiles 19:1193–1201
Hashimoto Y, Yano T, Kuramitsu S, Kagamiyama H (2001) Disruption of Thermus thermophilus genes by homologous recombination using a thermostable kanamycin-resistant marker. FEBS Lett 506:231–234
Heuermann K, Cosgrove J (2001) S-Gal: an autoclavable dye for color selection of cloned DNA inserts. Biotechniques 30:1142–1147
Koyama Y, Hoshino T, Tomizuka N, Furukawa K (1986) Genetic transformation of the thermophile Thermus thermophilus and of other Thermus spp. J Bacteriol 166:338–340
Koyama Y, Okamoto S, Furukawa K (1990) Cloning of α- and β-galactosidase genes from an extreme Thermophile, Thermus strain T2, and their expression in Thermus thermophilus HB27. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2251–2254
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Nakamura A, Takakura Y, Kobayashi H, Hoshino T (2005) In vivo directed evolution for thermostabilization of Escherichia coli hygromycin B phosphotransferase and the use of the gene as a selection marker in the host–vector system of Thermus thermophilus. J Biosci Bioeng 100:158–163
Ohsima T, Imabori K (1974) Description of Thermus thermophilus (Yoshida and Ohshima) comb. nov., a nonsporulating thermophilic bacterium from Japanese spa. Int J Syst Bacteriol 24:102–112
Ramaley FR, Hixson J (1970) Isolation of nonpigmented, thermophilic bacterium similar to Thermus aquaticus. J Bacteriol 103:527–528
Vieira J, Messing J (1982) The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene 19:259–268
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mr. Jiro Hasegawa for technical assistance, with illustrations. We would like to thank Editage (http://www.editage.jp) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by L. Huang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, A., Misumi, Y. Development of a new host–vector system for colour selection of cloned DNA inserts using a newly designed β-galactosidase gene containing multiple cloning sites in Thermus thermophilus HB27. Extremophiles 21, 1111–1117 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-017-0961-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-017-0961-z