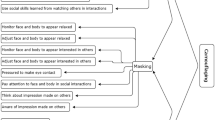
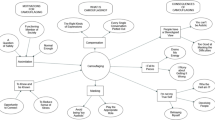
Abstract
While numerous studies suggest that emotion dysregulation is important in maintaining social anxiety among adults, the role of emotion regulation in children and adolescents with social anxiety is not yet well understood. In this systematic review, we use the process model of emotion regulation as a framework for understanding emotion regulation in children and adolescents with social anxiety. We performed a systematic literature search in the electronic data bases Medline and PsycINFO. Additional studies were identified by hand search. We identified 683 studies, screened their titles and abstracts, viewed 142 studies, and included 55 of these. Study results indicate that children and adolescents with social anxiety disorder or high social anxiety show emotion dysregulation across all five domains of emotion regulation, such as enhanced social avoidance, more safety behaviors, repetitive negative thinking, biased attention and interpretation of social information, and reduced emotional expression. While enhanced social avoidance seems to be specific to childhood social anxiety, other maladaptive emotion regulation strategies, such as repetitive negative thinking, seem to occur transdiagnostically across different childhood anxiety disorders. Implications for current theory, interventions and future research are discussed.

MAD mixed anxiety disorders
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed SP, Bittencourt-Hewitt A, Sebastian CL (2015) Neurocognitive bases of emotion regulation development in adolescence. Dev Cogn Neurosci 15:11–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2015.07.006
Aldao A (2013) The future of emotion regulation research: capturing context. Perspect Psychol Sci 8(2):155–172. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691612459518
Aldao A, Nolen-Hoeksema S, Schweizer S (2010) Emotion-regulation strategies across psychopathology: a meta-analytic review. Clin Psychol Rev 30(2):217–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2009.11.004
Alfano CA, Beidel DC, Turner SM (2006) Cognitive correlates of social phobia among children and adolescents. J Abnorm Child Psychol 34(2):189–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-005-9012-9
Alkozei A, Cooper PJ, Creswell C (2014) Emotional reasoning and anxiety sensitivity: associations with social anxiety disorder in childhood. J Affect Disord 152–154:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2013.09.014
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, D.C.
Anderson ER, Hope DA (2009) The relationship among social phobia, objective and perceived physiological reactivity, and anxiety sensitivity in an adolescent population. J Anxiety Disord 23(1):18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2008.03.011
Asbrand J, Svaldi J, Krämer M, Breuninger C, Tuschen-Caffier B (2016) Familial accumulation of social anxiety symptoms and maladaptive emotion regulation. PLoS One 11(4):e0153153. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153153
Bacow TL, May JE, Brody LR, Pincus DB (2010) Are there specific metacognitive processes associated with anxiety disorders in youth? Psychol Res Behav Manag 3:81–90. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S11785
Baer RA (2003) Mindfulness training as a clinical intervention: a conceptual and empirical review. Clin Psychol Sci Pract 10(2):125–143. https://doi.org/10.1093/clipsy/bpg015
Banerjee R, Watling D (2010) Self-presentational features in childhood social anxiety. J Anxiety Disord 24(1):34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2009.08.004
Barrett PM, Rapee RM, Dadds MM, Ryan SM (1996) Family enhancement of cognitive style in anxious and aggressive children. J Abnorm Child Psychol 24(2):187–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01441484
Barrett PM, Turner C, Lowry-Webster H (2000) FRIENDS program for children. Australian Academic Press, Brisbane
Bittner A, Egger HL, Erkanli A, Jane Costello E, Foley DL, Angold A (2007) What do childhood anxiety disorders predict? J Child Psychol Psychiatry 48(12):1174–1183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01812.x
Bögels SM, Snieder N, Kindt M (2003) Specifity of dysfunctional thinking in children with symptoms of social anxiety, separation anxiety and generalized anxiety. Behav Change 20(3):160–169. https://doi.org/10.1375/bech.20.3.160.24836
Bögels SM, Mansell W (2004) Attention processes in the maintenance and treatment of social phobia: hypervigilance, avoidance and self-focused attention. Clin Psychol Rev 24(7):827–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2004.06.005
Bonanno GA, Burton CL (2013) Regulatory flexibility: an individual differences perspective on coping and emotion regulation. Perspect Psychol Sci 8(6):591–612. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691613504116
Buckner JD, Schmidt NB, Lang AR, Small JW, Schlauch RC, Lewinsohn PM (2008) Specificity of social anxiety disorder as a risk factor for alcohol and cannabis dependence. J Psychiatr Res 42(3):230–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2007.01.002
Cederlund R, Öst L (2011) Perception of threat in children with social phobia. Comparison to nonsocially anxious children before and after treatment. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 40(6):855–863. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2011.618448
Chen E, Matthews KA (2001) Cognitive appraisal biases: an approach to understanding the relation between socioeconomic status and cardiovascular reactivity in children. Ann Behav Med 23(2):101–111. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15324796ABM2302_4
Clark DM (2001) A cognitive perspective on social phobia. In: Crozier WR, Alden LE (eds) International handbook of social anxiety: concepts, research and interventions relating to the self and shyness. Wiley, Chichester, pp 405–430
Clark DM, Wells A, Heimberg RG, Liebowitz MR, Hope DA, Schneier FR (1995) A cognitive model of social phobia. In: Heimberg RG, Liebowitz MR, Hope DA, Schneier FR (eds) Social phobia: diagnosis, assessment, and treatment. Guilford Press, New York, pp 69–93
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey
Cole PM, Michel MK, O’Donnell Teti L (1994) The development of emotion regulation and dysregulation: a clinical perspective. Monogr Soc Res Child Dev 59(2/3):73–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5834.1994.tb01278.x
Collin L, Bindra J, Raju M, Gillberg C, Minnis H (2013) Facial emotion recognition in child psychiatry: a systematic review. Res Dev Disabil 34:1505–1520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.01.008
Creswell C, Murray L, Cooper P (2014) Interpretation and expectation in childhood anxiety disorders: age effects and social specificity. J Abnorm Child Psychol 42(3):453–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-013-9795-z
Cunha M, Gouveia JP, do Céu Salvador M (2008) Social fears in adolescence: the social anxiety and avoidance scale for adolescents. Eur Psychol 13(3):197–213. https://doi.org/10.1027/1016-9040.13.3.197
Davidson JRT, Hughes DC, George LK, Blazer DG (1994) The boundary of social phobia: exploring the threshold. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51(12):975–983. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950120047008
Dudeney J, Sharpe L, Hunt C (2015) Attentional bias towards threatening stimuli in children with anxiety: a meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev 40:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2015.05.007
Easterbrook PJ, Gopalan R, Berlin JA, Matthews DR (1991) Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet 337(8746):867–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(91)90201-Y
Ehring T, Watkins ER (2008) Repetitive negative thinking as a transdiagnostic process. Int J Cogn Ther 1(3):192–205. https://doi.org/10.1521/ijct.2008.1.3.192
Eisenberg N, Spinrad TL, Eggum ND (2010) Emotion-related self-regulation and its relation to children’s maladjustment. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 6:495–525. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.121208.131208
Esbjørn BH, Bender PK, Reinholdt-Dunne ML, Munck L, Ollendick TH (2012) The development of anxiety disorders: considering the contributions of attachment and emotion regulation. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 15(2):129–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-011-0105-4
Eschenbeck H, Kohlmann C-W, Lohaus A (2007) Gender differences in coping strategies in children and adolescents. J Individ Differ 28(1):18–26. https://doi.org/10.1027/1614-0001.28.1.18
Feldner MT, Zvolensky MJ (2004) Prevention of anxiety psychopathology: a critical review of the empirical literature. Clin Psychol Sci Pract 11(4):405–424. https://doi.org/10.1093/clipsy.bph098
Field AP, Lester KJ (2010) Is there room for ‘development’ in developmental models of information processing biases to threat in children and adolescents? Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 13(4):315–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-010-0078-8
Fröjd S, Ranta K, Kaltiala-Heino R, Marttunen M (2011) Associations of social phobia and general anxiety with alcohol and drug use in a community sample of adolescents. Alcohol Alcohol 46(2):192–199. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agq096
Fusar-Poli P, Solmi M, Brondino N, Davies C, Chae C, Politi P, McGuire P (2019) Trandsiagnostic psychiatry: a systematic review. World Psychiatry 18:192–207. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20631
Garnefski N, Rieffe C, Jellesma F, Terwogt MM, Kraaij V (2007) Cognitive emotion regulation strategies and emotional problems in 9-11-year-old children: the development of an instrument. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 16(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-006-0562-3
Giannini M, Loscalzo Y (2016) Social anxiety and adolescence: interpretation bias in an italian sample. Scand J Psychol 57(1):65–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/sjop.12263
Ginsburg GS, La Greca AM, Silverman WK (1998) Social anxiety in children with anxiety disorders: relation with social and emotional functioning. J Abnorm Child Psychol 26(3):175–185. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022668101048
Gonzalez A, Rozenman M, Langley AK, Kendall PC, Ginsburg GS, Compton S, Piacentini J (2017) Social interpretation bias in children and adolescents with anxiety disorders: psychometric examination of the Self-report of Ambiguous Social Situations for Youth (SASSY) scale. Child Youth Care Forum 46(3):395–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-016-9381-y
Grob A, Smolenski C (2009) FEEL-KJ. Fragebogen zur Erhebung der Emotionsregulation bei Kindern und Jugendlichen. Huber, Bern
Gross JJ (1998) The emerging field of emotion regulation: an integrative review. Rev Gen Psychol 2(3):271–299. https://doi.org/10.1037/1089-2680.2.3.271
Gross JJ, Thompson RA (2007) Emotion regulation: Conceptual foundations. In: Gross JJ (ed) Handbook of emotion regulation. Guilford Press, New York, pp 3–24
Gross JJ (1998) Antecedent- and response-focused emotion regulation: divergent consequences for experience, expression, and physiology. J Pers Soc Psychol 74(1):224–237. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.74.1.224
Gross JJ (2013) Emotion regulation: taking stock and moving forward. Emotion 13(3):359–365. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0032135
Gross JJ (2015) Emotion regulation: current status and future prospects. Psychol Inq 26(1):1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/1047840X.2014.940781
Guyer AE, Lau JYF, McClure-Tone EB, Parrish J, Shiffrin ND, Reynolds RC, Nelson EE (2008) Amygdala and ventrolateral prefrontal cortex function during anticipated peer evaluation in pediatric social anxiety. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65(11):1303–1312. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.65.11.1303
Halldorsson B, Creswell C (2017) Social anxiety in pre-adolescent children: what do we know about maintenance? Behav Res Ther 99:19–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2017.08.013
Haller SPW, Raeder SM, Scerif G, Cohen Kadosh K, Lau JYF (2016) Measuring online interpretations and attributions of social situations: links with adolescent social anxiety. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 50:250–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbtep.2015.09.009
Hannesdottir DK, Ollendick TH (2007) The role of emotion regulation in the treatment of child anxiety disorders. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 10(3):275–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-007-0024-6
Hayward C, Killen JD, Kraemer HC, Taylor CB (1998) Linking self-reported childhood behavioral inhibition to adolescent social phobia. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 37(12):1308–1316. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-199812000-00015
Hearn CS, Donovan CL, Spence SH, March S, Holmes MC (2017) What’s the worry with social anxiety? Comparing cognitive processes in children with generalized anxiety disorder and social anxiety disorder. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 48(5):786–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-016-0703-y
Heinrichs N, Hofmann SG (2001) Information processing in social phobia: a critical review. Clin Psychol Rev 21(5):751–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-7358(00)00067-2
Heiy JE, Cheavens JS (2014) Back to basics: a naturalistic assessment of the experience and regulation of emotion. Emotion 14(5):878–891. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0037231
Henry SL, Jamner LD, Whalen CK (2012) I (should) need a cigarette: adolescent social anxiety and cigarette smoking. Ann Behav Med 43(3):383–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-011-9340-7
Hezel DM, McNally RJ (2014) Theory of mind impaiments in social anxiety disorder. Behav Ther 45:530–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2014.02.010
Hirsch CR, Clark DM (2004) Information-processing bias in social phobia. Clin Psychol Rev 24(7):799–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2004.07.005
Hodson KJ, McManus FV, Clark DM, Doll H (2008) Can Clark and Wells’ (1995) cognitive model of social phobia be applied to young people? Behav Cogn Psychother 36(04):449–461. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1352465808004487
Hunt M (1997) How science takes stock: the story of meta-analysis. Russel Stage Foundation, New York
In-Albon T, Dubi K, Rapee RM, Schneider S (2009) Forced choice reaction time paradigm in children with separation anxiety disorder, social phobia, and nonanxious controls. Behav Res Ther 47(12):1058–1065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2009.08.003
In-Albon T, Schneider S (2007) Psychotherapy of childhood anxiety disorders: a meta-analysis. Psychother Psychosom 76:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1159/000096361
Jazaieri H, Morrison AS, Goldin PR, Gross JJ (2015) The role of emotion and emotion regulation in social anxiety disorder. Curr Psychiatry Rep 17(531):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-014-0531-3
Jazaieri H, Urry H, Gross J (2013) Affective disturbance and psychopathology: an emotion regulation perspective. J Exp Psychopathol 4(5):584–599. https://doi.org/10.5127/jep.030312
Joormann J, Vanderlind WM (2014) Emotion regulation in depression: the role of biased cognition and reduced cognitive control. Clin Psychol Sci 2(4):402–421. https://doi.org/10.1177/2167702614536163
Kashdan TB, Steger MF (2006) Expanding the topography of social anxiety: an experience-sampling assessment of positive emotions, positive events, and emotion suppression. Psychol Sci 17(2):120–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01674.x
Keil V, Asbrand J, Tuschen-Caffier B, Schmitz J (2017) Children with social anxiety and other anxiety disorders show similar deficits in habitual emotional regulation: evidence for a transdiagnostic phenomenon. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 26(7):749–757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-017-0942-x
Keil V, Uusberg A, Blechert J, Tuschen-Caffier B, Schmitz J (2018) Facial gender but not emotion distinguishes neural responses of 10- to 13-year-old children with social anxiety disorder from healthy and clinical controls. Biol Psychol 135:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2018.02.004
Kessler RC, Petukhova M, Sampson NA, Zaslavsky AM, Wittchen H-U (2012) Twelve-month and lifetime prevalence and lifetime morbid risk of anxiety and mood disorders in the United States. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 21(3):169–184. https://doi.org/10.1002/mpr.1359
Kindt M, Bögels S, Morren M (2003) Processing bias in children with separation anxiety disorder, social phobia and generalised anxiety disorder. Behav Change 20(3):143–150. https://doi.org/10.1375/bech.20.3.143.24832
Klemanski DH, Curtiss J, McLaughlin KA, Nolen-Hoeksema S (2017) Emotion regulation and the transdiagnostic role of repetitive negative thinking in adolescents with social anxiety and depression. Cogn Ther Res 41(2):206–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-016-9817-6
Kley H, Tuschen-Caffier B, Heinrichs N (2012) Safety behaviors, self-focused attention and negative thinking in children with social anxiety disorder, socially anxious and non-anxious children. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 43(1):548–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbtep.2011.07.008
Koole S (2009) The psychology of emotion regulation: an integrative review. Cogn Emot 23:4–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699930802619031
Kross E, Ayduk O, Mischel W (2005) When asking why does not hurt: distinguishing rumination from reflective processing of negative emotions. Psychol Sci 16(9):709–715. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2005.01600.x
La Greca AM, Lopez N (1998) Social anxiety among adolescents: linkages with peer relations and friendships. J Abnorm Child Psychol 26(2):83–94
Lang PJ, McTeague LM (2009) The anxiety disorder spectrum: fear imagery, physiological reactivity, and differential diagnosis. Anxiety Stress Coping 22(1):5–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/10615800802478247
Lang PJ, McTeague LM, Bradley MM (2016) RDoC, DSM, and the reflex physiology of fear: a biodimensional analysis of the anxiety disorders spectrum. Psychophysiology 53(3):336–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.12462
Leehr EJ, Krohmer K, Schag K, Dresler T, Zipfel S, Giel KE (2015) Emotion regulation model in binge eating disorder and obesity: a systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 49:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.12.008
Legerstee JS, Garnefski N, Jellesma FC, Verhulst FC, Utens EMWJ (2010) Cognitive coping and childhood anxiety disorders. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 19(2):143–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-009-0051-6
Legerstee JS, Garnefski N, Verhulst FC, Utens EMWJ (2011) Cognitive coping in anxiety-disordered adolescents. J Adolesc 34(2):319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2010.04.008
López-Pérez B, Gummerum M, Wilson EL, Dellaria G (2017) Studying children’s intrapersonal emotion regulation strategies from the process model of emotion regulation. J Genet Psychol 178(2):73–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221325.2016.1230085
Loscalzo Y, Giannini M, Miers AC (2017) Social anxiety and interpretation bias: Examining clinical and subclinical components in adolescents. Child Adolesc Ment Health. https://doi.org/10.1111/camh.12221
Masia-Warner C, Storch EA, Pincus DB, Klein RG, Heimberg RG, Liebowitz MR (2003) The Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale for Children and Adolescents: an initial psychometric investigation. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42(9):1076–1084. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.CHI.0000070249.24125.89
McEvoy PM, Mahoney AEJ, Moulds ML (2010) Are worry, rumination, and post-event processing one and the same? Development of the repetitive thinking questionnaire. J Anxiety Disord 24(5):509–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2010.03.008
McEvoy PM, Watson H, Watkins ER, Nathan P (2013) The relationship between worry, rumination, and comorbidity: evidence for repetitive negative thinking as a transdiagnostic construct. J Affect Disord 151(1):313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2013.06.014
McGorry PD, Purcell R, Hickie IB, Yung AR, Pantelis C, Jackson HJ (2007) Clinical staging: a heuristic model for psychiatry and youth mental health. Med J Aust 187(7):40–42
McRae K (2016) Cognitive emotion regulation: a review of theory and scientific findings. Curr Opin Behav Sci 10:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobeha.2016.06.004
McRae K, Gross JJ, Weber J, Robertson ER, Sokol-Hessner P, Ray RD, Ochsner KN (2012) The development of emotion regulation: an fMRI study of cognitive reappraisal in children, adolescents and young adults. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci 7(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsr093
McTeague LM, Lang PJ (2012) The anxiety spectrum and the reflex physiology of defense: from circumscribed fear to broad distress. Depress Anxiety 29(4):264–281. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.21891
Melfsen S, Osterlow J, Florin I (2000) Deliberate emotional expressions of socially anxious children and their mothers. J Anxiety Disord 14(3):249–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0887-6185(99)00037-7
Miers AC, Blöte AW, Bögels SM, Westenberg PM (2008) Interpretation bias and social anxiety in adolescents. J Anxiety Disord 22(8):1462–1471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2008.02.010
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol 62(10):1006–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005
Mor N, Winquist J (2002) Self-focused attention and negative affect: a meta-analysis. Psychol Bull 128(4):638–662. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.128.4.638
Morris AS, Silk JS, Steinberg L, Myers SS, Robinson LR (2007) The role of the family context in the development of emotion regulation. Soc Dev 16(2):361–388. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9507.2007.00389.x
Mullen B (2003) Advanced BASIC meta-analysis, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah
Muris P, Merckelbach H, Damsma E (2000) Threat perception bias in nonreferred, socially anxious children. J Clin Child Psychol 29(3):348–359. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP2903_6
Myllyneva A, Ranta K, Hietanen JK (2015) Psychophysiological responses to eye contact in adolescents with social anxiety disorder. Biol Psychol 109:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2015.05.005
Parkinson B, Totterdell P (1999) Classifying affect-regulation strategies. Cogn Emot 13(3):277–303. https://doi.org/10.1080/026999399379285
Pergamin-Hight L, Bitton S, Pine DS, Fox NA, Bar-Haim Y (2016) Attention and interpretation biases and attention control in youth with social anxiety disorder. J Exp Psychopathol 7(3):484–498. https://doi.org/10.1037/t03750-000
Quartana PJ, Burns JW (2007) Painful consequences of anger suppression. Emotion 7(2):400–414. https://doi.org/10.1037/1528-3542.7.2.400
Ranta K, Tuomisto MT, Kaltiala-Heino R, Rantanen P, Marttunen M (2014) Cognition, imagery and coping among adolescents with social anxiety and phobia: testing the Clark and Wells model in the population. Clin Psychol Psychother 21(3):252–263. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.1833
Rapee RM, Spence SH (2004) The etiology of social phobia: empirical evidence and an initial model. Clin Psychol Rev 24(7):737–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2004.06.004
Rheingold AA, Herbert JD, Franklin MM (2003) Cognitive bias in adolescents with social anxiety disorder. Cogn Ther Res 27(6):639–655. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026399627766
Rodebaugh TL, Holaway RM, Heimberg RG (2004) The treatment of social anxiety disorder. Clin Psychol Rev 24(7):883–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2004.07.007
Roy AK, Vasa RA, Bruck M, Mogg K, Bradley BP, Sweeney M, Pine DS (2008) Attention bias toward threat in pediatric anxiety disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 47(10):1189–1196. https://doi.org/10.1097/CHI.0b013e3181825ace
Rubin KH, Burgess K (2001) Social withdrawal. In: Vasey MW, Dadds MR (eds) The developmental psychopathology of anxiety. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 407–434
Rubin KH, Coplan RJ, Bowker JC (2009) Social withdrawal in childhood. Annu Rev Psychol 60:141–171. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.60.110707.163642
Schäfer JÖ, Naumann E, Holmes EA, Tuschen-Caffier B, Samson AC (2017) Emotion regulation strategies in depressive and anxiety symptoms in youth: a meta-analytic review. J Youth Adolesc 46(2):261–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-016-0585-0
Schmidtendorf S, Wiedau S, Asbrand J, Tuschen-Caffier B, Heinrichs N (2018) Attentional bias in children with social anxiety disorder. Cogn Ther Res 42:273–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-017-9880-7
Schmitz J, Blechert J, Krämer M, Asbrand J, Tuschen-Caffier B (2012) Biased perception and interpretation of bodily anxiety symptoms in childhood social anxiety. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 41(1):92–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2012.632349
Schmitz J, Krämer M, Blechert J, Tuschen-Caffier B (2010) Post-event processing in children with social phobia. J Abnorm Child Psychol 38(7):911–919. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-010-9421-2
Schmitz J, Krämer M, Tuschen-Caffier B (2011) Negative post-event processing and decreased self-appraisals of performance following social stress in childhood social anxiety: an experimental study. Behav Res Ther 49(11):789–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2011.09.001
Schwab D, Schienle A (2017a) Facial affect processing in social anxiety disorder with early onset: Evidence of an intensity amplification bias. Soc Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2017.1304990
Schwab D, Schienle A (2017b) Facial emotion processing in pediatric social anxiety disorder: relevance of situational context. J Anxiety Disord 50:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2017.05.005
Seefeldt WL, Krämer M, Tuschen-Caffier B, Heinrichs N (2014) Hypervigilance and avoidance in visual attention in children with social phobia. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 45(1):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbtep.2013.09.004
Sharp C, Croudace TJ, Goodyer IM (2007) Biased mentalizing in children aged seven to 11: latent class confirmation of response styles to social scenarios and sssociations with psychopathology. Soc Dev 16(1):181–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9507.2007.00378.x
Sharp C, Williams LL, Ha C, Baumgardner J, Michonski J, Selas R, Fonagy P (2009) The development of a mentalization-based outcomees and research protocol for an adolescent inpatient unit. Bull Menn 73(4):311–338. https://doi.org/10.1521/bumc.2009.73.4.311
Spence SH, Donovan C, Brechman-Toussaint M (1999) Social skills, social outcomes, and cognitive features of childhood social phobia. J Abnorm Psychol 108(2):211–221. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.108.2.211
Spokas ME, Rodebaugh TL, Heimberg RG (2007) Cognitive biases in social phobia. Psychiatry 6(5):204–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mppsy.2007.02.006
Stegge H, Terwogt MM (2007) Awareness and regulation of emotion in typical and atypical development. In: Gross JJ (ed) Handbook of emotion regulation. Guilford Press, New York, pp 269–286
Storch EA, Masia-Warner C, Heidgerken AD, Fisher PH, Pincus DB, Liebowitz MR (2006) Factor structure of the Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale for children and adolescents. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 37(1):25–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-006-0017-6
Strauss CC, Forehand R, Smith K, Frame CL (1986) The association between social withdrawal and internalizing problems in children. J Abnorm Child Psychol 14(4):525–535
Stuijfzand S, Creswell C, Field AP, Pearcey S, Dodd H (2017) Research review: is anxiety associated with negative interpretations of ambiguity in children and adolescents? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Child Psychol Psychiatry Allied Discip. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12822(advance online publication)
Thomas SA, Daruwala SE, Goepel KA, de Los Reyes A (2012) Using the Subtle Avoidance Frequency Examination in adolescent social anxiety assessments. Child Youth Care Forum 41(6):547–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-012-9181-y
Troy AS, Shallcross AJ, Mauss IB (2016) Corrigendum: a person-by-situation approach to emotion regulation: cognitive reappraisal can either help or hurt, depending on the context. Psychol Sci 27(3):428–431. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797615627417
Walker AS, Nowicki S, Jones J, Heimann L (2011) Errors in identifying and expressing emotion in facial expressions, voices, and postures unique to social anxiety. J Genet Psychol 172(3):293–301. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221325.2010.535224
Waters AM, Bradley BP, Mogg K (2014) Biased attention to threat in paediatric anxiety disorders (generalized anxiety disorder, social phobia, specific phobia, separation anxiety disorder) as a function of ‘distress’ versus ‘fear’ diagnostic categorization. Psychol Med 44(3):607–616. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291713000779
Waters AM, Mogg K, Bradley BP, Pine DS (2011) Attention bias for angry faces in children with social phobia. J Exp Psychopathol 2(4):475–489. https://doi.org/10.5127/jep.018111
Watkins ER (2008) Constructive and unconstructive repetitive thought. Psychol Bull 134(2):163–206. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.134.2.163
Webb TL, Miles E, Sheeran P (2012) Dealing with feeling: a meta-analysis of the effectiveness of strategies derived from the process model of emotion regulation. Psychol Bull 138(4):775–808. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0027600
Weeks M, Coplan RJ, Kingsbury A (2009) The correlates and consequences of early appearing social anxiety in young children. J Anxiety Disord 23(7):965–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2009.06.006
Weiss JA, Thomson K, Chan L (2014) A systematic literature review of emotion regulation measurement in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res 7:629–648. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.1426
Werner KH, Goldin PR, Ball TM, Heimberg RG, Gross JJ (2011) Assessing emotion regulation in social anxiety disorder: the emotion regulation interview. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 33(3):346–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-011-9225-x
Werner KH, Gross JJ (2010) Emotion regulation and psychopathology: A conceptual framework. In: Kring AM, Sloan DM (eds) Emotion regulation and psychopathology: a transdiagnostic approach to etiology and treament. Guilford Press, New York, pp 13–37
White LK, Helfinstein SM, Reeb-Sutherland BC, Degnan KA, Fox NA (2009) Role of attention in the regulation of fear and anxiety. Dev Neurosci 31(4):309–317. https://doi.org/10.1159/000216542
Wilhelm I, Groch S, Preiss A, Walitza S, Huber R (2017) Widespread reduction in sleep spindle activity in socially anxious children and adolescents. J Psychiatr Res 88:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.12.018
Wilson EJ, MacLeod C, Mathews A, Rutherford EM (2006) The causal role of interpretive bias in anxiety reactivity. J Abnorm Psychol 115(1):103–111. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.115.1.103
Windle M, Windle RC (2012) Testing the specificity between social anxiety disorder and drinking motives. Addict Behav 37(9):1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2012.04.009
Winsler A, Naglieri J (2003) Overt and covert verbal problem-solving strategies: developmental trends in use, awareness, and relations with task performance in children aged 5 to 17. Child Dev 74(3):659–678. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00561
Wittchen HU, Fuetsch M, Sonntag H, Müller N, Liebowitz M (2000) Disability and quality of life in pure and comorbid social phobia: findings from a controlled study. European Psychiatry 15(1):46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-9938(00)00211-X
Wittchen H-U, Fehm L (2003) Epidemiology and natural course of social fears and social phobia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 108(s417):4–18. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0447.108.s417.1.x
Zeman J, Klimes-Dougan B, Cassano M, Adrian M (2007) Measurement issues in emotion research with children and adolescents. Clin Psychol Sci Pract 14:377–401. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2850.2007.00098.x
Zhang P, Ni W, Xie R, Xu J, Liu X (2017) Gender differences in the difficulty in disengaging from threat among children and adolescents with social anxiety. Front Psychol 8:419. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golombek, K., Lidle, L., Tuschen-Caffier, B. et al. The role of emotion regulation in socially anxious children and adolescents: a systematic review. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 29, 1479–1501 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-019-01359-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-019-01359-9