Abstract
Objective
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) may lead to irreversible joint damage. The role of histone modifications in RA has been emphasized. This study investigated the effect of histone methyltransferase EZH2 on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) in RA.
Materials and methods
Synovial tissues were collected from RA patients and non-RA patients (NC). RA-FLSs and NC-FLSs were isolated and identified using flow cytometry. EZH2 expression in synovial tissues and FLSs was detected using RT-qPCR and Western blot. The proliferation, migration, and invasion of RA-FLSs and NC-FLSs were measured using MTT, EdU, and Transwell assays. The binding of EZH2, H3K27me3, and miR-22-3p was analyzed using ChIP assay. The targeting relationship between miR-22-3p and CYR61 was verified using dual-luciferase assay. miR-22-3p and CYR61 expressions were detected using RT-qPCR. CYR61 and H3K27me3 levels were detected using Western blot. Functional rescue experiments were performed to verify the effect of miR-22-3p or CYR61 on RA-FLSs.
Results
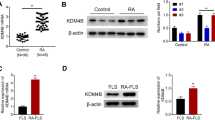
EZH2 was highly expressed in synovial tissues and FLSs from RA patients. The proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of RA-FLSs was stronger than that of NC-FLSs. Downregulation of EZH2 repressed proliferation, migration, and invasion of RA-FLSs. EZH2 inhibited miR-22-3p expression by binding to the miR-22-3p promoter and increasing H3K27me3 methylation level, and thereby upregulated CYR61 expression. Downregulation of miR-22-3p or overexpression of CYR61 annulled the inhibitory effect of EZH2 silencing on RA-FLS proliferation, migration, and invasion.
Conclusion
EZH2 bound to the miR-22-3p promoter and inhibited miR-22-3p expression by upregulating H3K27me3 level, thereby promoting CYR61 expression and inducing the proliferation, migration, and invasion of RA-FLSs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sparks JA (2019) Rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 170:ITC1–ITC16
Aletaha D, Smolen JS (2018) Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review. JAMA 320:1360–1372
Choy EH, Kavanaugh AF, Jones SA (2013) The problem of choice: current biologic agents and future prospects in RA. Nat Rev Rheumatol 9:154–163
Nygaard G, Firestein GS (2020) Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat Rev Rheumatol 16:316–333
Bartok B, Firestein GS (2010) Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 233:233–255
Choi C, Jeong W, Ghang B, Park Y, Hyun C, Cho M, Kim J (2020) Cyr61 synthesis is induced by interleukin-6 and promotes migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 22:275
Klein K, Gay S (2015) Epigenetics in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 27:76–82
Nemtsova MV, Zaletaev DV, Bure IV, Mikhaylenko DS, Kuznetsova EB, Alekseeva EA, Beloukhova MI, Deviatkin AA, Lukashev AN, Zamyatnin AA Jr (2019) Epigenetic changes in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Genet 10:570
Angiolilli C, Kabala PA, Grabiec AM, Van Baarsen IM, Ferguson BS, Garcia S, Malvar Fernandez B, McKinsey TA, Tak PP, Fossati G, Mascagni P, Baeten DL, Reedquist KA (2017) Histone deacetylase 3 regulates the inflammatory gene expression programme of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis 76:277–285
Bottini N, Firestein GS (2013) Epigenetics in rheumatoid arthritis: a primer for rheumatologists. Curr Rheumatol Rep 15:372
Yuan FL, Li X, Xu RS, Jiang DL, Zhou XG (2014) DNA methylation: roles in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Biochem Biophys 70:77–82
Klein K, Gay S (2013) Epigenetic modifications in rheumatoid arthritis, a review. Curr Opin Pharmacol 13:420–425
Trevino LS, Wang Q, Walker CL (2015) Phosphorylation of epigenetic “readers, writers and erasers”: implications for developmental reprogramming and the epigenetic basis for health and disease. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 118:8–13
Zhang X, Wang Y, Yuan J, Li N, Pei S, Xu J, Luo X, Mao C, Liu J, Yu T, Gan S, Zheng Q, Liang Y, Guo W, Qiu J, Constantin G, Jin J, Qin J, Xiao Y (2018) Macrophage/microglial Ezh2 facilitates autoimmune inflammation through inhibition of Socs3. J Exp Med 215:1365–1382
Trenkmann M, Brock M, Gay RE, Kolling C, Speich R, Michel BA, Gay S, Huber LC (2011) Expression and function of EZH2 in synovial fibroblasts: epigenetic repression of the Wnt inhibitor SFRP1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1482–1488
Xiao XY, Li YT, Jiang X, Ji X, Lu X, Yang B, Wu LJ, Wang XH, Guo JB, Zhao LD, Fei YY, Yang HX, Zhang W, Zhang FC, Tang FL, Zhang JM, He W, Chen H, Zhang X (2020) EZH2 deficiency attenuates Treg differentiation in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun 108:102404
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT et al (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Matsumoto S, Muller-Ladner U, Gay RE, Nishioka K, Gay S (1996) Ultrastructural demonstration of apoptosis, Fas and Bcl-2 expression of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. J Rheumatol 23:1345–1352
Park C, Kim GY, Jung JH, Kim WJ, Choi YH (2011) Pectenotoxin-2 induces G1 arrest of the cell cycle in synovial fibroblasts of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Med 27:783–787
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, Burmester GR, Emery P, Firestein GS, Kavanaugh A, McInnes IB, Solomon DH, Strand V, Yamamoto K (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4:18001
Bottini N, Firestein GS (2013) Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nat Rev Rheumatol 9:24–33
Smolen JS, Choe JY, Prodanovic N, Niebrzydowski J, Staykov I, Dokoupilova E, Baranauskaite A, Yatsyshyn R, Mekic M, Porawska W, Ciferska H, Jedrychowicz-Rosiak K, Zielinska A, Lee Y, Rho YH (2018) Safety, immunogenicity and efficacy after switching from reference infliximab to biosimilar SB2 compared with continuing reference infliximab and SB2 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results of a randomised, double-blind, phase III transition study. Ann Rheum Dis 77:234–240
Cao R, Wang L, Wang H, Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Jones RS, Zhang Y (2002) Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science 298:1039–1043
Kuzmichev A, Nishioka K, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Reinberg D (2002) Histone methyltransferase activity associated with a human multiprotein complex containing the Enhancer of Zeste protein. Gen Dev 16:2893–2905
Cai B, Li M, Zheng Y, Yin Y, Jin F, Li X, Dong J, Jiao X, Liu X, Zhang K, Li D, Wang J, Yin G (2020) EZH2-mediated inhibition of microRNA-22 promotes differentiation of hair follicle stem cells by elevating STK40 expression. Aging (Albany NY) 12:12726–12739
Lin J, Huo R, Xiao L, Zhu X, Xie J, Sun S, He Y, Zhang J, Sun Y, Zhou Z, Wu P, Shen B, Li D, Li N (2014) A novel p53/microRNA-22/Cyr61 axis in synovial cells regulates inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 66:49–59
Renman E, Brink M, Arlestig L, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Lejon K (2021) Dysregulated microRNA expression in rheumatoid arthritis families-a comparison between rheumatoid arthritis patients, their first-degree relatives, and healthy controls. Clin Rheumatol 40:2387–2394
Yang QY, Yang KP, Li ZZ (2020) MiR-22 restrains proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis by targeting IL6R and may be concerned with the suppression of NF-kappaB pathway. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 36:20–26
Fan Y, Yang X, Zhao J, Sun X, Xie W, Huang Y, Li G, Hao Y, Zhang Z (2019) Cysteine-rich 61 (Cyr61): a biomarker reflecting disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 21:123
Zhai T, Gao C, Huo R, Sheng H, Sun S, Xie J, He Y, Gao H, Li H, Zhang J, Li H, Sun Y, Lin J, Shen B, Xiao L, Li N (2017) Cyr61 participates in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis via promoting MMP-3 expression by fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Mod Rheumatol 27:466–475
Bustamante MF, Garcia-Carbonell R, Whisenant KD, Guma M (2017) Fibroblast-like synoviocyte metabolism in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 19:110
Karami J, Aslani S, Tahmasebi MN, Mousavi MJ, Sharafat Vaziri A, Jamshidi A, Farhadi E, Mahmoudi M (2020) Epigenetics in rheumatoid arthritis; fibroblast-like synoviocytes as an emerging paradigm in the pathogenesis of the disease. Immunol Cell Biol 98:171–186
Hu P, Dong ZS, Zheng S, Guan X, Zhang L, Li L, Liu Z (2021) The effects of miR-26b-5p on fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis (RA-FLS) via targeting EZH2. Tissue Cell 72:101591
Ye Z, Xu J, Li S, Cai C, Li T, Sun L (2017) LncIL7R promotes the growth of fibroblastlike synoviocytes through interaction with enhancer of zeste homolog 2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep 15:1412–1418
Duan R, Du W, Guo W (2020) EZH2: a novel target for cancer treatment. J Hematol Oncol 13:104
Evangelatos G, Fragoulis GE, Koulouri V, Lambrou GI (2019) MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: from pathogenesis to clinical impact. Autoimmun Rev 18:102391
Chen XM, Huang QC, Yang SL, Chu YL, Yan YH, Han L, Huang Y, Huang RY (2015) Role of Micro RNAs in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: novel perspectives based on review of the literature. Med (Baltim) 94:e1326
Wang C, Liu G, Yang H, Guo S, Wang H, Dong Z, Li X, Bai Y, Cheng Y (2021) MALAT1-mediated recruitment of the histone methyltransferase EZH2 to the microRNA-22 promoter leads to cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Sci Total Environ 766:142191
Tang J, Lin J, Yu Z, Jiang R, Xia J, Yang B, Ou Q, Lin J (2021) Identification of circulating miR-22–3p and let-7a-5p as novel diagnostic biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol
Jun JI, Lau LF (2011) Taking aim at the extracellular matrix: CCN proteins as emerging therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:945–963
Choi C, Jeong W, Ghang B, Park Y, Hyun C, Cho M, Kim J (2020) Correction to: Cyr61 synthesis is induced by interleukin-6 and promotes migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 22:287
Huang TL, Mu N, Gu JT, Shu Z, Zhang K, Zhao JK, Zhang C, Hao Q, Li WN, Zhang WQ, Liu NN, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Xue XC, Zhang YQ (2017) DDR2-CYR61-MMP1 signaling pathway promotes bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis through regulating migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Bone Miner Res 32:407–418
Chen CY, Fuh LJ, Huang CC, Hsu CJ, Su CM, Liu SC, Lin YM, Tang CH (2017) Enhancement of CCL2 expression and monocyte migration by CCN1 in osteoblasts through inhibiting miR-518a-5p: implication of rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Sci Rep 7:421
Xu T, He YH, Wang MQ, Yao HW, Ni MM, Zhang L, Meng XM, Huang C, Ge YX, Li J (2016) Therapeutic potential of cysteine-rich protein 61 in rheumatoid arthritis. Gene 592:179–185
Jie LG, Huang RY, Sun WF, Wei S, Chu YL, Huang QC, Du HY (2015) Role of cysteinerich angiogenic inducer 61 in fibroblastlike synovial cell proliferation and invasion in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep 11:917–923
Yang B, Ni J, Long H, Huang J, Yang C, Huang X (2018) IL-1beta-induced miR-34a up-regulation inhibits Cyr61 to modulate osteoarthritis chondrocyte proliferation through ADAMTS-4. J Cell Biochem 119:7959–7970
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LC designed the research and contributed unpublished reagents; RZ performed the research and wrote the paper. All authors provided critical comments on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, L., Zhou, R. Histone methyltransferase EZH2 in proliferation, invasion, and migration of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Miner Metab 40, 262–274 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-021-01299-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-021-01299-y