Abstract
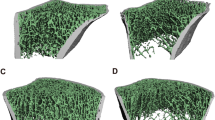
In the course of complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), local osteopenia in the subchondral/subcortical areas of the affected limb represents a central manifestation. Mechanistic aspects of CRPS-associated pathologies remain unclear, and knowledge about bone morphology in CRPS-affected areas is rare. The aim of this study was to assess trabecular and cortical bone microstructure in patients with CRPS of the distal tibiae. We retrospectively analysed 14 women diagnosed with unilateral CRPS type I of the lower limb whose affected and unaffected distal tibiae were examined by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT). Laboratory tests included serum levels of calcium, phosphate, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, bone alkaline phosphatase, parathyroid hormone, osteocalcin and urinary levels of deoxypyridinoline (DPD). Bone mineral density was measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) at the lumbar spine and both proximal femurs. Average urinary DPD levels, a biochemical marker of bone resorption, were elevated in the examined patient cohort (7.1 ± 1.9 nmol/mmol, reference 3.0–7.0 nmol/mmol). According to HR-pQCT, CRPS-affected distal tibiae showed significantly lower values of cortical BMD and cortical thickness compared to the unaffected contralateral side. Also, bone volume relative to total volume was significantly lower. Trabecular number and trabecular thickness tended to be lower in the affected tibiae. CRPS is associated with significant alterations in bone microstructure of the affected tibiae. Increased bone resorption seems to play a crucial role within a multifactorial process of CRPS-mediated bone atrophy. HR-pQCT could possibly serve as a diagnostic tool in specific CRPS therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruehl S (2015) Complex regional pain syndrome. BMJ 351:h2730
Gatti D, Rossini M, Adami S (2016) Management of patients with complex regional pain syndrome type I. Osteoporos Int 27:2423–2431
Harden RN, Bruehl S, Perez RS, Birklein F, Marinus J, Maihofner C, Lubenow T, Buvanendran A, Mackey S, Graciosa J, Mogilevski M, Ramsden C, Chont M, Vatine JJ (2010) Validation of proposed diagnostic criteria (the “Budapest Criteria”) for complex regional pain syndrome. Pain 150:268–274
Wei T, Guo TZ, Li WW, Kingery WS, Clark JD (2016) Acute versus chronic phase mechanisms in a rat model of CRPS. J Neuroinflammation 13:14
Giusti A, Bianchi G (2015) Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome type I with bisphosphonates. RMD Open 1:e000056
Varenna M, Zucchi F (2015) Algodystrophy: recent insight into the pathogenic framework. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab 12:27–30
Basle MF, Rebel A, Renier JC (1983) Bone tissue in reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome–Sudeck’s atrophy: structural and ultrastructural studies. Metab Bone Dis Relat Res 4:305–311
Renier JC, Basle M, Arlet J, Seret P, Acquaviva P, Schiano A, Roux C, Serratrice G, Amor B, May V, Ryckewaert A, Delcambre B, d’Eshougues R, Vincent G, Ducastelle, Desproges Gotteron R, Le Goff P, Gougeon J, Hautin et al (1983) Bone and phosphoro-calcium metabolism in reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic, 50:23–31
Cheung AM, Adachi JD, Hanley DA, Kendler DL, Davison KS, Josse R, Brown JP, Ste-Marie LG, Kremer R, Erlandson MC, Dian L, Burghardt AJ, Boyd SK (2013) High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography for the assessment of bone strength and structure: a review by the Canadian Bone Strength Working Group. Curr Osteoporos Rep 11:136–146
Pialat JB, Burghardt AJ, Sode M, Link TM, Majumdar S (2012) Visual grading of motion induced image degradation in high resolution peripheral computed tomography: impact of image quality on measures of bone density and micro-architecture. Bone 50:111–118
Pauchard Y, Liphardt AM, Macdonald HM, Hanley DA, Boyd SK (2012) Quality control for bone quality parameters affected by subject motion in high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography. Bone 50:1304–1310
Simm PJ, Briody J, McQuade M, Munns CF (2010) The successful use of pamidronate in an 11-year-old girl with complex regional pain syndrome: response to treatment demonstrated by serial peripheral quantitative computerised tomographic scans. Bone 46:885–888
Adami S, Fossaluzza V, Gatti D, Fracassi E, Braga V (1997) Bisphosphonate therapy of reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 56:201–204
Mussawy H, Schmidt T, Rolvien T, Ruther W, Amling M (2017) Evaluation of bone microstructure in CRPS-affected upper limbs by HR-pQCT. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab 14:54–59
Wang L, Guo TZ, Wei T, Li WW, Shi X, Clark JD, Kingery WS (2016) Bisphosphonates inhibit pain, bone loss, and inflammation in a rat tibia fracture model of complex regional pain syndrome. Anesth Analg 123:1033–1045
del Puente A, Pappone N, Mandes MG, Mantova D, Scarpa R, Oriente P (1996) Determinants of bone mineral density in immobilization: a study on hemiplegic patients. Osteoporos Int 6:50–54
Kazakia GJ, Tjong W, Nirody JA, Burghardt AJ, Carballido-Gamio J, Patsch JM, Link T, Feeley BT, Ma CB (2014) The influence of disuse on bone microstructure and mechanics assessed by HR-pQCT. Bone 63:132–140
Varenna M (2014) Bisphosphonates beyond their anti-osteoclastic properties. Rheumatol (Oxf) 53:965–967
Robins SP, Duncan A, Wilson N, Evans BJ (1996) Standardization of pyridinium crosslinks, pyridinoline and deoxypyridinoline, for use as biochemical markers of collagen degradation. Clin Chem 42:1621–1626
Chevreau M, Romand X, Gaudin P, Juvin R, Baillet A (2017) Bisphosphonates for treatment of complex regional pain syndrome type 1: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials versus placebo. Joint Bone Spine 84:393–399
Nitzsche EU (2011) Nuclear medicine imaging for diagnosis of CRPS I. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir 43:20–24
Maihofner C, Seifert F, Markovic K (2010) Complex regional pain syndromes: new pathophysiological concepts and therapies. Eur J Neurol 17:649–660
Amling M, Takeda S, Karsenty G (2000) A neuro (endo)crine regulation of bone remodeling. BioEssays 22:970–975
Elefteriou F, Ahn JD, Takeda S, Starbuck M, Yang X, Liu X, Kondo H, Richards WG, Bannon TW, Noda M, Clement K, Vaisse C, Karsenty G (2005) Leptin regulation of bone resorption by the sympathetic nervous system and CART. Nature 434:514–520
Goto T, Tanaka T (2002) Tachykinins and tachykinin receptors in bone. Microsc Res Tech 58:91–97
Kitaura H, Kimura K, Ishida M, Kohara H, Yoshimatsu M, Takano-Yamamoto T (2013) Immunological reaction in TNF-alpha-mediated osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vitro and in vivo. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:181849
Ediz L, Hiz O, Meral I, Alpayci M (2010) Complex regional pain syndrome: a vitamin K dependent entity? Med Hypotheses 75:319–323
Kramer HH, Hofbauer LC, Szalay G, Breimhorst M, Eberle T, Zieschang K, Rauner M, Schlereth T, Schreckenberger M, Birklein F (2014) Osteoprotegerin: a new biomarker for impaired bone metabolism in complex regional pain syndrome? Pain 155:889–895
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Felix N. Schmidt for his excellent assistance with the HR-pQCT imaging.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Oehler, N., Rolvien, T., Schmidt, T. et al. Bone microstructure is significantly altered in CRPS-affected distal tibiae as detected by HR-pQCT: a retrospective cross-sectional study. J Bone Miner Metab 37, 741–748 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-018-0976-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-018-0976-2