Abstract
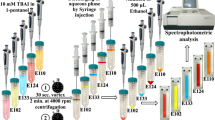
Two accurate and efficient reversed-phase methods, one by high-performance thin-layer chromatography with ultraviolet‒visible detection (RP-HPTLC‒UV/VIS) and the other by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection (RP-HPLC‒DAD), for the simultaneous determination of eight synthetic food dyes (Tartrazine, Ponceau 4R, Sunset yellow FCF, Allura red AC, Brilliant blue FCF, Carmoisine, Quinoline yellow, and Patent blue V) in drinks with simple pretreatment were developed and applied to analyze some alcoholic and soft drinks. Detection was performed in the visible range in both cases at wavelengths (nm) of maximum absorbance (420 yellow, 500 red, or 630 blue), depending on the color of each dye. Both developed methods were validated for selectivity, linearity, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), intra- and interday precision, and recovery, with good results. The RP-HPTLC‒UV/VIS method showed linearity (R2 > 0.998) in the 7–125 µg/mL calibration range, LOD of 0.27–0.92 µg/mL, LOQ of 0.82–1.49 µg/mL, intraday precision (%RSD) of 2.57–7.57, interday precision (%RSD) of 4.21–9.31, and recovery for alcoholic and soft drinks of 86.87–99.87% and 82.70–96.67%, respectively. The RP-HPLC–DAD method showed linearity (R2 > 0.999) in the 1.56–50.0 µg/mL calibration range, LOD of 0.11–0.29 µg/mL, LOQ of 0.32–0.90 µg/mL, intraday precision (%RSD) of 0.13–2.15, interday precision (%RSD) of 0.30–2.47, and recovery of 98.17–101.30% and 88.13–101.9% for alcoholic and soft drinks, respectively. These methods were successfully applied to analyze the 8 synthetic food dyes in 11 (3 alcoholic and 8 soft) drinks from the Romanian market to verify compliance with the label and the maximum permitted level of food dyes in drinks to ensure food safety.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barciela P, Perez-Vazquez A, Prieto MA (2023) Azo dyes in the food industry: features, classification, toxicity, alternatives, and regulation. Food Chem Toxicol 178:113935–113947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2023.113935
Banu C, Bărascu E, Stoica A, Nicolau A (2007) Dyes used in food industry. In: Banu C (ed) Sovereignty, security and food security (Suveranitate, securitate și siguranța alimentară—Romanian). ASAB Publishing House, Bucharest, pp 373–383. ISBN 978-973-7725-40-0
FAO, WHO (2018 Revision) General standard for the labelling of prepackaged foods CXS 1-1985 (2021 Revision) General standard for food additives CODEX STAN 192-1995. In: Codex Alimentarius. International food standards. https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/codex-texts/list-standards/en/. Accessed 20 Oct 2023
***Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on food additives (Text with EEA relevance). https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2008/1333/oj. Accessed 20 Oct 2023
***Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008, Romanian document 2008R1333-RO-25.05.2016-030.001-1. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/RO/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:02008R1333-20160525&from=FR. Accessed 20 Oct 2023
Zahedi M, Shakerian A, Rahimi E, Chaleshtori RS (2020) Validation of an analytical method for determination of eight food dyes in beverage and fruit roll-ups by ion-pair HPLC-DAD. J Shahrekord Univ Med Sci 22:126–134. https://doi.org/10.34172/jsums.2020.20
Hameed EA,·Abd-ElHamid GH, El-Darder OM, Ibrahim AK, Salam RAA, Hadad GM, Abdelshakour MA, (2022) Fast sensitive and accurate analysis of the most common synthetic food colorants in 65 Egyptian commercial products using new HPLC–DAD and UPLC-ESI–MS/MS methods. Food Anal Methods 15:3444–3457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-022-02370-8
Dong M-Y, Wu H-L, Long W-J, Wang T, Yu R-Q (2021) Simultaneous and rapid screening and determination of twelve azo dyes illegally added into food products by using chemometrics-assisted HPLC-DAD strategy. Microchem J 171:106775–106784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106775
Rovina K, Siddiquee S, Shaarani SM (2017) Review—toxicology, extraction and analytical methods for determination of Amaranth in food and beverage products. Trends Food Sci Technol 65:68–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.05.008
Minioti KS, Sakellariou CF, Thomaidis NS (2007) Determination of 13 synthetic food colorants in water-soluble foods by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector. Anal Chim Acta 583:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2006.10.002
Gosetti F, Frascarolo P, Mazzucco E, Gianotti V, Bottaro M, Gennaro MC (2008) Photodegradation of E110 and E122 dyes in a commercial aperitif: a high performance liquid chromatography–diode array–tandem mass spectrometry study. J Chromatogr A 1202:58–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2008.06.044
Feng F, Zhao Y, Yong W, Sun L, Jiang G, Chu X (2011) Highly sensitive and accurate screening of 40 dyes in soft drinks by liquid, chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 879:1813–1818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.04.014
Yamjala K, Nainar MS, Ramisetti NR (2016) Methods for the analysis of azo dyes employed in food industry—a review. Food Chem 192:813–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.085
Rovina K, Prabakaran PP, Siddiquee S, Shaarani SM (2016) Methods for the analysis of Sunset Yellow FCF (E110) in food and beverage products—a review. Trends Anal Chem 85:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.05.009
Ntrallou K, Gika H, Tsochatzis E (2020) Analytical and sample preparation techniques for the determination of food colorants in food matrices. Foods 9:58. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010058
Al Shamari YMG, Alwarthan AA, Wabaidur SM, Khan MA, Alqadami AA, Siddiqui MR (2020) New ultra performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometric method for the determination of Allura Red in soft drinks using corncob as solid phase extraction sorbent: analysis and food waste management approach. J King Saud Univ Sci 32(1):1135–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2019.10.011
Jang G-W, Choi S-I, Choi S-H, Han X, Men X, Kwon H-Y, Choi Y-E, Lee O-H (2021) Method validation of 12 kinds of food dye in chewing gums and soft drinks, and evaluation of measurement uncertainty for soft drinks. Food Chem 356:129705–129717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129705
Arslan M, Tahir HE, Zareef M, Shi J, Rakha A, Bilal M, Xiaowei H, Zhihua L, Xiaobo Z (2021) Recent trends in quality control, discrimination and authentication of alcoholic beverages using nondestructive instrumental techniques. Trends Food Sci Technol 107:80–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.11.021
Agbokponto JE, Kpaibe APS, Yemoa LA, Assanhou AG, Ganfon H, Gbassi GK, Aké M, Amin NC (2022) Simultaneous determination by HPLC–UV Vis of Tartrazine and Sunset Yellow in soft drinks sold in Benin. Am J Anal Chem 13:277–288. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2022.138019
Palianskikh A, Sychik SI, Leschev SM, Pliashak YM, Fiodarava TA, Belyshava LL (2022) Development and validation of the HPLC–DAD method for the quantification of 16 synthetic dyes in various foods and the use of liquid anion exchange extraction for qualitative expression determination. Food Chem 369:130947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130947
Herndon MS, Baker Phillips J, Pierce SS (2023) Determination of the concentration of food dyes in powdered drink mixes. Spectrum 10. https://doi.org/10.29173/spectrum172
Li W-J, Zhou X, Tong S-S, Jia Q (2013) Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N,N’-methylene bisacrylamide) monolithic column embedded with γ-alumina nanoparticles microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of synthetic food dyes in soft drink samples. Talanta 105:386–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.10.065
Chen XH, Zhao YG, Shen HY, Zhou LX, Pan SD, Jin MC (2014) Fast determination of seven synthetic pigments from wine and soft drinks using magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1346:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.04.060
Al-Degs YS (2009) Determination of three dyes in commercial soft drinks using HLA/GO and liquid chromatography. Food Chem 117:485–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.04.097
El-Sheikh AH, Al-Degs YS (2013) Spectrophotometric determination of food dyes in soft drinks by second order multivariate calibration of the absorbance spectra-pH data matrices. Dyes Pigments 97:330–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2013.01.007
Gosetti F, Chiuminatto U, Mazzucco E, Calabrese G, Gennaro MC, Marengo E (2013) Non-target screening of Allura Red AC photodegradation products in a beverage through ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with hybrid triple quadrupole/linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Food Chem 136:617–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.08.019
Turak F, Ozgur MU (2013) Simultaneous determination of Allura Red and Ponceau 4R in drinks with the use of four derivative spectrophotometric methods and comparison with high-performance liquid chromatography. J AOAC Int 96:1377–1386. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.12-393
de Andrade FI, Florindo Guedes MI, Pinto Vieira IG, Pereira Mendes FN, Salmito Rodrigues PA, Costa Maia CS, Marques Ávila MM, de Matos RL (2014) Determination of synthetic food dyes in commercial soft drinks by TLC and ion-pair HPLC. Food Chem 157:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.01.100
Yoshioka N, Ichihashi K (2008) Determination of 40 synthetic food colors in drinks and candies by high performance liquid chromatography using a short column with photodiode array detection. Talanta 74:1408–1413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.09.015
Culzoni MJ, Schenone AV, Llamas NE, Garrido M, Di Nezio MS, Band BSF, Goicoechea HC (2009) Fast chromatographic method for the determination of dyes in beverages by using high performance liquid chromatography–diode array detection data and second order algorithms. J Chromatogr A 1216:7063–7070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.08.077
Botelho BG, de Assis LP, Sena MM (2014) Development and analytical validation of a simple multivariate calibration method using digital scanner images for Sunset Yellow determination in soft beverages. Food Chem 159:175–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.03.048
Prado MA, Boas LFV, Bronze MR, Godoy HT (2006) Validation of methodology for simultaneous determination of synthetic dyes in alcoholic beverages by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1136:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.09.071
Ma M, Luo X, Chen B, Su S, Yao S (2006) Simultaneous determination of water-soluble and fat-soluble synthetic colorants in foodstuff by high-performance liquid chromatography–diode array detection–electrospray mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1103:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2005.11.061
Vachirapatama N, Mahajaroensiri J, Visessanguan W (2008) Identification and determination of seven synthetic dyes in foodstuffs and soft drinks on monolithic C18 column by high performance liquid chromatography. J Food Drug Anal 16:77–82. https://doi.org/10.38212/2224-6614.2323
Bonan S, Fedrizzi G, Menotta S, Caprai E (2013) Simultaneous determination of synthetic dyes in foodstuffs and beverages by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector. Dyes Pigments 99:36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2013.03.029
Hajimahmoodi M, Afsharimanesh M, Moghaddam G, Sadeghi N, Oveisi MR, Jannat B, Pirhadi E, Zamani Mazdeh F, Kanan H (2013) Determination of eight synthetic dyes in foodstuffs by green liquid chromatography. Food Addit Contam A 30:780–785. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2013.774465
Li XQ, Zhang QH, Ma K, Li HM, Guo Z (2015) Identification and determination of 34 water-soluble synthetic dyes in foodstuff by high performance liquid chromatography–diode array detection–ion trap time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 182:316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.03.019
Maria de Souza Santos Cheibub A, Silva Bahiense de Lyra E, Jardim Alves B, Andrade Donagemma R, Duarte Pereira Netto A (2020) Development and validation of a multipurpose and multicomponent method for the simultaneous determination of six synthetic dyes in different foodstuffs by HPLC–UV–DAD. Food Chem 323:126811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126811
Lipskikh OI, Korotkova EI, Barek J, Vyskocil V, Saqib M, Khristunova EP (2020) Simultaneous voltammetric determination of Brilliant blue FCF and Tartrazine for food quality control. Talanta 218:121136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121136
Kaya SI, Cetinkaya A, Ozkan SA (2021) Latest advances on the nanomaterials-based electrochemical analysis of azo toxic dyes Sunset yellow and Tartrazine in food samples. Food Chem Toxicol 156:112524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112524
Soponar F, Moț AC, Sârbu C (2008) Quantitative determination of some food dyes using digital processing of images obtained by thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1188:295–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2008.02.077
Kucharska M, Grabka J (2010) A review of chromatographic methods for determination of synthetic food dyes. Talanta 80:1045–1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2009.09.032
Tuzimski T (2011) Determination of sulfonated water-soluble azo dyes in foods by SPE coupled with HPTLC–DAD. J Planar Chromatogr 24(4):281–289. https://doi.org/10.1556/JPC.24.2011.4.2
Chanlon S, Joly-Pottuz L, Chatelut M, Vittoria O, Cretier JL (2005) Determination of Carmoisine, Allura Red and Ponceau 4R in sweets and soft drinks by differential pulse polarography. J Food Compos Anal 18:503–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2004.05.005
Ghoreishi SM, Behpour M, Golestaneh M (2012) Simultaneous determination of Sunset yellow and Tartrazine in soft drinks using gold nanoparticles carbon paste electrode. Food Chem 132:637–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.10.103
Chebotarev AN, Pliuta KV, Snigur DV (2020) Determination of Carmoisine onto carbon-paste electrode modified by silica impregnated with cetylpyridinium chloride. ChemistrySelect 5(12):3688–3693. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202000518
Ryvolova M, Taborsky P, Vrabe IP, Krasensky P, Preisler J (2007) Sensitive determination of erythrosine and other red food colours using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 1141:206–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.12.018
Fuh MR, Chia KJ (2002) Determination of sulphonated azo dyes in food by ion-pair liquid chromatography with photodiode array and electrospray mass spectrometry detection. Talanta 56:663–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0039-9140(01)00625-7
Khanavi M, Hajimahmoodi M, Ranjbar AM, Oveisi MR, Ardekani MRS, Mogaddam G (2012) Development of a green chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of food colorants. Food Anal Methods 5:408–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-011-9259-4
Pereira Alves S, Mares Brum D, Branco C, de Andrade E, Duarte Pereira Netto A (2008) Determination of synthetic dyes in selected foodstuffs by high performance liquid chromatography with UV–DAD detection. Food Chem 107:489–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.07.054
Diacu E, Ene CP (2009) Simultaneous determination of Tartrazine and Sunset Yellow in soft drinks by liquid chromatography. Rev Chim Bucharest 60(8):745–749
Jurcovan M, Diacu E (2014) Development of a reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of Allura Red AC and Ponceau 4R in soft drinks. Rev Chim Bucharest 65(2):137–141
Gosetti F, Chiuminatto U, Mazzucco E, Calabrese G, Gennaro MC, Marengo E (2012) Identification of photodegradation products of Allura Red AC (E129) in a beverage by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 746:84–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.08.020
Shewityo DH, Dejaegher B, Vande Heyden Y (2015) Validation of thin-layer chromatography methods. In: Poole CF (ed) Instrumental thin-layer chromatography, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 351–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-417223-4.00013-3
Jampilek J, Dolowy M, Pyka-Pajak A (2020) Estimating limits of detection and quantification of ibuprofen by TLC-densitometry at different chromatographic conditions. Processes 8:919. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080919
Mello dos Santos M, Jacobs C, Islam MK, Lim LY, Locher C (2023) Validation of a high-performance thin-layer chromatography method for the quantitative determination of trehalulose. J Planar Chromatogr 36:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00764-023-00243-2
Dong MW (2006) Method validation. In: Dong MW (ed) Modern HPLC for practicing scientists. Wiley-Interscience, Wiley, Hoboken, pp 227–235. https://download.e-bookshelf.de/download/0000/5855/65/L-G-0000585565-0002361539.pdf
ICH Harmonised tripartite guideline (Nov. 2005) Validation of analytical procedures: text and methodology Q2(R1), Step 4 Version. https://www.gmp-compliance.org/files/guidemgr/Q2(R1).pdf. Accessed 24 Oct 2023
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Romanian Programme of Research, Development, and Innovation (PNCDI II contract no. 51-072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vlassa, M., Filip, M. & Coman, V. RP-HPTLC‒UV/VIS and RP-HPLC‒DAD determination of eight synthetic food dyes in alcoholic and soft drinks from the Romanian market. JPC-J Planar Chromat 36, 441–454 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00764-023-00281-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00764-023-00281-w