Abstract
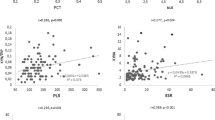
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease accompanied by increased release of proinflammatory cytokines that are known to activate the indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO-1) enzyme, which catalyzes the rate-limiting step of the kynurenine pathway (KP). This study aimed to measure KP metabolite levels in patients with SLE and investigate the relationship between disease activity, clinical findings, and KP. The study included 100 patients with SLE and 100 healthy controls. Serum tryptophan (TRP), kynurenine (KYN), kynurenic acid (KYNA), 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid (3HAA), 3-hydroxykynurenine (3HK), quinolinic acid (QA) concentrations were measured with tandem mass spectrometry. Serum KYN, KYNA, 3HAA, 3HK, and QA levels of the patients with SLE were significantly higher than the control group. Serum QA levels were elevated in patients with neurological involvement (four patients with peripheral neuropathy and two patients with mononeuropathy), serum KYN levels and KYN/TRP ratio increased in patients with joint involvement, and serum KYN, 3HK, and 3HAA levels and the KYN/TRP ratio were increased in patients with renal involvement. Moreover, KYN and KYN/TRP ratios were positively correlated with the disease activity score. These findings indicated that imbalances in KP metabolites may be associated with the pathogenesis, activation, and clinical manifestations of SLE.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Abusoglu S, Eryavuz Onmaz D, Abusoglu G, Humeyra Yerlikaya F, Unlu A (2023) Measurement of kynurenine pathway metabolites by tandem mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab 28:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsacl.2023.04.003
Al-Ghezi ZZ, Singh N, Mehrpouya-Bahrami P, Busbee PB, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti PS (2019) AhR activation by TCDD (2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin) attenuates pertussis toxin-induced inflammatory responses by differential regulation of Tregs and Th17 cells through specific targeting by microRNA. Front Microbiol 10:2349. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02349
Anderson EW, Jin Y, Shih A, Arazi A, Goodwin S, Roeser J, Furie RA, Aranow C, Volpe B, Diamond B, Mackay M (2022) Associations between circulating interferon and kynurenine/tryptophan pathway metabolites: support for a novel potential mechanism for cognitive dysfunction in SLE. Lupus Sci Med 9(1):e000808. https://doi.org/10.1136/lupus-2022-000808
Apalset EM, Gjesdal CG, Ueland PM, Midttun Ø, Ulvik A, Eide GE, Meyer K, Tell GS (2014) Interferon (IFN)-γ-mediated inflammation and the kynurenine pathway in relation to bone mineral density: the Hordaland health study. Clin Exp Immunol 176(3):452–460. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12288
Aregger F, Uehlinger DE, Fusch G, Bahonjic A, Pschowski R, Walter M, Schefold JC (2018) Increased urinary excretion of kynurenic acid is associated with non-recovery from acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. BMC Nephrol 19(1):44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-0841-5
Auyeung A, Wang HC, Aravagiri K, Knezevic NN (2023) Kynurenine pathway metabolites as potential biomarkers in chronic pain. Pharmaceuticals 16(5):681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050681
Ayano M, Horiuchi T (2023) Complement as a biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomolecules 13(2):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020367
Baranyi A, Amouzadeh-Ghadikolai O, Lewinski DV, Breitenecker RJ, Stojakovic T, März W, Robier C, Rothenhäusler HB, Mangge H, Meinitzer A (2017) Beta-trace protein as a new non-invasive immunological marker for quinolinic acid-induced impaired blood–brain barrier integrity. Sci Rep 7:43642. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43642
Basu A, Ramamoorthi G, Albert G, Gallen C, Beyer A, Snyder C, Koski G, Disis ML, Czerniecki BJ, Kodumudi K (2021) Differentiation and regulation of T(H) cells: a balancing act for cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol 12:669474. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.669474
Cathomas F, Guetter K, Seifritz E, Klaus F, Kaiser S (2021) Quinolinic acid is associated with cognitive deficits in schizophrenia but not major depressive disorder. Sci Rep 11(1):9992. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89335-9
Chen L-M, Bao C-H, Wu Y, Liang S-H, Wang D, Wu L-Y, Huang Y, Liu H-R, Wu H-G (2021) Tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism: a link between the gut and brain for depression in inflammatory bowel disease. J Neuroinflammation 18(1):135. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-021-02175-2
Cheng HB, Chen RY, Wu JP, Chen L, Liang YH, Pan HF, Pan ZF, Zhang QH, Li Q, Du TX, Lv YM, Shi JQ (2015) Complement C4 induces regulatory T cells differentiation through dendritic cell in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Biosci 5:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-015-0052-8
Cheng HH, Hung-Ke L, Sheu ML, Lee CY, Tsai YC, Lai DW (2023) AHR/TET2/NT5E axis downregulation is associated with the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus and its progression. Immunology 168(4):654–670. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13600
Ciapała K, Mika J, Rojewska E (2021) The kynurenine pathway as a potential target for neuropathic pain therapy design: from basic research to clinical perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 22(20):11055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011055
Fathi M, Vakili K, Yaghoobpoor S, Tavasol A, Jazi K, Mohamadkhani A, Klegeris A, McElhinney A, Mafi Z, Hajiesmaeili M, Sayehmiri F (2022) Dynamic changes in kynurenine pathway metabolites in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Front Immunol 13:1013784. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1013784
Gergianaki I, Bertsias G (2018) Systemic lupus erythematosus in primary care: an update and practical messages for the general practitioner. Front Med (lausanne) 5:161. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2018.00161
Gieseg SP, Baxter-Parker G, Lindsay A (2018) Neopterin, inflammation, and oxidative stress: what could we be missing? Antioxidants (basel) 7(7):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7070080
Giles GI, Collins CA, Stone TW, Jacob C (2003) Electrochemical and in vitro evaluation of the redox-properties of kynurenine species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 300(3):719–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02917-0
Gladman DD, Ibañez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29(2):288–291
Goswami TK, Singh M, Dhawan M, Mitra S, Emran TB, Rabaan AA, Mutair AA, Alawi ZA, Alhumaid S, Dhama K (2022) Regulatory T cells (Tregs) and their therapeutic potential against autoimmune disorders - advances and challenges. Hum Vaccin Immunother 18(1):2035117. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2022.2035117
Gottschalk TA, Tsantikos E, Hibbs ML (2015) Pathogenic inflammation and its therapeutic targeting in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol 6:550. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00550
Joisten N, Ruas JL, Braidy N, Guillemin GJ, Zimmer P (2021) The kynurenine pathway in chronic diseases: a compensatory mechanism or a driving force? Trends Mol Med 27(10):946–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2021.07.006
Kalaska B, Pawlak K, Domaniewski T, Oksztulska-Kolanek E, Znorko B, Roszczenko A, Rogalska J, Brzoska MM, Lipowicz P, Doroszko M, Pryczynicz A, Pawlak D (2017) Elevated levels of peripheral kynurenine decrease bone strength in rats with chronic kidney disease. Front Physiol 8:836. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00836
Kaul A, Gordon C, Crow MK, Touma Z, Urowitz MB, van Vollenhoven R, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Hughes G (2016) Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2(1):16039. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.39
Khalil F, Elwahab A, Lotfy M, Elshafy A, Khedr M (2018) Correlation of serum neopterin level with complement C3, C4 in assessment of systemic lupus erythematosus activity. Egypt J Hosp Med 73(5):6596–6607
Kim JT, Kim SH, Min HK, Jeon SJ, Sung SA, Park WH, Lee HK, Choi HS, Pak YK, Lee SY (2020) Effect of dialysis on aryl hydrocarbon receptor transactivating activity in patients with chronic kidney disease. Yonsei Med J 61(1):56–63. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2020.61.1.56
Krupa A, Kowalska I (2021) The kynurenine pathway-new linkage between innate and adaptive immunity in autoimmune endocrinopathies. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189879
Leaungwutiwong P, Ittiprasert W, Saikhun K, Tong-Ngam P, Akapirat S, Chattanadee S, Kitiyanant Y (2011) Impairment of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in C4-deficient mice. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 29(3):220–228
Lee WJ, Liu SH, Chiang CK, Lin SY, Liang KW, Chen CH, Tien HR, Chen PH, Wu JP, Tsai YC, Lai DW, Chang YC, Sheu WH, Sheu ML (2016) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficiency attenuates oxidative stress-related mesangial cell activation and macrophage infiltration and extracellular matrix accumulation in diabetic nephropathy. Antioxid Redox Signal 24(4):217–231. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2015.6310
Liu W, Zhang S, Wang J (2022) IFN-γ, should not be ignored in SLE. Front Immunol 13:954706. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.954706
Lu H, Lei X, Klaassen C (2006) Gender differences in renal nuclear receptors and aryl hydrocarbon receptor in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Kidney Int 70(11):1920–1928. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5001880
Mo Y, Lu Z, Wang L, Ji C, Zou C, Liu X (2020) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in chronic kidney disease: friend or foe? Front Cell Dev Biol 8:589752. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.589752
Moghazy A, Ibrahim A (2021) Mortality in a cohort of Egyptian systemic lupus erythematosus patients: retrospective two-center study. Egypt Rheumatol Rehabil. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43166-021-00062-5
Mor A, Kalaska B, Pawlak D (2020) Kynurenine pathway in chronic kidney disease: what’s old, what’s new, and what’s next? Int J Tryptophan Res 13:1178646920954882. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178646920954882
Muneer A (2020) Kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism in neuropsychiatric disorders: pathophysiologic and therapeutic considerations. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci 18(4):507–526. https://doi.org/10.9758/cpn.2020.18.4.507
Mustafa G, Mahrosh HS, Salman M, Sharif S, Jabeen R, Majeed T, Tahir H (2021) Identification of peptides as novel inhibitors to target IFN-γ, IL-3, and TNF-α in systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomed Res Int 2021:1124055. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1124055
Nassan FL, Gunn JA, Hill MM, Coull BA, Hauser R (2019) High phthalate exposure increased urinary concentrations of quinolinic acid, implicated in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders: Is this a potential missing link? Environ Res 172:430–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.02.034
Niewold TB, Clark DN, Salloum R, Poole BD (2010) Interferon alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:948364. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/948364
Oxenkrug GF (2015) Increased plasma levels of xanthurenic and kynurenic acids in type 2 diabetes. Mol Neurobiol 52(2):805–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9232-0
Pan L, Lu MP, Wang JH, Xu M, Yang SR (2020) Immunological pathogenesis and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. World J Pediatr 16(1):19–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-019-00229-3
Pan B, Zhang F, Sun J, Chen D, Huang W, Zhang H, Cao C, Wan X (2021) Correlation of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase and chronic kidney disease: a pilot study. J Immunol Res 2021:8132569. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8132569
Pattanaik SS, Panda AK, Pati A, Padhi S, Tripathy R, Tripathy SR, Parida MK, Das BK (2022) Role of interleukin-6 and interferon-α in systemic lupus erythematosus: a case–control study and meta-analysis. Lupus 31(9):1094–1103. https://doi.org/10.1177/09612033221102575
Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcón GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR, Bruce IN, Isenberg D, Wallace DJ, Nived O, Sturfelt G, Ramsey-Goldman R, Bae SC, Hanly JG, Sánchez-Guerrero J, Clarke A, Aranow C, Manzi S, Urowitz M, Gladman D, Kalunian K, Costner M, Werth VP, Zoma A, Bernatsky S, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Khamashta MA, Jacobsen S, Buyon JP, Maddison P, Dooley MA, van Vollenhoven RF, Ginzler E, Stoll T, Peschken C, Jorizzo JL, Callen JP, Lim SS, Fessler BJ, Inanc M, Kamen DL, Rahman A, Steinsson K, Franks AG Jr, Sigler L, Hameed S, Fang H, Pham N, Brey R, Weisman MH, McGwin G Jr, Magder LS (2012) Derivation and validation of the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64(8):2677–2686. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.34473
Postal M, Appenzeller S (2011) The role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cytokine 56(3):537–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2011.08.026
Rees F, Doherty M, Grainge MJ, Lanyon P, Zhang W (2017) The worldwide incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Rheumatology (oxford) 56(11):1945–1961. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kex260
Refaey ME, McGee-Lawrence ME, Fulzele S, Kennedy EJ, Bollag WB, Elsalanty M, Zhong Q, Ding KH, Bendzunas NG, Shi XM, Xu J, Hill WD, Johnson MH, Hunter M, Pierce JL, Yu K, Hamrick MW, Isales CM (2017) Kynurenine, a tryptophan metabolite that accumulates with age, induces bone loss. J Bone Miner Res 32(11):2182–2193. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.3224
Rossi F, Miggiano R, Ferraris DM, Rizzi M (2019) The synthesis of kynurenic acid in mammals: an updated kynurenine aminotransferase structural KATalogue. Front Mol Biosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2019.00007
Sakurai M, Yamamoto Y, Kanayama N, Hasegawa M, Mouri A, Takemura M, Matsunami H, Miyauchi T, Tokura T, Kimura H, Ito M, Umemura E, Boku AS, Nagashima W, Tonoike T, Kurita K, Ozaki N, Nabeshima T, Saito K (2020) Serum metabolic profiles of the tryptophan-kynurenine pathway in the high risk subjects of major depressive disorder. Sci Rep 10(1):1961. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58806-w
Song P, Ramprasath T, Wang H, Zou M-H (2017) Abnormal kynurenine pathway of tryptophan catabolism in cardiovascular diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 74(16):2899–2916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2504-2
Sutanto H, Yuliasih Y (2023) Disentangling the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: close ties between immunological, genetic and environmental factors. Medicina 59(6):1033
Takeda Y, Kaneda K, Jimma F, Shiobara N, Saniabadi AR, Wakabayashi I (2013) Suppression of Th1 cytokine production by a peptide derived from C4b. Inflamm Res 62(11):951–959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-013-0650-z
Tan Y, Yu F, Long J, Gan L, Wang H, Zhang L, Zhao M (2021) Frequency of systemic lupus erythematosus was decreasing among hospitalized patients from 2013 to 2017 in a national database in China. Front Med (lausanne) 8:648727. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.648727
Walczak K, Langner E, Makuch-Kocka A, Szelest M, Szalast K, Marciniak S, Plech T (2020) Effect of tryptophan-derived AhR ligands, kynurenine, kynurenic acid and FICZ, on proliferation, cell cycle regulation and cell death of melanoma cells-in vitro studies. Int J Mol Sci 21(21):7946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217946
Wang H, Liu M (2021) Complement C4, infections, and autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.694928
Wang Q, Liu D, Song P, Zou MH (2015) Tryptophan-kynurenine pathway is dysregulated in inflammation, and immune activation. Front Biosci (landmark Ed) 20(7):1116–1143. https://doi.org/10.2741/4363
Yu TY, Pang WJ, Yang GS (2015) Aryl hydrocarbon receptors in osteoclast lineage cells are a negative regulator of bone mass. PLoS ONE 10(1):e0117112. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117112
Yu H, Nagafuchi Y, Fujio K (2021) Clinical and immunological biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomolecules 11(7):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11070928
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Selcuk University for this study.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each named author has substantially contributed to conducting the research and drafting the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Ethical approval
This study was performed according to guidelines established by the 2013 Helsinki Declaration and protocol was approved by Selcuk University Faculty of Medicine Ethics Committee (Number: 2021/280, Date: 26.05.2021).
Additional information
Handling editor: D. Tsikas.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eryavuz Onmaz, D., Tezcan, D., Yilmaz, S. et al. Altered kynurenine pathway metabolism and association with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus. Amino Acids 55, 1937–1947 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03353-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03353-7