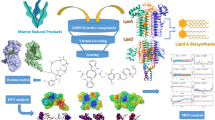
Abstract
The emergence of drug-resistant superbugs has necessitated a pressing need for innovative antibiotics. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have demonstrated broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, reduced susceptibility to resistance, and immunomodulatory effects, rendering them promising for combating drug-resistant microorganisms. This study employed computational simulation methods to screen and design AMPs specifically targeting ESKAPE pathogens. Particularly, AMPs were rationally designed to target the BamA and obtain novel antimicrobial peptide sequences. The designed AMPs were assessed for their antibacterial activities, mechanisms, and stability. Molecular docking and dynamics simulations demonstrated the interaction of both designed AMPs, 11pep and D-11pep, with the β1, β9, β15, and β16 chains of BamA, resulting in misfolding of outer membrane proteins and antibacterial effects. Subsequent antibacterial investigations confirmed the broad-spectrum activity of both 11pep and D-11pep, with D-11pep demonstrating higher potency against resistant Gram-negative bacteria. D-11pep exhibited MICs of 16, 8, and 32 μg/mL against carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli, carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, respectively, with a concomitant lower resistance induction. Mechanism of action studies confirmed that peptides could disrupt the bacterial outer membrane, aligning with the findings of molecular dynamics simulations. Additionally, D-11pep demonstrated superior stability and reduced toxicity in comparison to 11pep. The findings of this study underscore the efficacy of rational AMP design that targets BamA, along with the utilization of D-amino acid replacements as a strategy for developing AMPs against drug-resistant bacteria.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Additionally, a portion of the data supporting this study is publicly available through the following sources: APD3 (https://aps.unmc.edu), PDB (https://www.rcsb.org/), and EMSFold (https://esmatlas.com/).
Abbreviations
- CRE:
-
Carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli
- MRSA:
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- CRPA:
-
Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- MDRAB:
-
Multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- AMPs:
-
Antimicrobial peptides
- MIC:
-
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
- MHB:
-
Mueller–Hinton Broth
- LB:
-
Luria–Bertani Broth
- MBC:
-
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
- SEM:
-
Scanning Electron Microscopy
- FBS:
-
Fetal Bovine Serum
References
Antimicrobial Resistance C (2022) Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 399(10325):629–655
Basu S, Joshi SM, Ramaiah S, Anbarasu A (2022) Designing anti-microbial peptides against major beta-lactamase enzymes in clinically important gram-negative bacterial pathogens: an in-silico study. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 14(2):263–276
Boparai JK, Sharma PK (2020) Mini review on antimicrobial peptides, sources, mechanism and recent applications. Protein Pept Lett 27(1):4–16
Bowdish DME, Davidson DJ, Lau YE, Lee K, Scott MG, Hancock REW (2005) Impact of LL-37 on anti-infective immunity. J Leukoc Biol 77(4):451–459
Brown ED, Wright GD (2016) Antibacterial drug discovery in the resistance era. Nature 529(7586):336–343
Burley SK, Bhikadiya C, Bi C, Bittrich S, Chen L, Crichlow GV, Christie CH, Dalenberg K, Di Costanzo L, Duarte JM, Dutta S, Feng Z, Ganesan S, Goodsell DS, Ghosh S, Green RK, Guranovic V, Guzenko D, Hudson BP, Lawson CL, Liang Y, Lowe R, Namkoong H, Peisach E, Persikova I, Randle C, Rose A, Rose Y, Sali A, Segura J, Sekharan M, Shao C, Tao YP, Voigt M, Westbrook JD, Young JY, Zardecki C, Zhuravleva M (2021) RCSB Protein Data Bank: powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):D437–D451
Chen HL, Su PY, Shih C (2016) Improvement of in vivo antimicrobial activity of HBcARD peptides by D-arginine replacement. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(21):9125–9132
Furniss RCD, Kaderabkova N, Barker D, Bernal P, Maslova E, Antwi AAA, McNeil HE, Pugh HL, Dortet L, Blair JMA, Larrouy-Maumus G, McCarthy RR, Gonzalez D, Mavridou DAI (2022) Breaking antimicrobial resistance by disrupting extracytoplasmic protein folding. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.59046
Hancock RE, Sahl HG (2006) Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat Biotechnol 24(12):1551–1557
He X, Man VH, Yang W, Lee TS, Wang J (2020) A fast and high-quality charge model for the next generation general AMBER force field. J Chem Phys 153(11):114502
Homeyer N, Gohlke H (2015) Extension of the free energy workflow FEW towards implicit solvent/implicit membrane MM-PBSA calculations. Biochim Biophys Acta 1850(5):972–982
Hunter HN, Jing W, Schibli DJ, Trinh T, Park IY, Sun CK, Vogel HJ (2005) The interactions of antimicrobial peptides derived from lysozyme with model membrane systems. BBA Biomembranes 1668(2):175–189
Imai Y, Meyer KJ, Iinishi A, Favre-Godal Q, Green R, Manuse S, Caboni M, Mori M, Niles S, Ghiglieri M, Honrao C, Ma X, Guo JJ, Makriyannis A, Linares-Otoya L, Bohringer N, Wuisan ZG, Kaur H, Wu R, Mateus A, Typas A, Savitski MM, Espinoza JL, O’Rourke A, Nelson KE, Hiller S, Noinaj N, Schaberle TF, D’Onofrio A, Lewis K (2019) A new antibiotic selectively kills Gram-negative pathogens. Nature 576(7787):459–464
Ishikawa D, Yamamoto H, Tamura Y, Moritoh K, Endo T (2004) Two novel proteins in the mitochondrial outer membrane mediate beta-barrel protein assembly. J Cell Biol 166(5):621–627
Jakalian A, Jack DB, Bayly CI (2002) Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic charges AM1-BCC model: II Parameterization and validation. J Comput Chem 23(16):1623–1641
Kaur H, Jakob RP, Marzinek JK, Green R, Imai Y, Bolla JR, Agustoni E, Robinson CV, Bond PJ, Lewis K, Maier T, Hiller S (2021) The antibiotic darobactin mimics a beta-strand to inhibit outer membrane insertase. Nature 593(7857):125–129
Kim H, Jang JH, Kim SC, De CJH (2014) Novo generation of short antimicrobial peptides with enhanced stability and cell specificity. J Antimicrob Chemother 69(1):121–132
Kim EY, Rajasekaran G, Shin SY (2017) LL-37-derived short antimicrobial peptide KR-12-a5 and its d-amino acid substituted analogs with cell selectivity, anti-biofilm activity, synergistic effect with conventional antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory activity. Eur J Med Chem 136:428–441
Kuszak AJ, Noinaj N, Buchanan SK (2015) Methods to characterize folding and function of BamA Cross-Link mutants. Methods Mol Biol 1329:137–147
Lee J, Hitzenberger M, Rieger M, Kern NR, Zacharias M, Im W (2020) CHARMM-GUI supports the amber force fields. J Chem Phys 153(3):035103
Lewis K (2020) The science of antibiotic discovery. Cell 181(1):29–45
Lin Z, Akin H, Rao R, Hie B, Zhu Z, Lu W, Smetanin N, Verkuil R, Kabeli O, Shmueli Y, dos Santos Costa A, Fazel-Zarandi M, Sercu T, Candido S (2022) Rives, a. 22:665
Lu J, Xu H, Xia J, Ma J, Xu J, Li Y, Feng J (2020) D- and unnatural amino acid substituted antimicrobial peptides with improved proteolytic resistance and their proteolytic degradation characteristics. Front Microbiol 11:563030
Lwin TZ, Zhou R, Luo R (2006) Is poisson-boltzmann theory insufficient for protein folding simulations? J Chem Phys 124(3):167
Mahlapuu M, Hakansson J, Ringstad L, Bjorn C (2016) Antimicrobial Peptides: An Emerging Category of Therapeutic Agents. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 6:194
Maxian T, Gerlitz L, Riedl S, Rinner B, Zweytick D (2021) Effect of L- to D-amino acid substitution on stability and activity of antitumor peptide RDP215 against human melanoma and glioblastoma. Int J Mol Sci 22(16):8469
Miller BR, McGee TD, Swails JM, Homeyer N, Gohlke H, Roitberg AE (2012) An efficient program for end-state free energy calculations. J Chem Theory Comput 8(9):3314–3321
Mukhopadhyay S, Bharath Prasad AS, Mehta CH, Nayak UY (2020) Antimicrobial peptide polymers: no escape to ESKAPE pathogens-a review. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36(9):131
Mwangi J, Yin Y, Wang G, Yang M, Li Y, Zhang Z, Lai R (2019) The antimicrobial peptide ZY4 combats multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and acinetobacter baumannii infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116(52):26516–26522
Nguyen LT, Schibli DJ, Vogel D (2005) Structural studies and model membrane interactions of two peptides derived from bovine lactoferricin. J Pept Sci 11(7):379–389
Noinaj N, Rollauer SE, Buchanan SK (2015) The β-barrel membrane protein insertase machinery from Gram-negative bacteria. Curr Opin Struct Biol 31:35–42
Pal T, Abraham B, Sonnevend A, Jumaa P, Conlon JM (2006) Brevinin-1BYa: a naturally occurring peptide from frog skin with broad-spectrum antibacterial and antifungal properties. Int J Antimicrob Agents 27(6):525–529
Tan R, Wang M, Xu H, Qin L, Wang J, Cui P, Ru S (2021) Improving the activity of antimicrobial peptides against aquatic pathogen bacteria by amino acid substitutions and changing the ratio of hydrophobic residues. Front Microbiol 12:773076
Tian C, Kasavajhala K, Belfon KAA, Raguette L, Huang H, Migues AN, Bickel J, Wang Y, Pincay J, Wu Q, Simmerling C (2020) ff19SB: amino-acid-specific protein backbone parameters trained against quantum mechanics energy surfaces in solution. J Chem Theory Comput 16(1):528–552
Upert G, Luther A, Obrecht D, Ermert P (2021) Emerging peptide antibiotics with therapeutic potential. Med Drug Discov 9:100078
Vlieghe P, Lisowski V, Martinez J, Khrestchatisky M (2010) Synthetic therapeutic peptides: science and market. Drug Discov Today 15(1–2):40–56
Walesch S, Birkelbach J, Jezequel G, Haeckl FPJ, Hegemann JD, Hesterkamp T, Hirsch AKH, Hammann P, Muller R (2023) Fighting antibiotic resistance-strategies and (pre)clinical developments to find new antibacterials. EMBO Rep 24(1):e56033
Wang G, Li X, Wang Z (2016) APD3: the antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D1087–D1093
Wang Z, Liu X, Da T, Mao R, Hao Y, Yang N, Wang X, Li Z, Wang X, Wang J (2020) Development of chimeric peptides to facilitate the neutralisation of lipopolysaccharides during bactericidal targeting of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli. Commun Biol 3(1):41
Wei GX, Bobek LA (2005) Human salivary mucin MUC7 12-Mer-l and 12-Mer-d peptides: antifungal activity in saliva, enhancement of activity with protease inhibitor cocktail or EDTA, and cytotoxicity to human cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49(6):2336–2342
Zhao Y, Zhang M, Qiu S, Wang J, Peng J, Zhao P, Zhu R, Wang H, Li Y, Wang K, Yan W, Wang R (2016) Antimicrobial activity and stability of the D-amino acid substituted derivatives of antimicrobial peptide polybia-MPI. AMB Express 6(1):122
Zhong C, Zhu N, Zhu Y, Liu T, Gou S, Xie J, Yao J, Ni J (2020) Antimicrobial peptides conjugated with fatty acids on the side chain of D-amino acid promises antimicrobial potency against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Eur J Pharm Sci 141:105123
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX1327), the Innovation Project of Chongqing Stay and Create Program (cx2020012), the Graduate Education Research Fund of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission, and the Graduate Innovation Project of Chongqing University of Technology (gzlcx20223347).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW and LY collaborated on the conception and design of the study, with LY conducting the experiments, analyzing the data, and writing the manuscript. ML and SG offered insights into data interpretation and critically revised the manuscript. ZL, YL and ZL provided valuable technical guidance throughout the study. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Ethical approval
This research project does not involve any human or animal subjects and therefore does not require ethical approval. The study will be conducted using only publicly available data or secondary data analysis. As such, it does not pose any risks or harm to individuals, and the privacy and confidentiality of any data analyzed will be protected. We are committed to conducting this study in accordance with the highest ethical standards and will adhere to all relevant laws and regulations.
Additional information
Handling editor: J. Gonzalez-Lopez.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Luo, M., Liu, Z. et al. BamA-targeted antimicrobial peptide design for enhanced efficacy and reduced toxicity. Amino Acids 55, 1317–1331 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03307-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03307-z