Abstract
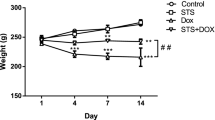
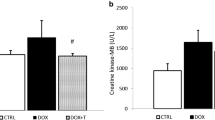
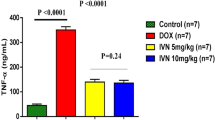
Doxorubicin (DOXO) may cause serious cardiotoxic effects that limit its use as an antineoplastic agent. We aimed to evaluate the protective role of taurine (TAU), a beta amino acid with antioxidant activity, against DOXO-induced cardiotoxicity in a rat model. Thirty-one male Sprague–Dawley rats (300–400 g) were randomized into four groups: control (n = 7, intraperitoneal [ip] saline for 14 days), TAU (n = 8, 150 mg/kg body weight TAU ip for 14 days), DOXO (n = 8, 25 mg/kg body weight DOXO ip on 12th, 13th, and 14th days), and DOXO + TAU (n = 8, TAU for 14 days and DOXO on 12th, 13th, and 14th days). The left ventricular functions were evaluated on 15th day by echocardiography. The heart tissues were then excised for histological evaluation. In DOXO group, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), fractional shortening (FS), and mitral lateral annulus (s') velocity were significantly lower, and the left ventricular end-diastolic and end-systolic diameters (LVEDD, LVESD) were significantly higher than control group (p < 0.05), indicating a significant deterioration in left ventricular functions. However, in comparison to DOXO group, LVESD, LVEDD, LVEF, FS, and s' were significantly improved in DOXO + TAU group (p < 0.05). On histological evaluation, contrary to the normal cellular structure of cardiomyocytes in control and TAU groups, DOXO group showed increased nuclear or cytoplasmic changes and infiltrative cell proliferation (p < 0.001), which were remarkably reduced in DOXO + TAU group (p < 0.001). TAU treatment has a protective effect against DOXO-induced cardiotoxicity on echocardiographical and histological evaluation. For common use of TAU to prevent DOXO-induced cardiotoxicity, our findings should be confirmed by clinical studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agustini FD, Arozal W, Louisa M, et al (2015) Cardioprotection mechanism of mangiferin on doxorubicin-induced rats: focus on intracellular calcium regulation. Pharm Biol 1–9
Angsutararux P, Luanpitpong S, Issaragrisil S (2015) Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity: overview of the roles of oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015:795602
Argun M, Uzum K, Sonmez MF, et al (2015) Cardioprotective effect of metformin against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in rats. Anatol J Cardiol
Azuma J, Sawamura A, Awata N et al (1985) Therapeutic effect of taurine in congestive heart failure: a double-blind crossover trial. Clin Cardiol 8(5):276–282
Cantafora A, Blotta I, Rossi SS, Hofmann AF, Sturman JA (1991) Dietary taurine content changes liver lipids in cats. J Nutr 121(10):1522–1528
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G et al (2015) Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulation 131:1981–1988
Chatterjee K, Zhang J, Honbo N, Karliner JS (2010) Doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. Cardiology 115(2):155–162
Childs AC, Phaneuf SL, Dirks AJ, Phillips T, Leeuwenburgh C (2002) Doxorubicin treatment in vivo causes cytochrome C release and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, as well as increased mitochondrial efficiency, superoxide dismutase activity, and Bcl-2: bax ratio. Cancer Res 62:4592–4598
Guo R, Wu K, Chen J et al (2013) Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects against doxorubicin-induced inflammation and cytotoxicity by inhibiting p38MAPK/NFkappaB pathway in H9c2 cardiac cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 32(6):1668–1680
Hanna AD, Lam A, Tham S, Dulhunty AF, Beard NA (2014) Adverse effects of doxorubicin and its metabolic product on cardiac RyR2 and SERCA2A. Mol Pharmacol 86(4):438–449
Harada H, Cusack BJ, Olson RD et al (1990) Taurine deficiency and doxorubicin: interaction with the cardiac sarcolemmal calcium pump. Biochem Pharmacol 39(4):745–751
Ito T, Muraoka S, Takahashi K, Fujio Y, Schaffer SW, Azuma J (2009) Beneficial effect of taurine treatment against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. Adv Exp Med Biol 643:65–74
Li YT, Maskos K, Chou CW, Cole RB, Li SC (2003) Presence of an unusual GM2 derivative, taurine-conjugated GM2, in Tay-Sachs brain. J Biol Chem 278(37):35286–35291
Narýn F, Demýr F, Akgün H et al (2004) Doxorubicin-induced experimental cardiotoxicity and effect of pentoxphylline on cardiotoxicity. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars 32(5):279–287
Pai VB, Nahata MC (2000) Cardiotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents: incidence, treatment and prevention. Drug Saf 22(4):263–302
Rapundalo ST (1998) Cardiac protein phosphorylation: functional and pathophysiological correlates. Cardiovasc Res 38(3):559–588
Razmaraii N, Babaei H, Nayebi AM, Asadnasab G, Helan JA, Azarmi Y (2015) Cardioprotective effect of phenytoin on doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in a rat model. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol
Renu K, Abilash VG, Tirupathi Pichiah PB, Arunachalam S (2018) Molecular mechanism of doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy—an update. Eur J Pharmacol 818:241–253
Rochette L, Guenancia C, Gudjoncik A et al (2015) Anthracyclines/trastuzumab: new aspects of cardiotoxicity and molecular mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci 36(6):326–348
Saad SY, Najjar TA, Al-Rikabi AC (2001) The preventive role of deferoxamine against acute doxorubicin-induced cardiac, renal and hepatic toxicity in rats. Pharmacol Res 43(3):211–218
Saleme B, Gurtu V, Zhang Y et al (2019) Tissue-specific regulation of p53 by PKM2 is redox dependent and provides a therapeutic target for anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Sci Transl Med 11(478)
Schaffer SW, Azuma J, Mozaffari M (2009) Role of antioxidant activity of taurine in diabetes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 87(2):91–99
Schaffer SW, Jong CJ, Ramila KC, Azuma J (2010) Physiological roles of taurine in heart and muscle. J Biomed Sci 17(Suppl 1):S2
Shiny KS, Kumar SH, Farvin KH, Anandan R, Devadasan K (2005) Protective effect of taurine on myocardial antioxidant status in isoprenaline-induced myocardial infarction in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 57(10):1313–1317
Vejpongsa P, Yeh ET (2014) Prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: challenges and opportunities. J Am Coll Cardiol 64(9):938–945
Wang Y, Mei X, Yuan J, Lu W, Li B, Xu D (2015) Taurine zinc solid dispersions attenuate doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 289(1):1–11
Wang J, Qi C, Liu L et al (2018) Taurine protects primary neonatal cardiomyocytes against apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide. Int Heart J 59(1):190–196
Yeh ET, Bickford CL (2009) Cardiovascular complications of cancer therapy: incidence, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. J Am Coll Cardiol 53(24):2231–2247
Zhang S, Meng T, Liu J, Zhang X, Zhang J (2015) Cardiac protective effects of dexrazoxane on animal cardiotoxicity model induced by anthracycline combined with trastuzumab is associated with upregulation of calpain-2. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(4):e445
Acknowledgements
We thank to Ersin Fadıllıoğlu MD, Davut Singer MD for the experiments.
Funding
The study was not funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
This research involves only animal participants; therefore informed consent was not needed.
Additional information
Handling Editor: H. Jakubowski.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barış, V.Ö., Gedikli, E., Yersal, N. et al. Protective effect of taurine against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats: echocardiographical and histological findings. Amino Acids 51, 1649–1655 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02801-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02801-7