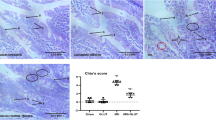
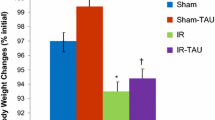
Abstract
Intestinal ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) causes cellular and tissue damage to the intestine and remote organs such as the liver. Increased production of ROS and nitric oxide and dysregulation of cytoprotective enzymes may be involved in intestinal I/R. The aim was to evaluate the protective effects of glutamine on the intestine and liver of rats with intestinal I/R injury. Twenty male Wistar rats (300 g) were divided into four groups: sham-operated (SO), glutamine + SO (G + SO), I/R, and glutamine + I/R (G + I/R). Occlusion of the SMA for 30 min was followed by 15-min reperfusion. Glutamine (25 mg/kg/day) was administered once daily 24 and 48 h before I/R induction. Blood and tissue of were collected for aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels, histopathological analysis, immunohistochemistry of IL-1β and TNF-α, thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) and nitric oxide, Nrf2/keap1, superoxide dismutase (SOD), NADPH quinone oxidoreductase1 (NQO1), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), heat shock protein (HSP70), glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF-6) by western blot. Statistic analysis by ANOVA–Student-Newman-Keuls test (mean ± SE) significantly was p < 0.05. Tissue damage, AST, ALT, IL-1β, TNF-α, TBARS, NO, Keap1, iNOS, GRP78, and ATF-6 expression were significantly lower in the G + I/R group as compared to the I/R group. Expression of Nrf2, SOD, NQO1, and HSP70, was significantly higher in the G + I/R group as compared to I/R group. Pre-treatment with glutamine provided protection against oxidative damage in the intestine and liver in an experimental model of intestinal I/R.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
One-way analysis of variance
- ATF-6:
-
Activating transcription factor 6
- ERS:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Gln:
-
Glutamine
- GRP78:
-
Glucose-regulated protein 78
- HSP 70:
-
Heat shock protein 70
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- I/R:
-
Ischemia-reperfusion
- LPO:
-
Lipid peroxidation
- NQO1:
-
NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
References
Abudunaibi M, Mulati A, Aisikaer S, Zulifeiya M, Qiao J, Gulibositan M, Aili A, Halmurat U (2015) Myocardial protective effects of Munziq in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury rats with abnormal Savda syndrome. Genet Mol Res 14:3426–3435
Akcılar R, Akcılar A, Koçak C, Koçak FE, Bayat Z, Şimşek H, Şahin S, Savran B (2015) Effects of Ukrain on intestinal apoptosis caused by ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:22158–22166
Bolekova A, Spakovska T, Kluchova D, Toth S, Vesela J (2011) NADPH-diaphorase expression in the rat jejunum after intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. Eur J Histochem 55:e23
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Chassaing B, Etienne-Mesmin L, Gewirtz AT (2014) Microbiota-liver axis in hepatic disease. Hepatology 59:328–339
Chen L, Cui H (2015) Targeting glutamine induces apoptosis: a cancer therapy approach. Int J Mol Sci 16:22830–22855
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ, Gurd FN (1970) Intestinal mucosal lesion in low-flow states. I. A morphological, hemodynamic, and metabolic reappraisal. Arch Surg 101:478–483
Cho SS, Rudloff I, Berger PJ, Irwin MG, Nold MF, Cheng W, Nold-Petry CA (2013) Remifentanil ameliorates intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. BMC Gastroenterol 13:69
da Silva de Souza AC, Borges SC, Beraldi EJ, de Sá-Nakanishi AB, Comar JF, Bracht A, Natali MR, Buttow NC (2015) Resveratrol reduces morphologic changes in the myenteric plexus and oxidative stress in the ileum in rats with ischemia/reperfusion injury. Dig Dis Sci 60:3252–3263
Doroudgar S, Thuerauf DJ, Marcinko MC, Belmont PJ, Glembotski CC (2009) Ischemia activates the ATF6 branch of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J Biol Chem 284:29735–29745
Elshaer D, Begun J (2016) The role of barrier function, autophagy, and cytokines in maintaining intestinal homeostasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol S1084-9521:30256–30257
Espinosa-Diez C, Miguel V, Mennerich D, Kietzmann T, Sánchez-Pérez P, Cadenas S, Lamas S (2015) Antioxidant responses and cellular adjustments to oxidative stress. Redox Biol 6:183–197
European Commission (2012) Working document on a severity assessment framework. http://ec.europa.eu/environment/chemicals/lab_animals. Accessed 20 May 2016
Fan Z, Jing H, Yao J, Li Y, Hu X, Shao H, Shen G, Pan J, Luo F, Tian X (2014) The protective effects of curcumin on experimental acute liver lesion induced by intestinal ischemia-reperfusion through inhibiting the pathway of NF-κB in a rat model. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2014:191624
Fleming SD, Starnes BW, Kiang JG, Stojadinovic A, Tsokos GC, Shea-Donohue T (2002) Heat stress protection against mesenteric I/R induced alterations in intestinal mucosa in rats. J Appl Physiol 92:2600–2607
Goldim JR, Raymundo MM (1997) Pesquisa em saúde e direitos dos animais. HCPA, Porto Alegre
Granger DL, Anstey NM, Miller WC, Weinberg JB (1999) Measuring nitric oxide production in human clinical studies. Methods Enzymol 301:49–61
He XH, Li QW, Wang YL, Zhang ZZ, Ke JJ, Yan XT, Chen K (2015) Transduced PEP-1-Heme oxygenase-1 fusion protein reduces remote organ injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. Med Sci Monit 21:1057–1065
Inan M, Uz YH, Kizilay G, Topcu-Tarladacalisir Y, Sapmaz-Metin M, Akpolat M, Aydogdu N (2013) Protective effect of sildenafil on liver injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. J Pediatr Surg 48:1707–1715
Kaser A, Tomczak M, Blumberg RS (2011) “ER stress(ed out)!”: Paneth cells and ischemia-reperfusion injury of the small intestine. Gastroenterology 140:393–396
Khan MM, Yang WL, Wang P (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in sepsis. Shock 44:294–304
Kiang JG, Agravante NG, Smith JT, Bowman PD (2011) 17-DMAG diminishes hemorrhage-induced small intestine injury by elevating Bcl-2 protein and inhibiting iNOS pathway, TNF-α increase, and caspase-3 activation. Cell Biosci 1:21
Kierulf-Lassen C, Kristensen ML, Birn H, Jespersen B, Nørregaard R (2015) No effect of remote ischemic conditioning strategies on recovery from renal ischemia-reperfusion injury and protective molecular mediators. PLoS One 10:e0146109
Kudoh K, Uchinami H, Yoshioka M, Seki E, Yamamoto Y (2014) Nrf2 activation protects the liver from ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Ann Surg 260:118–127
Laemmli U, Molbert E, Showe M, Kellenberger E (1970) Form determining function of the genes required for the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol 49:99–113
Liu KX, Wu WK, He W, Liu CL (2007) Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) attenuates lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats: roles of oxidative stress and nitric oxide. World J Gastroenterol 13:299–305
Liu J, Pan G, Liang T, Huang P (2014) HGF/c-Met signaling mediated mesenchymal stem cell-induced liver recovery in intestinal ischemia reperfusion model. Int J Med Sci 1:626–633
Ma L, Wang G, Chen Z, Li Z, Yao J, Zhao H, Wang S, Ma Z, Chang H, Tian X (2014) Modulating the p66shc signaling pathway with protocatechuic acid protects the intestine from ischemia-reperfusion injury and alleviates secondary liver damage. ScientificWorldJournal 2014:387640
Onder A, Kapan M, Gümüş M, Yüksel H, Böyük A, Alp H, Başarili MK, Firat U (2012) The protective effects of curcumin on intestine and remote organs against mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion injury. Turk J Gastroenterol 23:141–147
Ozban M, Aydin C, Cevahir N, Yenisey C, Birsen O, Gumrukcu G, Aydin B, Berber I (2015) The effect of melatonin on bacterial translocation following ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model of superior mesenteric artery occlusion. BMC Surg 15:8
Shiota M, Kusakabe H, Izumi Y, Hikita Y, Nakao T, Funae Y, Miura K, Iwao H (2010) Heat shock cognate protein 70 is essential for Akt signaling in endothelial function. Arteriscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:491–497
Sun Q, Meng QT, Jiang Y, Liu HM, Lei SQ, Su WT, Duan WN, Wu Y, Xia ZY, Xia ZY (2013) Protective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 against intestinal ischemia-reperfusion induced acute renal injury in mice. PLoS One 8:e80859
Sun Y, Pu LY, Lu L, Wang XH, Zhang F, Rao JH (2014) N-acetylcysteine attenuates reactive-oxygen-species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress during liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 20:15289–15298
Sun Y, Gao Q, Wu N, Li SD, Yao JX, Fan WJ (2015) Protective effects of dexmedetomidine on intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp Ther Med 10:647–652
Takizawa Y, Kitazato T, Ishizaka H, Kamiya N, Tomita M, Hayashi M (2011) Effect of aminoguanidine on ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat small intestine. Biol Pharm Bull 34:1737–1743
Tas U, Ayan M, Sogut E, Kuloglu T, Uysal M, Tanriverdi HI, Senel U, Ozyurt B, Sarsilmaz M (2015) Protective effects of Thymoquinone and melatonin on intestinal ischemia–reperfusion injury. Saudi J Gastroenterol 21:284–289
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1992) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Biotechnology 24:145–149
Vaikunthanathan T, Safinia N, Lombardi G, Lechler RI (2016) Microbiota, immunity and the liver. Immunol Lett 171:36–49
Vasconcelos PR, Costa Neto CD, Vasconcelos RC, Souza PP, Vasconcelos PR, Guimarães SB (2011) Effect of glutamine on the mRNA level of key enzymes of malate-aspartate shuttle in the rat intestine subjected to ischemia reperfusion. Acta Cir Bras 1:26–31
Wang G, Xiu P, Li F, Xin C, Li K (2014) Vitamin a supplementation alleviates extrahepatic cholestasis liver injury through Nrf2 activation. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2014:273692
Wernerman J (2008) Clinical use of glutamine supplementation. J Nutr 138:2040S–2044S
Wu GH, Wang H, Zhang YW, Wu ZH, Wu ZG (2004) Glutamine supplemented parenteral nutrition prevents intestinal ischemia- reperfusion injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol 10:2592–2594
Xu CL, Sun R, Qiao XJ, Xu CC, Shang XY, Niu WN (2014) Protective effect of glutamine on intestinal injury and bacterial community in rats exposed to hypobaric hypoxia environment. World J Gastroenterol 20:4662–4674
Yao W, Luo G, Zhu G, Chi X, Zhang A, Xia Z, Hei Z (2014) Propofol activation of the Nrf2 pathway is associated with amelioration of acute lung in a rat liver transplantation model. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2014:258567
Zabot GP, Carvalhal GF, Marroni NP, Hartmann RM, da Silva VD, Fillmann HS et al (2014) Glutamine prevents oxidative stress in a model of mesenteric ischemia and reperfusion. World J Gastroenterol 20:11406–11414
Zhao HD, Zhang F, Shen G, Li YB, Li YH, Jing HR, Ma LF, Yao JH, Tian XF (2010) Sulforaphane protects liver injury induced by intestinal ischemia reperfusion through Nrf2-ARE pathway. World J Gastroenterol 16:3002–3010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Christos D. Katsetos
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartmann, R.M., Licks, F., Schemitt, E.G. et al. Protective effect of glutamine on the main and adjacent organs damaged by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Protoplasma 254, 2155–2168 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1102-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1102-3