Abstract
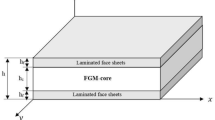
In this paper, the free vibration characteristics of stiffened sandwich plates with auxetic core and functionally graded piezoelectric face sheet are investigated. The sandwich plate configuration comprises three distinct layers: a top layer consisting of functionally graded piezoelectric material (FGPie), a core layer composed of auxetic material exhibiting a negative Poisson's ratio, and a bottom layer made of functionally graded material (FGM). The sandwich plate is reinforced by isotropic stiffeners along the x and y directions. A novel model is established based on the four-variable shear deformation refined plate theory and the pb2-Ritz method. This model offers the flexibility to analyze plates with diverse mechanical boundary conditions and supports two types of electrical boundary conditions: closed circuit and open circuit. The accuracy and convergence of the proposed model are validated through comparative analyses against published results, thereby confirming the reliability when analyzing the vibration characteristics of this complex sandwich structure. Furthermore, some new investigations are carried out to explore the influence of various parameters on the vibrational characteristics of the stiffened piezoelectric auxetic sandwich (SA-FGPie) plates. The results suggest that the properties of the reinforcing stiffeners, such as quantity or dimensions, alter the free vibration characteristics of the SA-FGPie plates significantly. In addition, parameters such as the volume fraction indexes of the FGPie and FGM layers, electrical boundary conditions or FGPie layer thickness, as well as geometric parameters of the auxetic unit cell also have a significant influence on the vibration response of SA-FGPie plates. However, the influence of these parameters depends on the specific boundary conditions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Y., Feng, Z., Hao, L., Huang, L., Xin, C., Wang, Y., Bilotti, E., Essa, K., Zhang, H., Li, Z.: A review on functionally graded materials and structures via additive manufacturing: from multi-scale design to versatile functional properties. Adv. Mater. Technol. 5(6), 1900981 (2020)
Mahesh, V.: Porosity effect on the nonlinear deflection of functionally graded magneto-electro-elastic smart shells under combined loading. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 29(19), 2707–2725 (2022)
Mahesh, V., Kattimani, S.: Finite element simulation of controlled frequency response of skew multiphase magneto-electro-elastic plates. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 30(12), 1757–1771 (2019)
Zhang, S.-Q., Zhao, G.-Z., Rao, M.N., Schmidt, R., Yu, Y.-J.: A review on modeling techniques of piezoelectric integrated plates and shells. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 30(8), 1133–1147 (2019)
Wu, X.-H., Chen, C., Shen, Y.-P., Tian, X.-G.: A high order theory for functionally graded piezoelectric shells. Int. J. Solids Struct. 39(20), 5325–5344 (2002)
Sedighi, M., Shakeri, M.: A three-dimensional elasticity solution of functionally graded piezoelectric cylindrical panels. Smart Mater. Struct. 18(5), 055015 (2009)
Bodaghi, M., Shakeri, M.: An analytical approach for free vibration and transient response of functionally graded piezoelectric cylindrical panels subjected to impulsive loads. Compos. Struct. 94(5), 1721–1735 (2012)
Farsangi, M.A., Saidi, A.: Levy type solution for free vibration analysis of functionally graded rectangular plates with piezoelectric layers. Smart Mater. Struct. 21(9), 094017 (2012)
Farsangi, M.A., Saidi, A., Batra, R.: Analytical solution for free vibrations of moderately thick hybrid piezoelectric laminated plates. J. Sound Vib. 332(22), 5981–5998 (2013)
Zhong, Z., Yu, T.: Vibration of a simply supported functionally graded piezoelectric rectangular plate. Smart Mater. Struct. 15(5), 1404 (2006)
Barati, M.R., Zenkour, A.M.: Electro-thermoelastic vibration of plates made of porous functionally graded piezoelectric materials under various boundary conditions. J. Vib. Control 24(10), 1910–1926 (2018)
Behjat, B., Salehi, M., Sadighi, M., Armin, A., Abbasi, M.: Static, dynamic, and free vibration analysis of functionally graded piezoelectric panels using finite element method. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 20(13), 1635–1646 (2009)
Alderson, A., Evans, K.: Microstructural modelling of auxetic microporous polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 30, 3319–3332 (1995)
Wan, H., Ohtaki, H., Kotosaka, S., Hu, G.: A study of negative Poisson’s ratios in auxetic honeycombs based on a large deflection model. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids. 23(1), 95–106 (2004)
Zhang, G., Ghita, O.R., Evans, K.E.: Dynamic thermo-mechanical and impact properties of helical auxetic yarns. Compos. B Eng. 99, 494–505 (2016)
Grujicic, M., Galgalikar, R., Snipes, J., Yavari, R., Ramaswami, S.: Multi-physics modeling of the fabrication and dynamic performance of all-metal auxetic-hexagonal sandwich-structures. Mater. Des. 51, 113–130 (2013)
Whitty, J., Alderson, A., Myler, P., Kandola, B.: Towards the design of sandwich panel composites with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties by variation of the in-plane Poisson’s ratios. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 34(6), 525–534 (2003)
Mahesh, V., Mahesh, V., Harursampath, D., Abouelregal, A.E.: Simulation-based assessment of coupled frequency response of magneto-electro-elastic auxetic multifunctional structures subjected to various electromagnetic circuits. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 236(11), 2281–2296 (2022)
Wang, T., Qin, Q., Wang, M., Yu, W., Wang, J., Zhang, J., Wang, T.: Blast response of geometrically asymmetric metal honeycomb sandwich plate: experimental and theoretical investigations. Int. J. Impact Eng 105, 24–38 (2017)
Qi, C., Remennikov, A., Pei, L.-Z., Yang, S., Yu, Z.-H., Ngo, T.D.: Impact and close-in blast response of auxetic honeycomb-cored sandwich panels: experimental tests and numerical simulations. Compos. Struct. 180, 161–178 (2017)
Tran, T.T., Pham, Q.H., Nguyen-Thoi, T., Tran, T.-V.: Dynamic analysis of sandwich auxetic honeycomb plates subjected to moving oscillator load on elastic foundation. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 1–16 (2020)
Nguyen, N.V., Nguyen-Xuan, H., Nguyen, T.N., Kang, J., Lee, J.: A comprehensive analysis of auxetic honeycomb sandwich plates with graphene nanoplatelets reinforcement. Compos. Struct. 259, 113213 (2021)
Dat, N.D., Quan, T.Q., Duc, N.D.: Vibration analysis of auxetic laminated plate with magneto-electro-elastic face sheets subjected to blast loading. Compos. Struct. 280, 114925 (2022)
Quan, T.Q., Anh, V.M., Mahesh, V., Duc, N.D.: Vibration and nonlinear dynamic response of imperfect sandwich piezoelectric auxetic plate. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 29(1), 127–137 (2022)
Mahesh, V.: Nonlinear damping of auxetic sandwich plates with functionally graded magneto-electro-elastic facings under multiphysics loads and electromagnetic circuits. Compos. Struct. 290, 115523 (2022)
Mahesh, V.: Nonlinear free vibration of multifunctional sandwich plates with auxetic core and magneto-electro-elastic facesheets of different micro-topological textures: FE approach. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 29(27), 6266–6287 (2022)
Chadha, K., Mahesh, V., Mangalasseri, A.S., Mahesh, V.: On analysing vibration energy harvester with auxetic core and magneto-electro-elastic facings. Thin-Walled Struct. 184, 110533 (2023)
Mahesh, V., Ponnusami, S.A.: Nonlinear damped transient response of sandwich auxetic plates with porous magneto-electro-elastic facesheets. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 137(5), 1–21 (2022)
Mahesh, V.: Integrated effects of auxeticity and pyro-coupling on the nonlinear static behaviour of magneto-electro-elastic sandwich plates subjected to multi-field interactive loads. In: Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science. 09544062221149300 (2023)
Goel, M.D., Matsagar, V.A., Gupta, A.K.: Blast resistance of stiffened sandwich panels with aluminum cenosphere syntactic foam. Int. J. Impact Eng 77, 134–146 (2015)
Rajasekaran, S.: Free vibration of centrifugally stiffened axially functionally graded tapered Timoshenko beams using differential transformation and quadrature methods. Appl. Math. Model. 37(6), 4440–4463 (2013)
Damnjanović, E., Marjanović, M., Nefovska-Danilović, M.: Free vibration analysis of stiffened and cracked laminated composite plate assemblies using shear-deformable dynamic stiffness elements. Compos. Struct. 180, 723–740 (2017)
Qin, X., Dong, C., Wang, F., Qu, X.: Static and dynamic analyses of isogeometric curvilinearly stiffened plates. Appl. Math. Model. 45, 336–364 (2017)
Lee, D.-M., Lee, I.: Vibration analysis of anisotropic plates with eccentric stiffeners. Comput. Struct. 57(1), 99–105 (1995)
Khayat, M., Rahnema, H., Baghlani, A., Dehghan, S.M.: A theoretical study of wave propagation of eccentrically stiffened FGM plate on Pasternak foundations based on higher-order shear deformation plate theory. Mater. Today Commun. 20, 100595 (2019)
Harik, I., Guo, M.: Finite element analysis of eccentrically stiffened plates in free vibration. Comput. Struct. 49(6), 1007–1015 (1993)
Van Dung, D., Nga, N.T.: Thermomechanical postbuckling analysis of eccentrically stiffened FGM sandwich plates with general Sigmoid and power laws based on TSDT. J. Sandwich Struct. Mater. 20(8), 907–945 (2018)
Sinha, L., Mishra, S., Nayak, A., Sahu, S.: Free vibration characteristics of laminated composite stiffened plates: Experimental and numerical investigation. Compos. Struct. 233, 111557 (2020)
Liu, Y., Wang, Q.: Computational study of strengthening effects of stiffeners on regular and arbitrarily stiffened plates. Thin-Walled Struct. 59, 78–86 (2012)
Pham, H.-A., Tran, H.-Q., Tran, M.-T., Nguyen, V.-L., Huong, Q.-T.: Free vibration analysis and optimization of doubly-curved stiffened sandwich shells with functionally graded skins and auxetic honeycomb core layer. Thin-Walled Struct. 179, 109571 (2022)
Brush, D. O.; Almroth, B. O.; Hutchinson, J.: Buckling of bars, plates, and shells. (1975)
Najafizadeh, M., Hasani, A., Khazaeinejad, P.: Mechanical stability of functionally graded stiffened cylindrical shells. Appl. Math. Model. 33(2), 1151–1157 (2009)
Tran, H.-Q., Vu, V.-T., Tran, M.-T.: Free vibration analysis of piezoelectric functionally graded porous plates with graphene platelets reinforcement by pb-2 Ritz method. Compos. Struct. 305, 116535 (2023)
Tham, V., Tran, H., Tu, T.: Vibration characteristics of piezoelectric functionally graded carbon nanotube-reinforced composite doubly-curved shells. Appl. Math. Mech. 42(6), 819–840 (2021)
Quoc, T.H., Van Tham, V., Tu, T.M.: Active vibration control of a piezoelectric functionally graded carbon nanotube-reinforced spherical shell panel. Acta Mech. 232, 1005–1023 (2021)
Huu Quoc, T., Minh, Tu., T., Van Tham, V.: Free vibration analysis of smart laminated functionally graded CNT reinforced composite plates via new four-variable refined plate theory. Materials. 12(22), 3675 (2019)
Sayyaadi, H., Rahnama, F., Farsangi, M.A.A.: Energy harvesting via shallow cylindrical and spherical piezoelectric panels using higher order shear deformation theory. Compos. Struct. 147, 155–167 (2016)
Shiyekar, S., Kant, T.: Higher order shear deformation effects on analysis of laminates with piezoelectric fibre reinforced composite actuators. Compos. Struct. 93(12), 3252–3261 (2011)
Zenkour, A.M., Alghanmi, R.A.: Bending of exponentially graded plates integrated with piezoelectric fiber-reinforced composite actuators resting on elastic foundations. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids. 75, 461–471 (2019)
Tran, H.-Q., Vu, V.-T., Nguyen, V.-L., Tran, M.-T.: Free vibration and nonlinear dynamic response of sandwich plates with auxetic honeycomb core and piezoelectric face sheets. Thin-Walled Structures. 191, 111141 (2023)
Zenkour, A.M., Alghanmi, R.A.: Static response of sandwich plates with FG core and piezoelectric faces under thermo-electro-mechanical loads and resting on elastic foundations. Thin-Walled Struct. 157, 107025 (2020)
Chevallier, G., Ghorbel, S., Benjeddou, A.: A benchmark for free vibration and effective coupling of thick piezoelectric smart structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 17(6), 065007 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by Hanoi University of Civil Engineering (HUCE) under grant number 24-2022/KHXD-TĐ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicting interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest in preparing this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Appendix A
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vu, VT., Tran, HQ. Free vibration characteristics of stiffened sandwich plates with auxetic core and functionally graded piezoelectric face sheet. Acta Mech (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-024-03932-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-024-03932-z