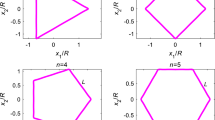
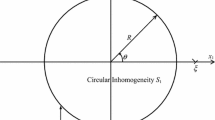
Abstract
We use Muskhelishvili’s complex variable formulation to derive a closed-form solution to the plane strain problem of a hypotrochoidal compressible liquid inclusion embedded in an infinite isotropic elastic matrix subjected to an edge dislocation located at an arbitrary position. The internal uniform hydrostatic tension within the hypotrochoidal liquid inclusion and all the unknown complex constants appearing in the two analytic functions characterizing the elastic field in the matrix are completely determined in an analytical manner. In principle, the solution to the problem of an edge dislocation interacting with an arbitrarily shaped compressible liquid inclusion can be obtained in closed-form as long as the adopted conformal mapping function which maps the exterior of the inclusion onto the exterior of the unit circle in the image plane contains a finite number of terms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Style, R.W., Boltyanskiy, R., Allen, B., Jensen, K.E., Foote, H.P., Wettlaufer, J.S., Dufresne, E.R.: Stiffening solids with liquid inclusions. Nat. Phys. 11(1), 82–87 (2015)
Ghosh, K., Lopez-Pamies, O.: Elastomers filled with liquid inclusions: theory, numerical implementation, and some basic results. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 166, 104930 (2022)
Ghosh, K., Lefevre, V., Lopez-Pamies, O.: The effective shear modulus of a random isotropic suspension of monodisperse liquid n-spheres: from the dilute limit to the percolation threshold. Soft Matter 19, 208–224 (2023)
Style, R.W., Wettlaufer, J.S., Dufresne, E.R.: Surface tension and the mechanics of liquid inclusions in compliant solids. Soft Matter 11(4), 672–679 (2015)
Wu, J., Ru, C.Q., Zhang, L.: An elliptical liquid inclusion in an infinite elastic plane. Proc. Royal Soc. A 474(2215), 20170813 (2018)
Chen, X., Li, M.X., Yang, M., Liu, S.B., Genin, G.M., Xu, F., Lu, T.J.: The elastic fields of a compressible liquid inclusion. Extreme Mech. Lett. 22, 122–130 (2018)
Dai, M., Hua, J., Schiavone, P.: Compressible liquid/gas inclusion with high initial pressure in plane deformation: modified boundary conditions and related analytical solutions. Euro. J. Mech. A-Solids 82, 104000 (2020)
Dai, M., Schiavone, P.: Modified closed-form solutions for three-dimensional elastic deformations of a composite structure containing macro-scale spherical gas/liquid inclusions. Appl. Math. Model. 97, 57–68 (2021)
Ti, F., Chen, X., Li, M.X., Sun, X.C., Liu, S.B., Lu, T.J.: Cylindrical compressible liquid inclusion with surface effects. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 161, 104813 (2022)
Ghosh, K., Lefevre, V., Lopez-Pamies, O.: Homogenization of elastomers filled with liquid inclusions: the small-deformation limit. J. Elasticity 154, 235–253 (2023)
Wang, X., Schiavone, P.: Interaction between an edge dislocation and a circular incompressible liquid inclusion. Math. Mech. Solids 29(3), 531–538 (2024)
Wang, X., Schiavone, P.: An edge dislocation interacting with an elliptical incompressible liquid inclusion. J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 19(1), 131–140 (2024)
Muskhelishvili, N.I.: Some Basic Problems of the Mathematical Theory of Elasticity. P. Noordhoff Ltd., Groningen (1953)
England, A.H.: Complex variable method in elasticity. Wiley, New York (1971)
Ting, T.C.T.: Anisotropic elasticity: theory and applications. Oxford University Press, New York (1996)
Dundurs, J.: Elastic interaction of dislocations with inhomogeneities. In: Mathematical Theory of Dislocations (ed. T. Mura), pp. 70−115, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York (1969).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by a Discovery Grant from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (Grant No: RGPIN-2023-03227 Schiavo).
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Schiavone, P. An edge dislocation interacting with a hypotrochoidal compressible liquid inclusion. Acta Mech (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-024-03888-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-024-03888-0