Abstract
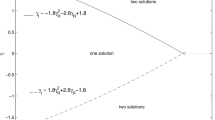
In this paper, the propagation of a Rayleigh-type wave is explored in a half-space of an incompressible nematic elastomer with a uniform director aligned orthogonal to the surface. The nematic elastomer is idealized so as to fit within the framework of linear viscoelasticity theory. The governing equations of nematic elastomers are subjected to the Tiersten-type impedance boundary conditions. An explicit secular equation of the Rayleigh wave is obtained which depends upon the non-dimensional anisotropy parameter, impedance parameters, frequency, rubber relaxation time, director rotation times, and the dynamic soft elasticity of nematic elastomers. The numerical computations of the Rayleigh wave speed are restricted for the case of ideal nematic rubbers. The Rayleigh wave speed is illustrated graphically to observe the effects of non-dimensional anisotropy parameter, frequency, impedance parameters, rubber relaxation time, and director rotation times.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Gennes, PG.: Liquid crystals of one- and two- dimensional order. In: Helfrich, W., Heppke, G. (eds) Springer, New York (1980)
Finkelmann, H., Kock, H.J., Rehage, H.: Liquid crystalline elastomers-a new type of liquid of liquid crystalline material. Makromol. Chem. Rapid Commun. 2, 317–322 (1981)
de Gennes, P.G., Prost, J.: The Physics of Liquid Crystals, 2nd edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1993)
Brand, H.R., Finkelmann, H.: Physical properties of liquid crystalline elastomers. In: Demus, D., et al. (eds.) Handbook of Liquid Crystals. Wiley VCH, Weinheim (1998)
Warner, M., Terentjev, E.M.: Liquid Crystal Elastomers. Clarendon Press, Oxford (2003)
Kupfer, J., Finkelmann, H.: Nematic liquid single-crystal elastomers. Makromol. Chem. Rapid Commun. 12, 717–726 (1991)
Kupfer, J., Finkelmann, H.: Liquid crystal elastomer: influence of the orientational distribution of the crosslinks on the phase behaviour and reorientation process. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 195, 1353–1367 (1994)
Brand, H.R., Plenier, H., Martinoty, P.: Selected macroscopic properties of liquid crystalline elastomers. Soft Matter 2, 182–199 (2006)
Finkelmann, H., Greve, A., Warner, M.: The elastic ansiotropy of nematic elastomers. Euro Phys. J. E 5, 281–293 (2001)
Bladon, P., Warner, M., Terentjev, E.M.: Orientational order in strained nematic networks. Macromolecules 27, 7067–7075 (1994)
Bladon, P., Terentjev, E.M., Warner, M.: Transitions and instabilities in liquid crystal elastomers. Phys. Rev. E 47, R3838–R3840 (1993)
Martinoty, P., Stein, P., Finkelmann, H., Pleiner, H., Brand, H.R.: Mechanical properties of monodomain side chain nematic elastomers. Euro Phys. J. E 14, 311–321 (2004)
Anderson, D.R., Carlson, D.E., Fried, E.: A continuum-mechanical theory of nematic elastomers. J. Elast. 56, 33–58 (1999)
Golubovic, L., Lubensky, T.C.: Nonlinear elasticity of amorphous solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, 1082–1085 (1989)
Teixeira, P.L.C., Warner, M.: Dynamics of soft and semisoft nematic elastomers. Phys. Rev. E 42, 603–609 (1999)
Uchida, N.: Soft and nonsoft structural transitions in disordered nematic networks. Phy Rev E. 62, 5119–5136 (2000)
Carlson, D.E., Fried, E., Sellers, S.: Force-free states, relative strains, and soft elasticity in nematic elastomers. J. Elast. 69, 161–180 (2002)
Stenull, O., Lubensky, T.C.: Anomalous elasticity of nematic elastomers. Europhys. Lett. 61, 776–782 (2003)
Stenull, O., Lubensky, T.C.: Dynamics of nematic elastomers. Phys. Rev. E 69, 051801/1-051801/13 (2004)
Fried, E., Sellers, S.: Free-energy density functions for nematic elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 52, 1671–1689 (2004)
Gallani, J.L., Hilton, L., Martinoty, P., Doublet, F., Mauzac, M.: Mechanical behaviour of side-chain liquid crystalline networks. J Physique II France 6, 443–452 (1996)
Terentjev, E.M., Warner, M.: Linear hydrodynamic and viscoelasticity of nematic elastomers. Eur. Phys. J. E 4, 343–353 (2001)
Terentjev, E.M., Kamotski, I.V., Zakharov, D.D., Fradkin, L.J.: Propagation of acoustic waves in nematic elastomers. Phys. Rev. E 66, 052701–4 (2002)
Fradkin, L.J., Kamotski, I.V., Terentjev, E.M., Zakharov, D.D.: Low frequency acoustic waves in nematic elastomers. Proc. R. Soc. London A 459, 2627–2642 (2003)
Singh, B.: Reflection of homogeneous elastic waves from free surface of nematic elastomer half-space. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 584–593 (2007)
Zakharov, D.D., Kaptsov, A.V.: Peculiarities of the surface and guided waves propagation in heterogeneous composites with nematic coatings. Proc. Appl. Math. Mech. 10, 501–502 (2010)
Zakharov, D.D., Kaptsov, A.V.: Effect of nematic coating on fundamental mode propagation in layered elastic plates. Acoust. Phys. 57, 59–65 (2011)
Zakharov, D.D.: Surface and edge waves in solids with nematic coating. Math. Mech. Solids 17, 67–80 (2011)
Zakharov, D.D.: Resonance phenomena in surface wave propagation in elastic bodies coated with nematic elastomers. Mech. Solids 48, 659–672 (2013)
Yang, S., Liu, Y., Gu, Y., Yang, Q.: Rayleigh wave propagation in nematic elastomers. Soft Matter 10, 4110–4117 (2014)
Yang, S., Liu, Y., Liang, T.: Band structures in the nematic elastomers phononic crystals. Phys. B 506, 55–64 (2017)
Zhao, D., Liu, Y., Liu, C.: Transverse vibration of nematic elastomer Timoshenko beams. Phys. Rev. E 95, 012703–13 (2017)
Zhao, D., Liu, Y.: Effects of director rotation relaxation on viscoelastic wave dispersion in nematic elastomer beams. Math. Mech. Solids 24, 1105–1113 (2019)
Zhao, D., Liu, Y.: Effects of director orientation on the vibration of anisotropic nematic elastomer plates under various boundary conditions. Smart Mater. Struct. 27, 075044 (2018)
Tiersten, H.F.: Elastic surface waves guided by thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 770–789 (1969)
Malischewsky, P.G.: Surface Waves and Discontinuities. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1987)
Godoy, E., Durn, M., Ndlec, J.-C.: On the existence of surface waves in an elastic half-space with impedance boundary conditions. Wave Motion 49, 585–594 (2012)
Vinh, P.C., Hue, T.T.T.: Rayleigh waves with impedance boundary conditions in anisotropic solids. Wave Motion 51, 1082–1092 (2014)
Vinh, P.C., Hue, T.T.T.: Rayleigh waves with impedance boundary conditions in incompressible anisotropic half-spaces. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 85, 175–185 (2014)
Singh, B.: Rayleigh waves in an incompressible fibre-reinforced elastic solid with impedance boundary conditions. J. Mech. Behav. Mater. 24, 183–186 (2015)
Vinh, P.C., Xuan, N.Q.: Rayleigh waves with impedance boundary condition: formula for the velocity, existence and uniqueness. Euro J. Mech. A Solids. 61, 180–185 (2017)
Saccomandi, G., Ogden, R.W.: Mechanics and Thermomechanics of Rubberlike Solids, CISM Courses and Lectures No. 452, International Centre for Mechanical Sciences. Springer (2014)
Ogden, R.W., Vinh, P.C.: On Rayleigh waves in incompressible orthotropic elastic solids. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115, 530–533 (2004)
Warner, M., Terentjev, E.M.: Nematic elastomers : A new state of matter? Prog. Polym. Sci. 21, 853–891 (1996)
Schonstein, M., Stille, W., Strobl, G.: Effect of the network on the director fluctuations in a nematic side-group elastomer analysed by static and dynamic light scattering. Euro Phys. J. E 5, 511–517 (2001)
Schmidtke, J., Stille, W., Strobl, G.: Static and dynamic light scattering of a nematic side-group polysiloxane. Macromolecules 33, 2922–2928 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, B. On Rayleigh-type surface wave in incompressible nematic elastomers. Acta Mech 234, 1033–1044 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03423-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03423-z