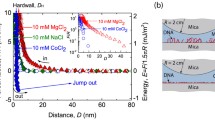
Abstract
Since its discovery, atomic force microscopy (AFM) is widely used to study biological objects and materials, including cells, proteins, and nucleic acids. AFM measurements are carried out in the air as well as in liquid with a very high resolution, even more complex bioprocesses can be monitored in situ under physiological conditions. Successful imaging of DNA molecules on the flat supporting surface typically requires appropriate treatment of mica. The original surface charge of mica is the same as of DNA, i.e. negative. Accordingly, immobilization using bivalent cations (Mg2+, Ni2+, and Co2+), deposition of ethanolamine, and mica surface silanization with alkoxysiloxane derivatives were reported to achieve an optimal concentration and surface arrangement of DNA molecules. Vapours of alkoxysiloxane derivatives led to uniform negatively charged mica surface and it was found that higher ionic radius causes a weaker bond. A better quality and sharper images of DNA molecules were achieved by adjusting the correct real amplitude of the cantilever. This amplitude should correspond with the expected size of the target objects—DNA molecules in the x–y plane of the image. The length of the observed DNA molecules was 1000 bp and the planar width of DNA was 7.8 nm (in reality 3 nm). The AFM spectroscopic mode was particularly useful.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Santos NC, Castanho MARB (2004) Biophys Chem 107:133
Riener CK, Stroh CM, Ebner A, Klampfl C, Gall AA, Romanin C, Lyubchenko YL, Hinterdorfer P, Gruber H (2003) Anal Chim Acta 479:59
Lyubchenko Y, Shlyakhtenko L, Harrington R, Oden P, Lindsay S (1993) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:2137
Wickramasinghe HK (2000) Acta Mater 48:347
Jalili N, Laxminarayana K (2004) Mechatronics 14:907
Ikai A (1996) Surf Sci Rep 26:261
Yin Y, Zech M, Williams TL, Hoffman JE (2009) Phys C 469:535
Alessandrini A, Facci P (2005) Meas Sci Technol 16:R65
Fotiadis D, Scheuring S, Müller SA, Engel A, Müller DJ (2002) Micron 33:385
Jandt KD (2001) Surf Sci 491:303
Butt HJ, Cappella B, Kappl M (2005) Surf Sci Rep 59:1
Braga PC, Ricci D (2004) Atomic force microscopy: biomedical methods and applications. Humana Press, New Jersey
Alonso JL, Goldmann WH (2003) Life Sci 72:2553
Ando T, Uchihashi T, Fukuma T (2008) Prog Surf Sci 83:337
Bhushan B, Kawata S (2006) Applied scanning probe methods VI: characterization. In: Thomson NH (ed) Atomic force microscopy of DNA structure and interactions. Springer, Berlin, p 127
Lyubchenko YL, Shlyakhtenko LS, Ando T (2011) Methods 54:274
Bezanilla M, Manne S, Laney DE, Lyubchenko YL, Hansma HG (1995) Langmuir 11:655
Zheng J, Li Z, Wu A, Zhou H (2003) Biophys Chem 104:37
Sun XG, Cao EH, Zhang X, Liu D, Bai C (2002) Inorg Chem Commun 5:181
Sasou M, Sugiyama S, Yoshino T, Ohtani T (2003) Langmuir 19:9845
White LD, Tripp CP (2000) J Colloid Interface Sci 232:400
Costa LT, Pinto JR, Moraes MB, De Souza GGB, Sorenson MM, Bisch PM, Weissmuller G (2004) Biophys Chem 109:63
Campbell PA, Sinnamon LJ, Thompson CE, Walmsley DG (1998) Surf Sci 410:L768
Liu Z, Li Z, Zhou H, Wei G, Song Y, Wang L (2005) Micron 36:525
Ouerghi O, Touhami A, Othmane A, Ben Ouada H, Martelet C, Fretigny C, Jaffrezic-Renault N (2002) Sens Actuators B Chem 84:167
Thormann E, Pettersson T, Kettle J, Claesson PM (2010) Ultramicroscopy 110:313
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Central European Institute of Technology (CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0068) from European Regional Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horňáková, V., Přibyl, J. & Skládal, P. Study of DNA immobilization on mica surface by atomic force microscopy. Monatsh Chem 147, 865–871 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-016-1695-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-016-1695-9