Abstract
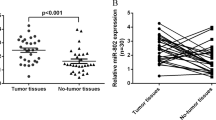
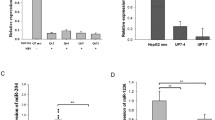
miR-HCC2 has been reported to markedly promote the growth, metastasis, and stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells in vitro and in vivo. Deep sequencing showed that miR-HCC2 was significantly upregulated in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-positive (HBV+) HCC tissue samples compared with HBV-negative (HBV-) HCC tissue samples. miR-HCC2 expression was further evaluated in HCC tissues and cells, and the expression of miR-HCC2 was found to be significantly higher in HBV+ HCC tissues and cells than in HBV- HCC tissues and cells, suggesting that high miR-HCC2 expression could be induced by HBV infection. To explore the relationship between miR-HCC2 and HBV, we investigated the effect of miR-HCC2 on HBV antigen expression, transcription, and replication. We found that miR-HCC2 was involved in the negative feedback regulation of HBV replication. Further mechanistic studies revealed that miR-HCC2 suppressed HBV replication by inhibiting the activity of the enhancer I/X promoter. Our study demonstrates the effect of the inhibition of miR-HCC2 on HBV gene expression and replication, which can help to illustrate the complex regulatory network involving host miRNAs and HBV.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Levrero M, Zucman-Rossi J (2016) Mechanisms of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 64:S84–S101
Kew MC (2010) Epidemiology of chronic hepatitis B virus infection, hepatocellular carcinoma, and hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Biol (Paris) 58:273–277
Nassal M (2015) HBV cccDNA: viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 64:1972–1984
Guo YH, Li YN, Zhao JR, Zhang J, Yan Z (2011) HBc binds to the CpG islands of HBV cccDNA and promotes an epigenetic permissive state. Epigenetics 6:720–726
Lucifora J, Xia Y, Reisinger F, Zhang K, Stadler D, Cheng X, Sprinzl MF, Koppensteiner H, Makowska Z, Volz T, Remouchamps C, Chou WM, Thasler WE, Huser N, Durantel D, Liang TJ, Munk C, Heim MH, Browning JL, Dejardin E, Dandri M, Schindler M, Heikenwalder M, Protzer U (2014) Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science 343:1221–1228
Su H, Yee JK (1992) Regulation of hepatitis B virus gene expression by its two enhancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:2708–2712
Seeger C, Mason WS (2015) Molecular biology of hepatitis B virus infection. Virology 479–480:672–686
Morikawa K, Suda G, Sakamoto N (2016) Viral life cycle of hepatitis B virus: host factors and druggable targets. Hepatol Res 46:871–877
Croce CM (2009) Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 10:704–714
Esteller M (2011) Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet 12:861–874
Ratnasari N, Lestari P, Renovaldi D, Raditya Ningsih J, Qoriansas N, Wardana T, Hakim S, Signa Aini Gumilas N, Indrarti F, Triwikatmani C, Bayupurnama P, Setyo Heriyanto D, Astuti I, Mubarika Harjana S (2022) Potential plasma biomarkers: miRNA-29c, miRNA-21, and miRNA-155 in clinical progression of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. PLoS ONE 17:e0263298
Kitab B, Alj HS, Ezzikouri S, Benjelloun S (2015) MicroRNAs as important players in host-hepatitis B virus interactions. J Clin Transl Hepatol 3:149–161
Zhang GL, Li YX, Zheng SQ, Liu M, Li X, Tang H (2010) Suppression of hepatitis B virus replication by microRNA-199a-3p and microRNA-210. Antivir Res 88:169–175
Xing T, Zhu J, Xian J, Li A, Wang X, Wang W, Zhang Q (2019) miRNA-548ah promotes the replication and expression of hepatitis B virus by targeting histone deacetylase 4. Life Sci 219:199–208
Li F, Deng Y, Zhang S, Zhu B, Wang J, Wang X, Zhao Z, Deng W, Mao R, Shen Z, Chen J, Broering R, Lin Y, Lu M, Zhang J (2022) Human hepatocyte-enriched miRNA-192-3p promotes HBV replication through inhibiting Akt/mTOR signalling by targeting ZNF143 in hepatic cell lines. Emerg Microbes Infect 11:616–628
Fan H, Lv P, Lv J, Zhao X, Liu M, Zhang G, Tang H (2017) miR-370 suppresses HBV gene expression and replication by targeting nuclear factor IA. J Med Virol 89:834–844
Lin Y, Deng W, Pang J, Kemper T, Hu J, Yin J, Zhang J, Lu M (2017) The microRNA-99 family modulates hepatitis B virus replication by promoting IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt/mTOR/ULK1 signaling-induced autophagy. Cell Microbiol 19:e12709
Deng W, Zhang X, Ma Z, Lin Y, Lu M (2017) MicroRNA-125b-5p mediates post-transcriptional regulation of hepatitis B virus replication via the LIN28B/let-7 axis. RNA Biol 14:1389–1398
Zhang X, Zhang E, Ma Z, Pei R, Jiang M, Schlaak JF, Roggendorf M, Lu M (2011) Modulation of hepatitis B virus replication and hepatocyte differentiation by MicroRNA-1. Hepatology 53:1476–1485
Gao H, Fan H, Xie H (2023) The regulatory effect of the YY1/miR-HCC2/BAMBI axis on the stemness of liver cancer cells. Int J Oncol 62:31
Lin X, Yuan ZH, Wu L, Ding JP, Wen YM (2001) A single amino acid in the reverse transcriptase domain of hepatitis B virus affects virus replication efficiency. J Virol 75:11827–11833
Edwards M, Wong SC, Chotpadiwetkul R, Smirlis D, Phillips R, Shephard EA (2006) Transfection of primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Methods Mol Biol 320:273–282
Yi J, Fan Y, Zhang L, Wang H, Mu T, Xie H, Gao H, Liu M, Li S, Tang H (2019) MiR-HCC2 up-regulates BAMBI and ELMO1 expression to facilitate the proliferation and EMT of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Cancer 10:3407–3419
Zhang L, Cai X, Chen K, Wang Z, Wang L, Ren M, Huang A, Tang H (2011) Hepatitis B virus protein up-regulated HLJ1 expression via the transcription factor YY1 in human hepatocarcinoma cells. Virus Res 157:76–81
Petruzziello A (2018) Epidemiology of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) related hepatocellular carcinoma. Open Virol J 12:26–32
Bouchard MJ, Schneider RJ (2004) The enigmatic X gene of hepatitis B virus. J Virol 78:12725–12734
Kwon JA, Rho HM (2002) Hepatitis B viral core protein activates the hepatitis B viral enhancer II/pregenomic promoter through the nuclear factor kappaB binding site. Biochem Cell Biol 80:445–455
Yang X, Li H, Sun H, Fan H, Hu Y, Liu M, Li X, Tang H (2017) Hepatitis B virus-encoded MicroRNA controls viral replication. J Virol 91:10–128
Shen C, Feng X, Mao T, Yang D, Zou J, Zao X, Deng Q, Chen X, Lu F (2020) Yin-Yang 1 and HBx protein activate HBV transcription by mediating the spatial interaction of cccDNA minichromosome with cellular chromosome 19p13.11. Emerg Microbes Infect 9:2455–2464
Nakanishi-Matsui M, Hayashi Y, Kitamura Y, Koike K (2000) Integrated hepatitis B virus DNA preserves the binding sequence of transcription factor Yin and Yang 1 at the virus-cell junction. J Virol 74:5562–5568
Hayashi Y, Kitamura Y, Nakanishi M, Koike K (2000) The binding site of transcription factor YY1 is required for intramolecular recombination between terminally repeated sequences of linear replicative hepatitis B virus DNA. J Virol 74:9471–9478
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81602410 and 81773002) and the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (17JCQNJC11300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GHJ contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by all authors. The draft of the manuscript was written by GHJ and XH. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval for this work was granted by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Michael A. Purdy.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, H., Fan, H. & Xie, H. miR-HCC2 suppresses hepatitis B virus replication by inhibiting the activity of the enhancer I/X promoter. Arch Virol 168, 282 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-023-05899-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-023-05899-z